Abstract
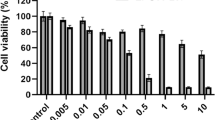
Brevilaterins as antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) secreted by a newly discovered species Brevibacillus laterosporus, had been demonstrated to display excellent antibacterial and antifungal activities; however, very limited information about their new bioactivity was ever developed. Herein, we discovered Brevilaterin B, an AMP produced by Br. laterosporus S62-9, exhibited a new anticancer activity and investigated its anticancer details. Proliferation, membrane permeability and apoptotic rate of cell lines were studied by methods of CCK-8 Assay, LDH Assay and Annexin V-FITC/PI Kits, respectively. ROS levels and mitochondrial membrane potential of tested cells were further detected through the fluorescent probes DCFH-DA and JC-1. Brevilaterin B exhibited broad-spectrum anticancer activity in a dose-dependent manner. It selectively inhibited the proliferation of epidermal cancer cell A431 but had no effect on its control normal cells in a dose of 2.0 µg/mL. In comparision, typical morphological characteristics of apoptosis and an apoptotic ratio of 71.0% in A431 were observed after treatment by 2.0–3.0 µg/mL of Brevilaterin B. The ROS levels increased by 21.3% and mitochondrial membrane potential reduced by 48.8% from A431 were further occurred, indicating Brevilaterin B’s anticancer action was mainly focus on the mitochondrion of cancer cells. In total, Brevilaterin B we reported above maybe believed to be a potential application as an anticancer medicament, increasing its commercial value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baindara P, Singh N, Ranjan M, Nallabelli N, Chaudhry V, Pathania GL, Sharma N, Kumar A, Patil PB, Korpole S (2016) Laterosporulin 10: a novel defensing like Class IId bacteriocin from Brevibacillus sp. strain SKDU10 with inhibitory activity against microbial pathogens. Microbiology 162:1286–1299. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000316
Barsby T, Warabi K, Sørensen D, Zimmerman WT, Kelly MT, Andersen RJ (2006) The Bogorol family of antibiotics: template-based structure elucidation and a new approach to positioning enantiomeric pairs of amino acids. J Org Chem 71(16):6031–6037 PMID: 16872185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jo060667p
Cerón JM, Contreras-Moreno J, Puertollano E, Cienfuegos A, Puertollano MA, Pablo MA (2010) The antimicrobial peptide cecropin A induces caspase-independent cell death in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Peptides 31(8):1494–1503. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.05.008
Chen XL, Zhang LY, Ma CB, Zhang YQ, Xi XP, Wang L, Zhou M, Burrows JF, Chen TB (2018) A novel antimicrobial peptide, Ranatuerin-2PLx, showing therapeutic potential in inhibiting proliferation of cancer cells. Biosci Rep 38(6). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180710
Chen Z, Wang XX, Han PP, Liu YL, Hong D, Li ST, Ma AJ, Jia YM (2022) Discovery of novel antimicrobial peptides, Brevilaterin V, from Brevibacillus laterosporus S62-9 after regulated by exogenously-added L-valine. LWT-Food Sci Technol 155:112962. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112962
Deslouches B, Di YP (2017) Antimicrobial peptides with selective antitumor mechanisms: prospect for anticancer applications. Oncotarget 8(28):46635–46651. DOI:https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16743
Deslouches B, Steckbeck JD, Craigo JK, Doi Y, Burns JL, Montelaro RC (2015) Engineered cationic antimicrobial peptides to overcome multidrug resistance by ESKAPE pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:1329–1333. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03937-14
Deslouches B, Steckbeck JD, Craigo JK, Doi Y, Mietzner TA, Montelaro RC (2013) Rational design of engineered cationic antimicrobial peptides consisting exclusively of arginine and tryptophan, and their activity against multidrugresistant pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(6):2511–2521. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02218-12
Flores-Guzmán F, Alvarado-Sansininea JJ, López-Muñoz H, Escobar ML (2019) Antiproliferative, cytotoxic and apoptotic activity of the bentonite transformation of sesquiterpene lactone glaucolide B to 5β-hydroxy-hirsutinolide on tumor cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol 856:172406. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172406
Gaspar D, Veiga AS, Castanho MARB (2013) From antimicrobial to anticancer peptides. A review. Front Microbiol 4: 294. PMID: 24101917. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00294
Gerard JM, Haden P, Kelly MT, Andersen RJ (1999) Loloatins A-D, Cyclic decapeptide antibiotics produced in culture by a tropical marine bacterium. J Nat Prod 62(1):80–85. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/np980219f
Giuliani A, Pirri G, Nicoletto SF (2007) Antimicrobial peptides: an overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Cent Eur J Biology 2(1):1–33
He NW, Shi XL, Zhao Y, Tian LM, Wang DY, Yang XB (2013) Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanisms of selenium-containing tea polysaccharides on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Agric Food Chem 61(3):579–588. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3036929
Jiang HX, Ji C, Sui JK, Sa RB, Wang XH, Liu XL, Guo TL (2017) Antibacterial and antitumor activity of Bogorol B-JX isolated from Brevibacillus laterosporus JX-5. World J Microbial Biotechnol 33:177. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2337-z
Kim S, Kim JY, Kim S, Bae HJ, Yi H, Yoon SH, Koo BS, Kwon M, Cho JY, Lee C, Hong S (2007) Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis displays anti-proliferative effect via apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest and survival signaling suppression. FEBS Lett 581(5):865–871. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.059
Krachkovskii SA, Sobol AG, Ovchinnikova TV, Tagaev AA, Yakimenko ZA, Azizbekyan RR, Kuznetsova NI, Shamshina TN, Arseniev AS (2002) Isolation, biological properties, and spatial structure of antibiotic loloatin A. Russ J Bioorg Chem 28(4):269–273. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019531505769
Li X, Fan XX, Jiang ZB, Loo WTY, Yao XJ, Leung ELH, Chow WC, Liu L (2017) Shikonin inhibits gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting TrxR and activating the EGFR proteasomal degradation pathway. Pharmacol Res 115:45–55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.011
Li CY, Liu HY, Yang YQ, Xu XX, Lv TT, Zhang HD, Liu KH, Zhang SQ, Chen YQ (2018) N-myristoylation of antimicrobial peptide CM4 enhances its anticancer activity by interacting with cell membrane and targeting mitochondria in breast cancer cells. Front Pharmacol 9:1297 PMID: 30483133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01297
Nishikawa K, Shibasaki C, Takahashi K, Nakamura T, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H (1996) Antitumor activity of Spergualin, a novel antitumor antibiotic. J Antibiot 39(10):1461–1466 PMID: 3781914. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.39.1461
Oyston PC, Fox MA, Richards SJ, Clark GC (2009) Novel peptide therapeutics for treatment of infections. J Med Microbiol 58(Pt8):977–987. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.011122-0
Park SY, Kim J, Lee YJ, Lee SJ (2013) Surfactin suppresses TPA-induced breast cancer cell invasion through the inhibition of MMP-9 expression. Int J Oncol 42(1):287–296. DOI:https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1695
Shahrestanaki MK, Bagheri M, Ghanadian M, Aghaei M, Jafari SM (2019) Centaurea cyanus extracted 13-O-acetylsolstitialin A decrease Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and expression of cyclin D1/Cdk-4 to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem 120(10):18309–18319. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29141
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21208 PMID: 24399786
Singh PK, Solanki V, Sharma S, Thakur KG, Krishnan B (2015) The intramolecular disulfide-stapled structure of laterosporulin, a class IId bacteriocin, conceals a human defensin-like structural module. FEBS J 282(2):203–214. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13129
Steckbeck JD, Deslouches B, Montelaro RC (2014) Antimicrobial peptides: new drugs for bad bugs? Expert Opin Biol Ther 14:11–14
Tareq FS, Lee MA, Lee HS, Lee JS, Lee YJ, Shin HJ (2014) Gageostatins A–C, antimicrobial linear lipopeptides from a marine Bacillus subtilis. Mar Drugs 12:871–885. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/md12020871
Ting CH, Huang HN, Huang TC, Wu CJ, Chen JY (2014) The mechanisms by which pardaxin, a natural cationic antimicrobial peptide, targets the endoplasmic reticulum and induces c-FOS. Biomaterials 35(11):3627–3640. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.032 PMID: 24477193
Xue ML, Ji XQ, Xue CX, Liang H, Ge YL, He XJ, Zhang L, Bian K, Zhang LH (2017) Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent induction of apoptosis in breast cancer by fucoidan via the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother 94:898–908. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.013
Wang S, Wang QW, Zeng XF, Ye QH, Huang S, Yu HT, Yang TR, Qiao SY (2017) Use of the antimicrobial peptide sublancin with combined antibacterial and immunomodulatory activities to protect against methicillin-resisitant Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. J Agric Food Chem 65(39):8595–8605 PMID: 28906115. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02592
Wang C, Zhou Y, Li S, Li HB, Tian LL, Wang H, Shang DJ (2013) Anticancer mechanisms of temporin-1CEa, an amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptide, in Bcap-37 human breast cancer cells. Life Sci 92(20–21):1004–1014. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2013.03.016
Xia LJ, Wu YL, Ma J, Yang JH, Zhang FC (2016) The antibacterial peptide from Bombyx mori cecropinXJ induced growth arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett 12(1):57–62. DOI:https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4601
Zhao HB, Yan L, Xu XG, Jiang CM, Shi JL, Zhang YW, Lei SZ, Shao DY, Huang QS (2018) Potential of Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides in anti-cancer I: induction of apoptosis and paraptosis and inhibition of autophagy in K562 cells. Amb Express 8(1):1–16 PMID: 29777449. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0606-3
Funding
This study was supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation [No. KZ201810011016]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 31771951, No. 31801510 & No. 32072199].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wang, L., Liu, Y. et al. Brevilaterin B from Brevibacillus laterosporus has selective antitumor activity and induces apoptosis in epidermal cancer. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 201 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03372-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03372-8