Abstract
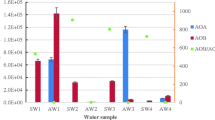
Ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms (AOM) play crucial roles in the degradation of ammonia nitrogen in freshwater lakes. Hence, it is necessary to reveal the spatiotemporal dynamic changes of AOM in freshwater lakes. Here, we conducted a study on the spatial and temporal dynamic changes of AOM in different lake regions under gradient nutrient levels in Lake Taihu, and found that the abundance of AOM had significant spatial changes, while the seasonal changes had relatively little effect on the abundance of AOM. We also found that ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) were adapted to freshwater habitats with low nutrient levels, while ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AAOB) had higher abundance in high nutrient level lake regions. Moreover, the amoA gene abundance of AOB was much higher than that of AOA, indicating that AOB was the dominant aerobic ammonia oxidizer in the water of Lake Taihu. In addition, temperature, pH and dissolved oxygen all had a positive effect on AOM, especially AOB; while C- and N-related physicochemical factors had a significant positive effect on AAOB, but exhibited a significant negative correlation with AOA. The community structure of AOM also had obvious spatial changes and Group I.1a, Nitrosomonas and Candidatus Brocadia fulgida were the dominant cluster of AOA, AOB and AAOB, respectively.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison SD, Wallenstein MD, Bradford MA (2010) Soil-carbon response to warming dependent on microbial physiology. Nat Geosci 3:336–340
Bollmann A, Schmidt I, Saunders AM, Nicolaisen MH (2005) Influence of starvation on potential ammonia-oxidizing activity and amoA mRNA levels of Nitrosospira briensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1276–1282
Cai Y, Gong Z, Qin B (2012) Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure in Lake Taihu, China: effects of trophic status, wind-induced disturbance and habitat complexity. J Great Lakes Res 38:39–48
Colwell RK, Elsensohn JE (2014) EstimateS turns 20: statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples, with non-parametric extrapolation. Ecography 37:609–613
Dai J, Gao G, Chen D, Tang X, Shao K, Cai X (2013) Effects of trophic status and temperature on communities of sedimentary ammonia oxidizers in Lake Taihu. Geomicrobiol J 30:886–896
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P, Han P, Herbold C, Albertsen M, Jehmlich N, Palatinszky M, Vierheilig J, Bulaev A, Kirkegaard RH, Von Bergen M, Rattei T, Bendinger B, Nielsen PH, Wagner M (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528:504–509
Dietl A, Ferousi C, Maalcke WJ, Menzel A, De Vries S, Keltjens JT, Jetten MS, Kartal B, Barends TR (2015) The inner workings of the hydrazine synthase multiprotein complex. Nature 527:394–397
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14683–14688
Francis CA, Beman JM, Kuypers MM (2007) New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: the microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J 1:19–27
Gori F, Tringe SG, Kartal B, Marchiori E, Jetten MS (2011) The metagenomic basis of anammox metabolism in Candidatus “Brocadia fulgida.” Biochem Soc Trans 39:1799–1804
Guo L (2007) Ecology. Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317:1166
Guo X, Liu X, Wu L, Pan J, Yang H (2016) The algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp. strain GLY-2107 against bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa is regulated by N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. Environ Microbiol 18:3867–3883
Habteselassie MY, Li X, Norton JM (2013) Ammonia-oxidizer communities in an agricultural soil treated with contrasting nitrogen sources. Front Microbiol 4:326
Han P, Klumper U, Wong A, Li M, Lin JG, Quan Z, Denecke M, Gu JD (2017) Assessment of molecular detection of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in different environmental samples using PCR primers based on 16S rRNA and functional genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7689
Holmes DE, Dang Y, Smith JA (2019) Nitrogen cycling during wastewater treatment. Adv Appl Microbiol 106:113–192
Hou J, Song C, Cao X, Zhou Y (2013) Shifts between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in relation to nitrification potential across trophic gradients in two large Chinese lakes (Lake Taihu and Lake Chaohu). Water Res 47:2285–2296
Huang R, Zhao D, Zeng J, Luo J, Shen F, Cao X, Jiang C, Huang F, Feng J, Zhou C, Sun Z, Yu Z, Wu QL (2016) Abundance and community composition of ammonia oxidizers in rhizosphere sediment of two submerged macrophytes. J Freshw Ecol 31:407–419
Humbert S, Zopfi J, Tarnawski S-E (2012) Abundance of anammox bacteria in different wetland soils. Environ Microbiol Rep 4:484–490
Jung MY, Park SJ, Min D, Kim JS, Rijpstra WI, Sinninghe Damste JS, Kim GJ, Madsen EL, Rhee SK (2011) Enrichment and characterization of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing archaeon of mesophilic crenarchaeal group I.1a from an agricultural soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:8635–8647
Ke X, Lu Y (2012) Adaptation of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms to environment shift of paddy field soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80:87–97
Keshri J, Pradeep Ram AS, Sime-Ngando T (2018) Distinctive patterns in the taxonomical resolution of bacterioplankton in the sediment and pore waters of contrasted freshwater lakes. Microb Ecol 75:662–673
Kuenen JG (2008) Anammox bacteria: from discovery to application. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:320–326
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kuypers MMM, Marchant HK, Kartal B (2018) The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:263–276
Lehtovirta-Morley LE (2018) Ammonia oxidation: Ecology, physiology, biochemistry and why they must all come together. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny058
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Ling W, Hongyi Q, Mengyuan Z, Cheng H, Guangwei Z, Wenhui Z (2017) Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of nitrifying microorganisms in freshwater and sediment of eutrophic zones in Lake Taihu in autumn. J Lake Sci 29:1312–1323
Oshiki M, Shimokawa M, Fujii N, Satoh H, Okabe S (2011) Physiological characteristics of the anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacterium “Candidatus Brocadia sinica.” Microbiology 157:1706–1713
Oshiki M, Satoh H, Okabe S (2016) Ecology and physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Environ Microbiol 18:2784–2796
Ostle N, Whiteley AS, Bailey MJ, Sleep D, Ineson P, Manefield M (2003) Active microbial RNA turnover in a grassland soil estimated using a 13CO2 spike. Soil Biol Biochem 35:877–885
Park BJ, Park SJ, Yoon DN, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damste JS, Rhee SK (2010) Cultivation of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing archaea from marine sediments in coculture with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7575–7587
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Sun W, Xia C, Xu M, Guo J, Sun G, Wang A (2014) Community structure and distribution of planktonic ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the Dongjiang River, China. Res Microbiol 165:657–670
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2008) Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ Microbiol 10:1357–1364
Van Kessel MA, Speth DR, Albertsen M, Nielsen PH, Op Den Camp HJ, Kartal B, Jetten MS, Lucker S (2015) Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature 528:555–559
Wan Y, Bai Y, He J, Zhang Y, Li R, Ruan X (2017) Temporal and spatial variations of aquatic environmental characteristics and sediment bacterial community in five regions of Lake Taihu. Aquat Ecol 51:343–358
Wang S, Zhu G, Zhuang L, Li Y, Liu L, Lavik G, Berg M, Liu S, Long XE, Guo J, Jetten MSM, Kuypers MMM, Li F, Schwark L, Yin C (2019) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation is a major N-sink in aquifer systems around the world. ISME J 14:151
Wu X, Xi W, Ye W, Yang H (2007) Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:85–96
Wu X, Kong F, Chen Y, Qian X, Zhang L, Yu Y, Zhang M, Xing P (2010a) Horizontal distribution and transport processes of bloom-forming Microcystis in a large shallow lake (Taihu, China). Limnologica 40:8–15
Wu Y, Xiang Y, Wang J, Zhong J, He J, Wu QL (2010b) Heterogeneity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizing communities in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:569–576
Wu L, Han C, Qin H, Zhu G, Zhong W (2018) Responses of active ammonia oxidizers to eutrophication and oxygen statuses in taihu freshwater sediments. Geomicrobiol J 35:829
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Wang X, Li J, Feng S, Zhao Q, Liu M, Qin B (2007) A study of absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particles in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 592:105–120
Zhao DY, Luo J, Zeng J, Wang M, Yan WM, Huang R, Wu QL (2014) Effects of submerged macrophytes on the abundance and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in a eutrophic lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:389–398
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21477077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL and HY designed experiments. TL performed the experiments. TL and HY analyzed the data. TL wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Tt., Yang, H. Different nutrient levels, rather than seasonal changes, significantly affected the spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in Lake Taihu. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03053-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03053-y