Abstract
Lipids produced by oleaginous microorganisms enrich the supply of feedstock for bio-fuel. In this study, a mutant (Mut) obtained by UV-nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis turned its colony color from orange–red to light-yellow and showed higher lipid productivity at 37 °C than the original strain Rhodotorula sp. U13N3 (Rht) in the glycerol medium. The metabolic changes between Mut and Rht in batch fermentation were investigated by transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling at the biomass accumulation (30 h) and lipid production (96 h) stages. The average base number in each strain was 5.80 × 109 ± 0.38 × 109 bp (mean ± SD) with 62.43% ± 0.13% GC ratio, and 7499 unigenes were assembled after Illumina sequencing. Moreover, 33 metabolites were quantified by 1H NMR-based profiling. The multi-omics results demonstrated that Mut showed increased glycerol transport and utilization capabilities especially at the first stage (30 h). Then the carbon flux shifted from the TCA cycle to lipid production (96 h). The increased lipid productivity of Mut was partially attributed to the down-regulation of mannitol biosynthesis. However, the mechanism for color change was elusive. At 96 h, the low level of cytosol glycerol probably restricted the lipid production. As a result, supplementation of glycerol in fed-batch fermentation remarkably improved the biomass, lipid production, and lipid content to 34.60 g/L, 25.72 g/L, and 74.3% (w/w dcw), respectively. The cell morphology implied that excessively prolonging the fermentation time was detrimental to the final lipid yield due to cell breakage. In conclusion, the Rhodotorula mutant provided a candidate strain for lipid production with glycerol as the carbon source.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bommareddy RR, Sabra W, Maheshwari G, Zeng AP (2015) Metabolic network analysis and experimental study of lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides grown on single and mixed substrates. Microb Cell Fact 14:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0217-5
Bonturi N, Matsakas L, Nilsson R, Christakopoulos P, Miranda EA, Berglund KA, Rova U (2015) Single cell oil producing yeasts Lipomyces starkeyi and Rhodosporidium toruloides: selection of extraction strategies and biodiesel property prediction. Energies 8:5040–5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8065040
Castañeda MT, Nuñez S, Garelli F, Voget C, De Battista H (2018) Comprehensive analysis of a metabolic model for lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides. J Biotechnol 280:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.05.010
Delitheos B, Papamichael K, Tiligada E (2010) Histamine modulates the cellular stress response in yeast. Amino Acids 38:1219–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0333-9
Dias C, Silva C, Freitas C, Reis A, da Silva TL (2016) Effect of medium pH on Rhodosporidium toruloides NCYC 921 carotenoid and lipid production evaluated by flow cytometry. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179:776–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2030-y
Dourou M, Aggeli D, Papanikolaou S, Aggelis G (2018) Critical steps in carbon metabolism affecting lipid accumulation and their regulation in oleaginous microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:2509–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8813-z
Dulermo T, Lazar Z, Dulermo R, Rakicka M, Haddouche R, Nicaud J-M (2015) Analysis of ATP-citrate lyase and malic enzyme mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica points out the importance of mannitol metabolism in fatty acid synthesis. Biochem Biophys Acta 1851:1107–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.04.007
Gonzalez B, François J, Renaud M (1997) A rapid and reliable method for metabolite extraction in yeast using boiling buffered ethanol. Yeast 13:1347–1355. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0061(199711)13:14%3c1347::aid-yea176%3e3.0.co;2-o
Hassanpour M, Abbasabadi M, Strong J, Gebbie L, Te’o VSJ, O’Hara IM, Zhang Z (2020) Scale-up of two-step acid-catalysed glycerol pretreatment for production of oleaginous yeast biomass from sugarcane bagasse by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biores Technol 313:123666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123666
Kim HK, Choi YH, Verpoorte R (2010) NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat Protoc 5:536–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.237
Koutinas AA, Chatzifragkou A, Kopsahelis N, Papanikolaou S, Kookos IK (2014) Design and techno-economic evaluation of microbial oil production as a renewable resource for biodiesel and oleochemical production. Fuel 116:566–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.045
Li M-H et al (2017) Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics approach to evaluate the prevention effect of Camellia nitidissima Chi on Colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Front Pharmacol 8:447. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00447
Madeira-Jr JV, Gombert AK (2018) Towards high-temperature fuel ethanol production using Kluyveromyces marxianus: on the search for plug-in strains for the Brazilian sugarcane-based biorefinery. Biomass Bioenergy 119:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.09.010
Papadaki A et al (2018) Bioprocess development for biolubricant production using microbial oil derived via fermentation from confectionery industry wastes. Bioresour Technol 267:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.016
Park Y-K, Nicaud J-M, Ledesma-Amaro R (2018) The engineering potential of Rhodosporidium toruloides as a workhorse for biotechnological applications. Trends Biotechnol 36:304–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.10.013
Qadeer S, Khalid A, Mahmood S, Anjum M, Ahmad Z (2017) Utilizing oleaginous bacteria and fungi for cleaner energy production. J Clean Prod 168:917–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.093
Qi F et al (2017) Integrative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the mutant lignocellulosic hydrolyzate-tolerant Rhodosporidium toruloides. Eng Life Sci 17:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201500143
Qin L, Liu L, Zeng A-P, Wei D (2017) From low-cost substrates to single cell oils synthesized by oleaginous yeasts. Biores Technol 245:1507–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.163
Saran S, Mathur A, Dalal J, Saxena RK (2017) Process optimization for cultivation and oil accumulation in an oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides A29. Fuel 188:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.051
Singh G, Jawed A, Paul D, Bandyopadhyay KK, Kumari A, Haque S (2016) Concomitant production of lipids and carotenoids in Rhodosporidium toruloides under osmotic stress using response surface methodology. Front Microbiol 7:01686. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01686
Soccol CR, Dalmas Neto CJ, Soccol VT, Sydney EB, da Costa ESF, Medeiros ABP, Vandenberghe LPdS (2017) Pilot scale biodiesel production from microbial oil of Rhodosporidium toruloides DEBB 5533 using sugarcane juice: performance in diesel engine and preliminary economic study. Bioresour Technol 223:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.055
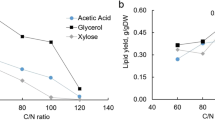
Somashekar D, Joseph R (2000) Inverse relationship between carotenoid and lipid formation in Rhodotorula gracilis according to the C/N ratio of the growth medium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:491–493. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008917612616
Tchakouteu SS et al (2017) Rhodosporidium toruloides cultivated in NaCl-enriched glucose-based media: adaptation dynamics and lipid production. Eng Life Sci 17:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201500125
Thakur MS, Prapulla SG, Karanth NG (1988) Microscopic observation of Sudan Black B staining to monitor lipid production by microbes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 42:129–134. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.280420206
Uprety BK, Reddy JV, Dalli SS, Rakshit SK (2017) Utilization of microbial oil obtained from crude glycerol for the production of polyol and its subsequent conversion to polyurethane foams. Bioresour Technol 235:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.126
Wang Y et al (2018) Systems analysis of phosphate-limitation-induced lipid accumulation by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1134-8
Wen Z, Zhang S, Odoh CK, Jin M, Zhao ZK (2020) Rhodosporidium toruloides—a potential red yeast chassis for lipids and beyond. FEMS Yeast Res 20:foaa038. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foaa038
Xu J, Zhao X, Du W, Liu D (2017) Bioconversion of glycerol into lipids by Rhodosporidium toruloides in a two-stage process and characterization of lipid properties. Eng Life Sci 17:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201600062
Xu H, Li J, Wang L, Fu R, Cheng R, Wang S, Zhang J (2018) Purification and characterization of a highly viscous polysaccharide produced by Paenibacillus strain. Eur Polym J 101:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.02.040
Xue S-J et al (2018) Fatty acids from oleaginous yeasts and yeast-like fungi and their potential applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38:1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2018.1428167
Yamada R, Yamauchi A, Kashihara T, Ogino H (2017) Evaluation of lipid production from xylose and glucose/xylose mixed sugar in various oleaginous yeasts and improvement of lipid production by UV mutagenesis. Biochem Eng J 128:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.09.010
Zheng Z, Sun D, Li J, Zhan X, Gao M (2018) Improving oxygen transfer efficiency by developing a novel energy-saving impeller. Chem Eng Res Des 130:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.12.021
Zhu Z et al (2012) A multi-omic map of the lipid-producing yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. Nat Commun 3:1112. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2112
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the research Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31500418) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grants No. BK20150773). The authors thank these organizations for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and JZ conceived and designed research. YZ, YZ, RF, and TZ conducted experiments and computational analysis. JL analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. JZ improved the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhao, Y., Fu, R. et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling of a Rhodotorula color mutant to improve its lipid productivity in fed-batch fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 77 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03043-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03043-0