Abstract
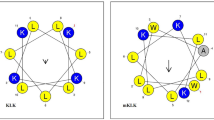
Conventional antibiotics might fail in the treatment of biofilm-associated infections causing infection recurrence and chronicity. The search for antimicrobial peptides has been performed with the aim to discover novel anti-infective agents active on pathogens in both planktonic and biofilm associated forms. The fragment 9–19 of human thymosin β4 was studied through 1 μs MD simulation. Two main conformations of the peptide were detected, both constituted by a central hydrophobic core and by the presence of peripheral charged residues suggesting a possible mechanism of interaction with two models of biological membranes, related to eukaryotic or bacterial membrane respectively. In addition, the peptide was chemically synthesized and its antimicrobial activity was tested in vitro against planktonic and biofilm form of a group of reference strains of Staphylococcus spp. and one P. aeruginosa strain. The human thymosin β4 fragment EIEKFDKSKLK showed antibacterial activity against staphylococcal strains and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 at concentrations from 12.5 to 6.2 mg/ml and inhibited biofilm formation at sub-inhibitory concentrations (3.1–0.75 mg/ml). The activity of the fragment in inhibiting biofilm formation, could be due to the conformations highlighted by the MD simulations, suggesting its interaction with the bacterial membrane. Human thymosin β4 fragment can be considered a promising lead compound to develop novel synthetic or recombinant derivatives with improved pharmaceutical potential.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade FBd, Oliveira JCd, Yoshie MT, Guimarães BM, Gonçalves RB, Schwarcz WD (2014) Antimicrobial activity and synergism of lactoferrin and lysozyme against cariogenic microorganisms. Braz Dent J 25(2):165–169
Auvynet C, El Amri C, Lacombe C, Bruston F, Bourdais J, Nicolas P, Rosenstein Y (2008) Structural requirements for antimicrobial versus chemoattractant activities for dermaseptin S9. FEBS J 275(16):4134–4151
Badamchian M, Damavandy AA, Damavandy H, Wadhwa SD, Katz B, Goldstein AL (2007) Identification and quantification of thymosin β4 in human saliva and tears. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1112(1):458–465
Batoni G, Maisetta G, Lisa Brancatisano F, Esin S, Campa M (2011) Use of antimicrobial peptides against microbial biofilms: advantages and limits. Curr Med Chem 18(2):256–279
Bocchinfuso G, Bobone S, Mazzuca C, Palleschi A, Stella L (2011) Fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations in studies on the mechanism of membrane destabilization by antimicrobial peptides. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(13):2281–2301
Brogden NK, Brogden KA (2011) Will new generations of modified antimicrobial peptides improve their potential as pharmaceuticals? Int J Antimicrob Agents 38(3):217–225
Cascioferro S, Cusimano MG, Schillaci D (2014a) Antiadhesion agents against Gram-positive pathogens. Future Microbiol 9(10):1209–1220. doi:10.2217/fmb.14.56
Cascioferro S, Totsika M, Schillaci D (2014b) Sortase A: an ideal target for anti-virulence drug development. Microb Pathog 77:105–112
Cascioferro S, Raffa D, Maggio B, Raimondi MV, Schillaci D, Daidone G (2015) Sortase A inhibitors: recent advances and future perspectives. J Med Chem 58(23):9108–9123. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00779
Chambers HF, Deleo FR (2009) Waves of resistance: staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(9):629–641. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2200
Chan C, Burrows LL, Deber CM (2004) Helix induction in antimicrobial peptides by alginate in biofilms. J Biol Chem 279(37):38749–38754
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg E (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284(5418):1318–1322
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: an N·log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092
Di Luca M, Maccari G, Nifosì R (2014) Treatment of microbial biofilms in the post-antibiotic era: prophylactic and therapeutic use of antimicrobial peptides and their design by bioinformatics tools. Pathog Dis 70(3):257–270
Di Luca M, Maccari G, Maisetta G, Batoni G (2015) BaAMPs: the database of biofilm-active antimicrobial peptides. Biofouling 31(2):193–199
Dunkin CM, Pokorny A, Almeida PF, Lee H-S (2010) Molecular dynamics studies of transportan 10 (tp10) interacting with a POPC lipid bilayer. J Phys Chem B 115(5):1188–1198
Esteban-Martín S, Salgado J (2007) Self-assembling of peptide/membrane complexes by atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 92(3):903–912
Farrotti A, Bocchinfuso G, Palleschi A, Rosato N, Salnikov E, Voievoda N, Bechinger B, Stella L (2015) Molecular dynamics methods to predict peptide locations in membranes: LAH4 as a stringent test case. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848(2):581–592
Gilbert P, Allison D, McBain A (2002) Biofilms in vitro and in vivo: do singular mechanisms imply cross‐resistance? J Appl Microbiol 92(s1):98S–110S
Goldstein AL (2007) History of the discovery of the thymosins. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1112(1):1–13
Hancock RE, Lehrer R (1998) Cationic peptides: a new source of antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol 16(2):82–88
Huang Y, Huang J, Chen Y (2010) Alpha-helical cationic antimicrobial peptides: relationships of structure and function. Protein Cell 1(2):143–152
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33–38
Jämbeck JP, Lyubartsev AP (2012a) Another piece of the membrane puzzle: extending slipids further. J Chem Theory Comput 9(1):774–784
Jämbeck JP, Lyubartsev AP (2012b) An extension and further validation of an all-atomistic force field for biological membranes. J Chem Theory Comput 8(8):2938–2948
Kaur H, Mutus B (2012) Platelet function and thymosin β4. Biol Chem 393(7):595–598
Khatami MH, Bromberek M, Saika-Voivod I, Booth V (2014) Molecular dynamics simulations of histidine-containing cod antimicrobial peptide paralogs in self-assembled bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838(11):2778–2787
Lentini L, Melfi R, Di Leonardo A, Spinello A, Barone G, Pace A, Palumbo Piccionello A, Pibiri I (2014) Toward a rationale for the PTC124 (Ataluren) promoted readthrough of premature stop codons: a computational approach and GFP-reporter cell-based assay. Mol Pharm 11(3):653–664
Lequin O, Ladram A, Chabbert L, Bruston F, Convert O, Vanhoye D, Chassaing G, Nicolas P, Amiche M (2006) Dermaseptin S9, an α-Helical antimicrobial peptide with a hydrophobic core and cationic termini. Biochemistry 45(2):468–480
Lindorff-Larsen K, Piana S, Palmo K, Maragakis P, Klepeis JL, Dror RO, Shaw DE (2010) Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 78(8):1950–1958
Liu LP, Deber CM (1998) Guidelines for membrane protein engineering derived from de novo designed model peptides. Pept Sci 47(1):41–62
Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin EG, Martínez JM (2009) Packmol: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 30(13):2157–2164
Metcalf DG, Bowler PG (2014) Clinician perceptions of wound biofilm. Int Wound J. doi:10.1111/iwj.12358
Parachin NS, Franco OL (2014) New edge of antibiotic development: antimicrobial peptides and corresponding resistance. Front Microbiol 5:147. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00147
Percival SL, Vuotto C, Donelli G, Lipsky BA (2015) Biofilms and wounds: an identification algorithm and potential treatment options. Adv Wound Care 4(7):389–397
Pronk S, Páll S, Schulz R, Larsson P, Bjelkmar P, Apostolov R, Shirts MR, Smith JC, Kasson PM, van der Spoel D (2013) GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 29(7):845–854
Rabin N, Zheng Y, Opoku-Temeng C, Du Y, Bonsu E, Sintim HO (2015) Agents that inhibit bacterial biofilm formation. Future Med Chem 7(5):647–671
Raimondi MV, Maggio B, Raffa D, Plescia F, Cascioferro S, Cancemi G, Schillaci D, Cusimano MG, Vitale M, Daidone G (2012) Synthesis and anti-staphylococcal activity of new 4-diazopyrazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 58:64–71
Rossetti DV, Martelli C, Longhi R, Iavarone F, Castagnola M, Desiderio C (2013) Quantitative analysis of thymosin β4 in whole saliva by capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry using multiple ions monitoring (CE-MIM-MS). Electrophoresis 34(18):2674–2682
Safer D, Golla R, Nachmias VT (1990) Isolation of a 5-kilodalton actin-sequestering peptide from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87(7):2536–2540
Schillaci D, Maggio B, Raffa D, Daidone G, Cascioferro S, Cusimano MG, Raimondi MV (2008) 4-Diazopyrazole derivatives as potential new antibiofilm agents. Chemotherapy 54(6):456–462
Schillaci D, Arizza V, Parrinello N, Di Stefano V, Fanara S, Muccilli V, Cunsolo V, Haagensen J, Molin S (2010a) Antimicrobial and antistaphylococcal biofilm activity from the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. J Appl Microbiol 108(1):17–24
Schillaci D, Petruso S, Raimondi MV, Cusimano MG, Cascioferro S, Scalisi M, La Giglia MA, Vitale M (2010b) Pyrrolomycins as potential anti-staphylococcal biofilms agents. Biofouling 26(4):433–438. doi:10.1080/08927011003718673
Schillaci D, Cusimano MG, Cunsolo V, Saletti R, Russo D, Vazzana M, Vitale M, Arizza V (2013) Immune mediators of sea-cucumber Holothuria tubulosa (Echinodermata) as source of novel antimicrobial and anti-staphylococcal biofilm agents. AMB Express 3(1):35
Schillaci D, Cusimano MG, Spinello A, Barone G, Russo D, Vitale M, Parrinello D, Arizza V (2014) Paracentrin 1, a synthetic antimicrobial peptide from the sea-urchin Paracentrotus lividus, interferes with staphylococcal and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. AMB Express 4(1):1–9
Sosne G, Qiu P, Dunn SP, Crockford D (2012) Thymosin β4: a potential novel dry eye therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1270(1):45–50
Stark M, Liu L-P, Deber CM (2002) Cationic hydrophobic peptides with antimicrobial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(11):3585–3590
Suman P, Ramachandran H, Sahakian S, Gill KZ, Horst BA, Modak SM, Hardy MA (2012) The use of angiogenic-antimicrobial agents in experimental wounds in animals: problems and solutions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1270(1):28–36
Wang Z, Wang G (2004) APD: the antimicrobial peptide database. Nucleic Acids Res 32(suppl 1):D590–D592
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2009) APD2: the updated antimicrobial peptide database and its application in peptide design. Nucleic Acids Res 37(suppl 1):D933–D937
Wang Y, Schlamadinger DE, Kim JE, McCammon JA (2012) Comparative molecular dynamics simulations of the antimicrobial peptide CM15 in model lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818(5):1402–1409
Wang K, Yan J, Dang W, Liu X, Chen R, Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhang W, Kai M, Yan W (2013) Membrane active antimicrobial activity and molecular dynamics study of a novel cationic antimicrobial peptide polybia-MPI, from the venom of Polybia paulista. Peptides 39:80–88
Xue B, Leyrat C, Grimes JM, Robinson RC (2014) Structural basis of thymosin-β4/profilin exchange leading to actin filament polymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(43):E4596–E4605
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415(6870):389–395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schillaci, D., Spinello, A., Cusimano, M.G. et al. A peptide from human β thymosin as a platform for the development of new anti-biofilm agents for Staphylococcus spp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32, 124 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2096-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2096-2