Abstract
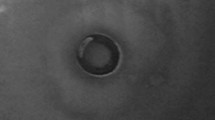
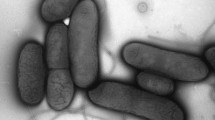
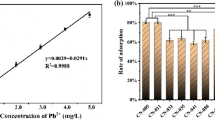
In this work, we investigated the lead(II) biosorption mechanism of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) 016 through batch and microscopic experiments. We found that the maximum lead(II) biosorption capacity of Bt 016 was 164.77 mg/g (dry weight). The pH value could affect the biosorption of lead(II) in a large extent. Fourier transform infrared analyses and selective passivation experiments suggested that the carboxyl, amide and phosphate functional groups of Bt 016 played an important role in lead(II) biosorption. Scanning electron microscopy observation showed that noticeable lead(II) precipitates were accumulated on bacterial surfaces. Further transmission electron microscopy thin section analysis coupled with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy as well as selected area electron diffraction indicated that lead(II) immobilized on the bacteria could be transformated into random-shaped crystalline lead-containing minerals eventually. This work provided a new insight into lead(II) uptake of Bt, highlighting the potential of Bt in the restoration of lead(II) contaminated repositories.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiking H, Govers H, Vantriet J (1985) Detoxification of mercury, cadmium, and lead in Klebsiella aerogenes NCTC 418 growing in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:1262–1267
Akar T, Tunali S (2006) Biosorption characteristics of Aspergillus flavus biomass for removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from an aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 97:1780–1787. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.09.009
Akar ST, Gorgulu A, Anilan B, Kaynak Z, Akar T (2009) Investigation of the biosorption characteristics of lead(II) ions onto Symphoricarpus albus: Batch and dynamic flow studies. J Hazard Mater 165:126–133. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.089
Al-Qadiri HM, Al-Alami NI, Al-Holy MA, Rasco BA (2008) Using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) absorbance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to study the effect of chlorine-induced bacterial injury in water. J Agric Food Chem 56:8992–8997. doi:10.1021/jf801604p
Brar SK, Verma M, Tyagi RD, Valero JR, Surampalli RY (2009) Concurrent degradation of dimethyl phthalate (DMP) during production of Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. J Hazard Mater 171:1016–1023. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.108
Bravo A, Gill SS, Soberon M (2007) Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 49:423–435. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.022
Bueno B, Torem ML, Molina F, de Mesquita L (2008) Biosorption of lead(II), chromium(III) and copper(II) by R. opacus: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Miner Eng 21:65–75. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2007.08.013
Cheng YJ, Yan FB, Huang F, Chu WS, Pan DM, Chen Z, Zheng JS, Yu MJ, Lin Z, Wu ZY (2010) Bioremediation of Cr(VI) and Immobilization as Cr(III) by Ochrobactrum anthropi. Environ Sci Technol 44:6357–6363. doi:10.1021/es100198v
Cho DH, Kim EY (2003) Characterization of Pb2+ biosorption from aqueous solution by Rhodotorula glutinis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25:271–277. doi:10.1007/s00449-002-0315-8
Dave SR, Dave RH (2009) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis for Acid red 119 dye decolourisation. Bioresour Technol 100:249–253. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.019
De J, Ramaiah N, Vardanyan L (2008) Detoxification of toxic heavy metals by marine bacteria highly resistant to mercury. Mar Biotechnol 10:471–477. doi:10.1007/s10126-008-9083-z
Edris G, Alhamed Y, Alzahrani A (2014) Biosorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solutions by Chlorella vulgaris biomass: equilibrium and kinetic study. Arab J Sci Eng 39:87–93. doi:10.1007/s13369-013-0820-x
Fowler BA (1998) Roles of lead-binding proteins in mediating lead bioavailability. Environ Health Perspect 1066:1585–1587. doi:10.1289/ehp.98106s61585
Gordon JN, Taylor A, Bennett PN (2002) Lead poisoning: case studies. Br J Clin Pharmacol 53:451–458. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01580.x
Huang TP, Xiao Y, Pan JR, Chen Z, Li LF, Xu L, Zhang LL, Guan X (2014) Aerobic Cr(VI) reduction by an indigenous soil isolate Bacillus thuringiensis BRC-ZYR2. Pedosphere 5:652–661. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(14)60051-5
Kapoor A, Viraraghavan T (1997) Heavy metal biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 61:221–227. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(97)00055-2
Karaduman AB, Yamac M, Pat Z, Amoroso MJ, Cuozzo SA (2011) Lead(II) biosorption by a metal tolerant Streptomyces strain. Environ Eng Manag J 10:1761–1771
Kebria DY, Khodadadi A, Ganjidoust H, Badkoubi A, Amoozegar MA (2009) Isolation and characterization of a novel native Bacillus strain capable of degrading diesel fuel. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6:435–442. doi:10.1007/BF03326082
Mire CE, Tourjee JA, O’Brien WF, Ramanujachary KV, Hecht GB (2004) Lead precipitation by Vibrio harveyi: evidence for novel quorum-sensing interactions. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:855–864. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.2.855-864.2004
Muneer B, Rehman A, Shakoori F, Shakoori A (2009) Evaluation of consortia of microorganisms for efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from Industrial wastewater. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:597–600. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9662-3
Murugesan A, Ravikumar L, SathyaSelvaBala V, SenthilKumar P, Vidhyadevi T, Kirupha SD, Kalaivani SS, Krithiga S, Sivanesan S (2011) Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution using polyazomethineamides: equilibrium and kinetic approach. Desalination 271:199–208. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.12.029
Naik MM, Dubey SK (2013) Lead resistant bacteria: lead resistance mechanisms, their applications in lead bioremediation and biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.039
Naik MM, Khanolkar D, Dubey SK (2013) Lead-resistant Providencia alcalifaciens strain 2EA bioprecipitates Pb+2 as lead phosphate. Lett Appl Microbiol 56:99–104. doi:10.1111/lam.12026
Pan JH, Ge XP, Liu RX, Tang HX (2006) Characteristic features of Bacillus cereus cell surfaces with biosorption of Pb(II) ions by AFM and FT-IR. Colloid Surf B 52:89–95. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.05.016
Park D, Yun YS, Park JM (2005) Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically treated biomass of Ecklonia sp. Chemosphere 60:1356–1364. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.020
Park JH, Bolan N, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Concomitant rock phosphate dissolution and lead immobilization by phosphate solubilizing bacteria (Enterobacter sp.). J Environ Manage 92:1115–1120. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.031
Rhee YJ, Hillier S, Pendlowski H, Gadd GM (2014) Pyromorphite formation in a fungal biofilm community growing on lead metal. Environ Microbiol 16:1441–1451. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12416
Sahin I, Keskin SY, Keskin CS (2013) Biosorption of cadmium, manganese, nickel, lead, and zinc ions by Aspergillus tamarii. Desalin Water Treat 51:4524–4529. doi:10.1080/19443994.2012.752332
Sari A, Tuzen M (2009) Kinetic and equilibrium studies of biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by macrofungus (Amanita rubescens) biomass. J Hazard Mater 164:1004–1011. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.002
Sellami S, Zghal T, Cherif M, Zalila-Kolsi I, Jaoua S, Jamoussi K (2013) Screening and identification of a Bacillus thuringiensis strain S1/4 with large and efficient insecticidal activities. J Basic Microbiol 53:539–548. doi:10.1002/jobm.201100653
Shamala TR, Divyashree MS, Davis R, Kumari K, Vijayendra S, Raj B (2009) Production and characterization of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers and evaluation of their blends by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Indian J Microbiol 49:251–258. doi:10.1007/s12088-009-0031-z
Soberon M, Gill SS, Bravo A (2009) Signaling versus punching hole: how do Bacillus thuringiensis toxins kill insect midgut cells? Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1337–1349. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8330-9
Subhashini SS, Velan M, Kaliappan S (2013) Biosorption of lead by Kluyveromyces marxianus immobilized in alginate beads. J Environ Biol 34:831–835
Tong S, von Schirnding YE, Prapamontol T (2000) Environmental lead exposure: a public health problem of global dimensions. Bull World Health Organ 78:1068–1077
Tuzun I, Bayramoglu G, Yalcin E, Basaran G, Celik G, Arica MY (2005) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions onto microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Environ Manage 77:85–92. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.01.028
Watt G, Britton A, Gilmour HG, Moore MR, Murray GD, Robertson SJ (2000) Public health implications of new guidelines for lead in drinking water: a case study in an area with historically high water lead levels. Food Chem Toxicol 381:S73–S79. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00137-4
Zhang BG, Fan RM, Bai ZH, Wang S, Wang L, Shi JP (2013) Biosorption characteristics of Bacillus gibsonii S-2 waste biomass for removal of lead (II) from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:1367–1373. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1146-z
Zhuang L, Zhou SG, Wang YQ, Liu Z, Xu RX (2011) Cost-effective production of Bacillus thuringiensis biopesticides by solid-state fermentation using wastewater sludge: effects of heavy metals. Bioresour Technol 102:4820–4826. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.098
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program 863 (Grant No. 2011AA10A203), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Nos. 2010CB933501, 2013CB934302), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21477129), the Outstanding Youth Fund (21125730), the Leading Talents of Fujian Province College (k8012012a) and the Technology Key Project of Fujian Province (2013H0058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Pan, X., Chen, H. et al. Investigation of lead(II) uptake by Bacillus thuringiensis 016. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 1729–1736 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1923-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1923-1