Abstract
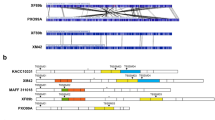
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc) cause two major seed quarantine diseases in rice, bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak, respectively. Xoo and Xoc share high similarity in genomic sequence, which results in hard differentiation of the two pathogens. Genomic-associated Markers and comparative Genome Maps database (GMGM) is an integrated database providing comprehensive information including compared genome maps and full genomic-coverage molecular makers of Xoo and Xoc. This database was established based on bioinformatic analysis of complete sequenced genomes of several X. oryzae pathovars of which the similarity of the genomes was up to 91.39 %. The program was designed with a series of specific PCR primers, including 286 pairs of Xoo dominant markers, 288 pairs of Xoc dominant markers, and 288 pairs of Xoo and Xoc co-dominant markers, which were predicted to distinguish two pathovars. Test on a total of 40 donor pathogen strains using randomly selected 120 pairs of primers demonstrated that over 52.5 % of the primers were efficacious. The GMGM web portal (http://biodb.sdau.edu.cn/gmgm/) will be a powerful tool that can present highly specific diagnostic markers, and it also provides information about comparative genome maps of the two pathogens for future evolution study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanove AJ, Koebnik R, Lu H, Furutani A, Angiuoli SV, Patil PB et al (2011) Two new complete genome sequences offer insight into host and tissue specificity of plant pathogenic Xanthomonas spp. J Bacteriol 193:5450–5464
Cho MS, Kang MJ, Kim CK, Seol Y-J, Hahn JH, Park SC et al (2011) Sensitive and specific detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by real-time bio-PCR using pathovar-specific primers based on an rhs family gene. Plant Dis 95:589–594
Kang MJ, Shim JK, Cho MS, Seol YJ, Hahn JH, Hwang DJ, Park DS (2008) Specific detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in infected rice plant by use of PCR assay targeting a membrane fusion protein gene. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1492–1495
Kang M, Kim M, Hwang D, Cho M, Seol Y, Hahn J et al (2012) Quantitative in planta PCR assay for specific detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola using putative membrane protein based primer set. Crop Prot 40:22–27
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol İ, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D et al (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645
Lanar DE, Kain KC (1994) Expression-PCR (E-PCR): overview and applications. Genome Res 4:S92–S96
Lang JM, Hamilton JP, Diaz MGQ, Van Sluys MA, Burgos MRG, Vera Cruz CM et al (2010) Genomics-based diagnostic marker development for Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant Dis 94:311–319
Lang JM, Langlois P, Nguyen MHR, Triplett LR, Purdie L, Holton TA et al (2014) Sensitive detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars oryzae and oryzicola by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:4519–4530
Lee B-M, Park Y-J, Park D-S, Kang H-W, Kim J-G, Song E-S et al (2005) The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Nucleic Acids Res 33:577–586
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P et al (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629
Mount DW (2007) Using the basic local alignment search tool (BLAST). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols 2007: pdb. top17
Niño-Liu DO, Ronald PC, Bogdanove AJ (2006) Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7:303–324
Salzberg SL, Sommer DD, Schatz MC, Phillippy AM, Rabinowicz PD, Tsuge S et al (2008) Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genom 9:204
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115–e115
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 30900780, 30900050), Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 20123702110014) and Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of PR China (Grant No. 201132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wenjie Feng and Yi Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, W., Wang, Y., Huang, L. et al. Genomic-associated Markers and comparative Genome Maps of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 1353–1359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1883-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1883-5