Abstract
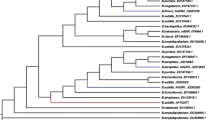
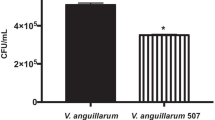
Acute gastroenteritis caused by pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus is one of the major factors affecting the development of aquaculture and the safety of seafood. Using the antagonism of probiotics against pathogens is an alternative strategy to antibiotics and a common trend to control food-borne pathogenic bacteria. In this study, a total of 249 isolates were isolated from four types of seafood (Litopenaeus vannamei, Oratosquilla oratoria, Mactra veneriformis and Portunus trituberculatus) and coastal sediment from Liaodong Bay in the Bohai Sea, China with five different separation agars. The most isolates came from the sample of coastal sediment and on agar of 2216E, which accounted for 36.14 and 54.62 % respectively. Twenty-four among 249 isolates displayed direct antimicrobial activity to V. parahaemolyticus with spot inoculation. Sixteen active isolates were selected for extracellular antimicrobial activity using the Oxford cup method. Only strains of B16 and J7 showed extracellular antimicrobial activity and were identified as Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus mojavensis respectively based on the physiological identification and 16S rRNA sequence analysis. Both of the strains B16 and J7 exhibited extracellular hydrolytic enzyme activity and antagonism against more than one indicator bacteria in vitro, which indicates that the two strains have broad potential application as suitable probiotic candidates in aquaculture while B. mojavensis was first reported to inhibit pathogenic Vibrio spp. in vitro. There is no particular trait as to antagonism of B. pumilus B16 or B. mojavensis J7 to Gram-positive or Gram-negative indicator bacteria.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai N, Rajeswari MV, Sahu SK, Balasubramanian T (2014) Purification and characterization of solvent stable, alkaline protease from Bacillus firmus CAS7 by microbial conversion of marine wastes and molecular mechanism underlying solvent stability. Process Biochem 49:1012–1019
Aranda CP, Valenzuela C, Barrientos J, Paredes J, Leal P, Maldonado M, Godoy FA, Osorio CG (2012) Bacteriostatic anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus activity of Pseudoalteromonas sp. strains DIT09, DIT44 and DIT46 isolated from Southern Chilean intertidal Perumytilus purpuratus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2365–2374
Aunpad R, Na-Bangchang K (2007) Pumilicin 4, a novel bacteriocin with anti-MRSA and anti-VRE activity produced by newly isolated bacteria Bacillus pumilus strain WAPB4. Curr Micobiol 55:308–313
Aunpad R, Panbangred W (2012) Evidence for two putative holin-like peptides encoding genes of Bacillus pumilus strain WAPB4. Curr Microbiol 64:343–348
Bacon CW, Hinton DM (2002) Endophytic and biological control potential of Bacillus mojavensis and related species. Biol Control 23:274–284
Bacon CW, Hinton DM, Mitchell TR, Snook ME, Olubajo B (2012) Characterization of endophytic strains of Bacillus mojavensis and their production of surfactin isomers. Biol Control 62:1–9
Barman P, Banerjee A, Bandyopadhyay P, Chandra MK, Mohapatra PKD (2011) Isolation, identification and molecular characterization of potential probiotic bacterium, Bacillus subtilis PPP 13 from Penaeus monodon. Biotechnol Bioinf Bioeng 1:473–482
Chahad OB, El Bour M, Calo-Mata P, Boudabous A, Barros-Velàzquez J (2012) Discovery of novel biopreservation agents with inhibitory effects on growth of food-borne pathogens and their application to seafood products. Res Microbiol 163:44–54
Donio MBS, Velmurugan S, Raman K, Babu MM, Citarasu T (2014) Antagonistic Bacillus cereus TC-1 isolated from solar salt work in southern India. J Microb Biochem Technol 6:242–246
Fernandez-Piquer J, Bowman JP, Ross T, Tamplin ML (2011) Predictive models for the effect of storage temperature on Vibrio parahaemolyticus viability and counts of total viable bacteria in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Appl Environ Microbiol 77:8687–8695
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. J Appl Bacteriol 66:365–378
Griffitt KJ, Noriea NF III, Johnson CN, Grimes DJ (2011) Enumeration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the viable but nonculturable state using direct plate counts and recognition of individual gene fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Microbiol Methods 85:114–118
Hong HA, Duc LH, Cutting SM (2005) The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:813–835
Irianto A, Austin B (2003) Use of dead probiotic cells to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 26:59–62
Iwamoto M, Ayers T, Mahon BE, Swerdlow DL (2010) Epidemiology of seafood-associated infections in the United States. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:399–411
Lai WB, Wong HC (2013) Influence of combinations of sublethal stresses on the control of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its cellular oxidative response. Food Control 33:186–192
Li GG, Liu BS, Shang YJ, Yu ZQ, Zhang RJ (2012) Novel activity evaluation and subsequent partial purification of antimicrobial peptides produced by Bacillus subtilis LFB112. Ann Microbiol 62:667–674
Nair AV, Vijayan KK, Chakrabort K, Antony ML (2012) Diversity and characterization of antagonistic bacteria from tropical estuarine habitats of Cochin, India for fish health management. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2581–2592
Newaj-Fyzul A, Al-Harbi AH, Austin B (2014) Review: developments in the use of probiotics for disease control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 431:1–11
Nimrat S, Boonthai T, Vuthiphandchai V (2011) Effects of probiotic forms, compositions of and mode of probiotic administration on rearing of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae and postlarvae. Anim Feed Sci Technol 169:244–258
Nithya C, Aravindraja C, Pandian SK (2010) Bacillus pumilus of Palk Bay origin inhibits quorum-sensing-mediated virulence factors in Gram-negative bacteria. Res Microbiol 161:293–304
Raghunath P, Acharya S, Bhanumathi A, Iddya Karunasagar, Indrani Karunasagar (2008) Detection and molecular characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from seafood harvested along the southwest coast of India. Food Microbiol 25:824–830
Ravi AV, Musthafa KS, Jegathammbal G, Kathiresan K, Pandian SK (2007) Screening and evaluation of probiotics as a biocontrol agent against pathogenic Vibrios in marine aquaculture. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:219–223
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1994) Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:256–264
Salminen S, Ouwehand A, Benno Y, Lee YK (1999) Probiotics: How should they be defined? Trends Food Sci Technol 10:107–110
Snook ME, Mitchell T, Hinton DM, Bacon CW (2009) Isolation and characterization of Leu7-surfactin from the endophytic bacterium Bacillus mojavensis RRC 101, a biocontrol agent for Fusarium verticillioides. J Agric Food Chem 57:4287–4292
Touraki M, Karamanlidou G, Karavida P, Chrysi K (2012) Evaluation of the probiotics Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum bioencapsulated in Artemia nauplii against vibriosis in European sea bass larvae (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2425–2433
Vynne NG, Månsson M, Nielsen KF, Gram L (2011) Bioactivity, chemical profiling, and 16S rRNA-based phylogeny of Pseudoalteromonas strains collected on a global research cruise. Mar Biotechnol 13:1062–1073
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51:221–271
World Health Organization, Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2011) Risk assessment of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood: interpretative summary and technical report
Wu WJ, Ahn BY (2011) Isolation and identification of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BY01 with high productivity of menaquinone for Cheonggukjang production. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 54:783–789
Wu YN, Wen J, Ma Y, Ma XC, Chen Y (2014) Epidemiology of foodborne disease outbreaks caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, China, 2003–2008. Food Control 46:197–202
Xu P, Zeng YC, Fong Q, Lone T, Liu YY (2012) Chinese consumers’ willingness to pay for green- and eco-labeled seafood. Food Control 28:74–82
Xu HM, Rong YJ, Zhao MX, Song B, Chi ZM (2014) Antibacterial activity of the lipopetides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M1 against multidrug-resistant Vibrio spp. isolated from diseased marine animals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:127–136
Yu WT, Jong KJ, Lin YR, Tsai SE, Tey YH, Wong HC (2013) Prevalence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oyster and clam culturing environments in Taiwan. Int J Food Microbiol 160:185–192
Zarei M, Borujeni MP, Jamnejad A, Khezrzadeh M (2012) Seasonal prevalence of Vibrio species in retail shrimps with an emphasis on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 25:107–109
Zhang XY, He F, Wang GH, Bao J, Xu XY, Qi SH (2013) Diversity and antibacterial activity of culturable actinobacteria isolated from five species of the South China Sea gorgonian corals. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1107–1116
Zokaeifar H, Balcázar JL, Saad CR, Kamarudin MS, Sijam K, Arshad A, Nejat N (2012) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:683–689
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the National Key Technologies R & D Programme of China during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period (2012BAD29B06), Food Safety Key Laboratory of Liaoning Province, and Engineering and Technology Research Centre for Food Preservation, Processing, and Safety Control of Liaoning Province (LNSAKF2011031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XF., Li, Y., Li, JR. et al. Isolation and characterisation of Bacillus spp. antagonistic to Vibrio parahaemolyticus for use as probiotics in aquaculture. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 795–803 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1833-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1833-2