Abstract
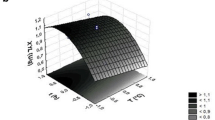
Endoglucanase activity produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa BEb-40 was studied. In submerged culture with minimal medium supplemented with carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), this microorganism produced up to 0.37 U/mL endoglucanase activity with high specific activity (14.3 U/mgtotal protein). Detection of endoglucanase activity through zymography revealed at least 14 isoenzymes with molecular weights between 38 and 220 kDa. This high variety of secreted endoglucanases has not been described previously in Paenibacillus genus. The optimum conditions, determined by response surface methodology, were 48 °C and pH 3.4, which allowed an increase of 33.7 % in the relative endoglucanase activity obtained with respect to the standard conditions. Nevertheless, high levels of hydrolysis of at least 70 % of the maximum activity could be obtained at wide ranges of pH (2–9) and temperature (40–60 °C). Under optimal conditions, high levels of CMC hydrolysis were reached, of about 40 %, after only 12 h of reaction with substrate/total protein ratios between 19 and 76. Kinetic analysis revealed that endoglucanase activity followed a mixed inhibition model (K m = 8.4 mM, K ic = 0.03 mM, K iu = 0.35 mM, V max = 33.3 U/mgtotal protein). These results allow to consider P. polymyxa BEb-40 as a promising microorganism for the production of endoglucanases, with possibilities of application in the breakdown of lignocellulosic biomass. The high specific activity at wide ranges of pH and temperature can allow its use in a wide variety of processes, under both acidic and alkaline conditions, as well as in mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures, further reducing the amount of enzymes used.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlakha N, Rajagopal R, Kumar S, Reddy VS, Yazdani SS (2011) Synthesis and characterization of chimeric proteins based on cellulase and xylanase from an insect gut bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(14):4859–4866. doi:10.1128/AEM.02808-10
Adlakha N, Sawant S, Anil A, Lali A, Yazdani SS (2012) Specific fusion of β-1,4-endoglucanase and β-1,4-glucosidase enhances cellulolytic activity and helps in channeling of intermediates. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(20):7447–7454. doi:10.1128/AEM.01386-12
Afzal S, Saleem M, Yasmin R, Naz M, Imran M (2009) Pre and post cloning characterization of a β-1,4-endoglucanase from Bacillus sp. Mol Biol Rep 37(4):1717–1723. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9592-5
Asha BM, Revathi M, Yadav A, Sakthivel N (2012) Purification and characterization of a thermophilic cellulase from a novel cellulolytic strain, Paenibacillus barcinonensis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(11):1501–1509. doi:10.4014/jmb.1202.02013
Baş D, Boyacı İH (2007) Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78(3):836–845. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.11.024
Banerjee G, Scott-Craig JS, Walton JD (2010) Improving enzymes for biomass conversion: a basic research perspective. Bioenergy Res 3(1):82–92. doi:10.1007/s12155-009-9067-5
Bezerra RMF, Dias AA (2004) Discrimination among eight modified Michaelis–Menten kinetics models of cellulose hydrolysis with a large range of substrate/enzyme ratios: inhibition by cellobiose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 112(3):173–184. doi:10.1385/ABAB:112:3:173
Bezerra RMF, Dias AA (2007) Utilization of integrated Michaelis–Menten equation to determine kinetic constants. Biochem Mol Biol Educ 35(2):145–150. doi:10.1002/bmb.32
Box GEP, Hunter JS, Hunter WG (2005) Statistics for experimenters: design, innovation, and discovery, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. doi:10.1385/0-89603-268-X:9
Castro AM, Pedro KCNR, Cruz JC, Ferreira MC, Leite SGF, Pereira N Jr (2010) Trichoderma harzianum IOC-4038: a promising strain for the production of a cellulolytic complex with significant β-glucosidase activity from sugarcane bagasse cellulignin. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162(7):2111–2122. doi:10.1007/s12010-010-8986-0
Chiriac AI, Cadena EM, Vidal T, Torres AL, Diaz P, Pastor FIJ (2010) Engineering a family 9 processive endoglucanase from Paenibacillus barcinonensis displaying a novel architecture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86(4):1125–1134. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2350-8
Davies MT (1959) A universal buffer solution for use in ultra-violet spectrophotometry. Analyst 84(997):248–251. doi:10.1039/AN9598400248
Elzhov TV, Mullen KM, Spiess AN, Bolker B (2013) minpack.lm: R interface to the Levenberg–Marquardt nonlinear least-squares algorithm found in MINPACK, plus support for bounds. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=minpack.lm
Farinas CS, Loyo MM, Baraldo A, Tardioli PW, Neto VB, Couri S (2010) Finding stable cellulase and xylanase: evaluation of the synergistic effect of pH and temperature. New Biotechnol 27(6):810–815. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2010.10.001
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59(2):257–268. doi:10.1351/pac198759020257
Ko CH, Chen WL, Tsai CH, Jane WN, Liu CC, Tu J (2007) Paenibacillus campinasensis BL11: a wood material-utilizing bacterial strain isolated from black liquor. Bioresour Technol 98(14):2727–2733. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.034
Ko CH, Tsai CH, Lin PH, Chang KC, Tu J, Wang YN, Yang CY (2010) Characterization and pulp refining activity of a Paenibacillus campinasensis cellulase expressed in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 101(20):7882–7888. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.043
Kumar D, Ashfaque M, Muthukumar M, Singh M, Garg N (2012) Production and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulase from Paenibacillus polymyxa using mango peel as substrate. J Environ Biol 33(1):81–84. http://jeb.co.in/journal_issues/201201_jan12/paper_13.pdf
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Lee YJ, Kim BK, Lee BH, Jo KI, Lee NK, Chung CH, Lee YC, Lee JW (2008) Purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Bacillus amyoliquefaciens DL-3 utilizing rice hull. Bioresour Technol 99(2):378–386. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.12.013
Lenth RV (2009) Response-surface methods in R, using rsm. J Stat Softw 32(7):1–17. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v32/i07/
Li W, Zhang WW, Yang MM, Chen YL (2008) Cloning of the thermostable cellulase gene from newly isolated Bacillus subtilis and its expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Biotechnol 40(2):195–201. doi:10.1007/s12033-008-9079-y
Lockington RA, Rodbourn L, Barnett S, Carter CJ, Kelly JM (2002) Regulation by carbon and nitrogen sources of a family of cellulases in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 37(2):190–196. doi:10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00504-2
Maki M, Leung KT, Qin W (2009) The prospects of cellulase-producing bacteria for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Int J Biol Sci 5(5):500–516. doi:10.7150/ijbs.5.500
Manchenko GP (2002) Handbook of detection of enzymes on electrophoretic gels, 2nd edn. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton. http://books.google.com.mx/books?id=bBkTz04RCmQC
Mannervik B (1982) Regression analysis, experimental error, and statistical criteria in the design and analysis of experiments for discrimination between rival kinetic models. In: Purich DL (ed) Enzyme kinetics and mechanism: part C: intermediates, stereochemistry, and rate studies: methods in enzymology, vol 87, Academic Press, New York, pp 370–390. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(82)87023-7
Martínez A, Ramírez OT, Valle A (1997) Improvement of culture conditions to overproduce β-galactosidase from Escherichia coli in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47(1):40–45. doi:10.1007/s002530050885
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030
Ogawa A, Suzumatsu A, Takizawa S, Kubota H, Sawada K, Hakamada Y, Kawai S, Kobayashi T, Ito S (2007) Endoglucanases from Paenibacillus spp. form a new clan in glycoside hydrolase family 5. J Biotechnol 129(3):406–414. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.01.020
Pandey S, Singh S, Yadav AN, Nain L, Saxena AK (2013) Phylogenetic diversity and characterization of novel and efficient cellulase producing bacterial isolates from various extreme environments. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77(7):1474–1480. doi:10.1271/bbb.130121
Park IH, Chang J, Lee YS, Fang SJ, Choi YL (2012) Gene cloning of endoglucanase Cel5A from cellulose-degrading Paenibacillus xylanilyticus KJ-03 and purification and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Protein J 31(3):238–245. doi:10.1007/s10930-012-9396-7
Pason P, Kyu KL, Ratanakhanokchai K (2006) Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus strain B-6 xylanolytic-cellulolytic enzyme system that degrades insoluble polysaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(4):2483–2490. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.4.2483-2490.2006
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Rojas-Rejón OA, Poggi-Varaldo HM, Ramos-Valdivia AC, Martínez-Jiménez A, Cristiani-Urbina E, de la Torre Martínez M, Ponce-Noyola T (2011) Production of cellulases and xylanases under catabolic repression conditions from mutant PR-22 of Cellulomonas flavigena. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(1):257–264. doi:10.1007/s10295-010-0821-7
Singhania RR, Sukumaran RK, Patel AK, Larroche C, Pandey A (2010) Advancement and comparative profiles in the production technologies using solid-state and submerged fermentation for microbial cellulases. Enzyme Microb Technol 46(7):541–549. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2010.03.010
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00212-7
Suwannarangsee S, Bunterngsook B, Arnthong J, Paemanee A, Thamchaipenet A, Eurwilaichitr L, Laosiripojana N, Champreda V (2012) Optimisation of synergistic biomass-degrading enzyme systems for efficient rice straw hydrolysis using an experimental mixture design. Bioresour Technol 119:252–261. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.098
Taylor LE II, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Ekborg NA, Hutcheson SW, Weiner RM (2006) Complete cellulase system in the marine bacterium Saccharophagus degradans strain 2–40. J Bacteriol 188(11):3849–3861. doi:10.1128/JB.01348-05
Van Dyk JS, Sakka M, Sakka K, Pletschke BI (2009) The cellulolytic and hemi-cellulolytic system of Bacillus licheniformis SVD1 and the evidence for production of a large multi-enzyme complex. Enzyme Microb Technol 45(5):372–378. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2009.06.016
Wang CM, Shyu CL, Ho SP, Chiou SH (2008) Characterization of a novel thermophilic, cellulose-degrading bacterium Paenibacillus sp. strain B39. Lett Appl Microbiol 47(1):46–53. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02385.x
Watson BJ, Zhang H, Longmire AG, Moon YH, Hutcheson SW (2009) Processive endoglucanases mediate degradation of cellulose by Saccharophagus degradans. J Bacteriol 191(18):5697–5705. doi:10.1128/JB.00481-09
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Mexican Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT). Argel Gastelum-Arellanez held a scholarship from CONACyT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gastelum-Arellanez, A., Paredes-López, O. & Olalde-Portugal, V. Extracellular endoglucanase activity from Paenibacillus polymyxa BEb-40: production, optimization and enzymatic characterization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2953–2965 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1723-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1723-z