Abstract
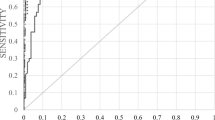
In this study, randomized patient sera were used to simultaneously evaluate an automated C-reactive protein (CRP) assay and a commercial semi-automated microCRP assay with respect to correlation, linearity, and accuracy. Patient specimens were analyzed; two independent assay runs were performed on i-CHROMA (Boditech Med Inc., Korea) and IMMAGE 800 (Beckman Coulter Inc., USA) analyzers to estimate the between- and within-run precision. All systems were calibrated, and quality-control materials were analyzed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The results using the control materials were within the respective manufacturers’ specified limits. The comparison studies were designed using the CLSI EP9-2A guidelines. The mean serum CRP concentrations were 123.2 ± 123.5 mg/L (95 % confidence of interval (CI) 97.9–148.3) using the CRP assay and 130.1 ± 109.3 mg/L (95 % CI 107.9–152.4) using the microCRP assay. The variance values were σ = 15,252.6 and 11,935.8 for the CRP and microCRP assays, respectively. The concordance correlation coefficient value was calculated as 0.8314 (95 % CI 0.7594–0.8833). There was a significant correlation between the CRP and microCRP assays: r = 0.8392 and 95 % CI 0.7675–0.8902 (p < 0.0001). The CRP and microCRP detection methods were well correlated. The i-CHROMA has many advantages over the IMMAGE 800 with respect to space required, analysis time, and system setup/application costs in a laboratory. It may be an attractive instrument for small and intermediate medical centers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris RI, Stone PCW, Hudson AG, Stuard J (1984) C reactive protein rapid assay techniques for monitoring resolution of infection in immunosuppressed patients. J Clin Pathol 37:821–828
Hemmila I (1985) Fluoroimmunoassay and immunofluorometric assay. Clin Chem 31(3):359–370
Lolekha PH, Chittamma A, Roberts WL, Sritara P, Cheepudomwit S, Suriyawongpaisal P (2005) Comparative study of two automated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein methods in a large population. Clin Biochem 38:31–35
NCCLS (2002) Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline—second edition. NCCLS document EP9-A2. NCCLS, Wayne. ISBN:1-56238-472-4
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM (2003) C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest. 111:1805–1812
Punyadeera C, Dimeski G, Kostner K, Beyerlein P, Cooper-White J (2011) One-step homogeneous C-reactive protein assay for saliva. J Immunol Methods 373(1):19–25
Shaw AC (1991) Serum C-reactive protein and neopterin concentrations in patients with viral or bacterial infection. J Clin Pathol 44(7):9–596
Sisman AR, Kume T, Tas G, Akan P, Tuncel P (2007) Comparison and evaluation of two C-reactive protein assays based on particle-enhanced immunoturbidimetry. J Clin Lab Anal 21:71–76
Zhu X, Duan D, Publicover NG (2010) Magnetic bead based assay for C-reactive protein using quantum-dot fluorescence labeling and immunoaffinity separation. Analyst 135:381–389
Acknowledgments
This was an experimental, randomized study that evaluated in vitro samples prospectively. No additional samples were taken from patients.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciftci, İ.H., Koroglu, M. & Karakece, E. Comparison of novel and familiar commercial kits for detection of C-reactive protein levels. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2295–2298 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1653-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1653-9