Abstract
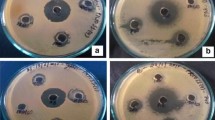
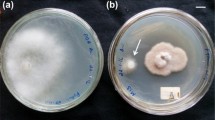
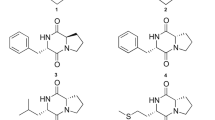
Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPN) are well-known as biological control agents and are found to have associated bacteria which can produce a wide range of bioactive secondary metabolites. We report herewith isolation of six proline containing cyclic dipeptides cyclo(d-Pro-l-Leu), cyclo(l-Pro-l-Met), cyclo(d-Pro-l-Phe), cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe), cyclo(l-Pro-l-Tyr) and cyclo(l-Pro-d-Tyr) from ethyl acetate extract of the Luria Broth (LB) cell free culture filtrate of Bacillus sp. strain N associated with a new EPN Rhabditis sp. from sweet potato weevil grubs collected from Central Tuber Crops Research Institute farm. Antimicrobial studies of these 2,5-diketopiperazines (DKPs) against both medicinally and agriculturally important bacterium and fungi showed potent inhibitory values in the range of μg/mL. Cyclic dipeptides showed significantly higher activity than the commercial fungicide bavistin against agriculturally important fungi, viz., Fusarium oxysporum, Rhizoctonia solani, and Pencillium expansum. The highest activity of 2 μg/mL by cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe) was recorded against P. expansum, a plant pathogen responsible for causing post harvest decay of stored apples and oranges. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the isolation of these DKPs from Rhabditis EPN bacterial strain Bacillus sp.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhurst RJ (1982) Antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus spp., bacteria symbiotically associated with insect pathogenic nematodes of the families Hettrorhabditidae and Steinernematidae. J Gen Microbiol 128:3061–3065
Anteunis MJO (1978) The cyclic dipeptides: proper model compounds in peptide research. Bull Soc Chim Belg 87:627–650
Bowen D, Blackburn M, Rocheleau T, Grutzmacher C, Ffrench-Constant RH (2000) Secreted proteases from Photorhabdus luminescens: separation of the extracellular proteases from the insecticidal Tc toxin complexes. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:69–74
Brachmann AO, Forst S, Furgani GM, Fodor A, Bode HB (2006) Xenofuranones A and B: phenylpyruvate dimmers from Xenorhabdus szentirmaii. J Nat Prod 69:1830–1832
Burnell AM, Stock SP (2000) Heterorhabditis, Steinernema and their bacterial symbionts lethal pathogens of insects. Nematology 2:31–42
Cain CC, Lee D, Waldo RH, Henry AT, Casida EJ, Wani MC, Wall ME, Oberlies NH, Falkinham JO (2003) Synergistic antimicrobial activity of metabolites produced by a nonobligate bacterial predator. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:2113–2117
Campbell J, Lin Q, Geske GD, Blackwell HE (2009) New and unexpected insights into the modulation of LuxR-type quorum sensing by cyclic dipeptides. ACS Chem Biol 4:1051–1059
Chen G, Dunphy GB, Webster JM (1994) Antifungal activity of two Xenorhabdus species and Photorhabdus luminescens, bacteria associated with the nematodes Steinernema species and Heterorhabditis megidis. Biol Control 4:157–162
CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2006) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. CLSI documents M27-S3, Wayne
CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2008) Reference methods for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility tests of yeasts. CLSI documents M27-S3, Wayne
Deepa I, Mohandas C, Makesh KT, Siji JV, Prakash KBS, Babu B (2010) Identification of new entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) based on sequences of D2–D3 expansion fragments of the 28SrRNA. J Root Crops 36(2):227–232
Fdhila F, Vazquez V, Sanchez JL, Riguera R (2003) DD-Diketopiperazines: antibiotics active against Vibrio anguillarum isolated from marine bacteria associated with cultures of Pecten maximus. J Nat Prod 66:1299–1301
Forst S, Dowds B, Boemare N, Stackebrandt E (1997) Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp. Bugs that kill bugs. Annu Rev Microbiol 51:47–72
Gaugler R, Kaya HK (1990) Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 75–90
Gualtieri M, Aumelasm A, Thaler JO (2009) Identification of a new antimicrobial lysine-rich cyclolipopeptide family from Xenorhabdus nematophila. J Antibiot 62:295–302
Holden MTG, Chhabra SR, de Nys R, Stead P, Bainton NJ, Hill PJ, Manefield M, Kumar N, Labatte M, England D, Rice S, Givskov M, Salmond GPC, Stewartm GSAB, Bycroft BW, Kjelleberg SA, Williams P (1999) Quorum-sensing cross talk: isolation and chemical characterization of cyclic dipeptides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol 33:1254
Hu K, Li J, Webster JM (1999) Nematicidal metabolites produced by Photorhabdus luminescens (Enterobacteriaceae), bacterial symbiont of entomopathogenic nematodes. Nematology 1:457–469
Huang RM, Ma W, Dong JD, Zhou XF, Xu T, Lee KJ, Yang X, Xu SH, Liu Y (2010) A new 1,4-diazepine from South China Sea marine sponge Callyspongia species. Molecules 15:871–877
Jayatilake GS, Thornton MP, Leonard AC, Grimwade JE, Baker BJ (1996) Metabolites from an Antarctic sponge-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nat Prod 59:293–296
Ji DJ, Yi YK, Kang GH (2004) Identification of an antibacterial compound, benzylideneacetone, from Xenorhabdus nematophila against major plant-pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 239:241–248
Lang G, Kalvelage T, Peters A, Wiese J, Imhoff JF (2006) Linear and cyclic peptides from the entomopathogenic bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophilus. J Nat Prod 71:1074–1077
Lang G, Kalvelage T, Peters A, Wiese J, Imhoff JF (2008) Peptides from the entomopathogenic bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophilus. J Nat Prod 71:1074–1077
Li JX, Chen GH, Webster JM (1997) Nematophin, a novel antimicrobial substance produced by Xenorhabdus nematophilus (Enterobactereaceae). Can J Microbiol 43:770–773
Li J, Wenliang W, Stacey XX, Magarvey NA, McCormick JK (2011) Lactobacillus reuteri-produced cyclic dipeptides quench agr-mediated expression of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 in staphylococci. PNAS 108:3360–3365
Marfey P (1984) Determination of D-amino acids. II. Use of a bifunctional reagents, 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Carlsberg Res Commun 49:591–596
McInerney BV, Gregson RP, Lacey MJ, Akhurst RJ, Lyons GR, Rhodes SH, Smith DRJ, Engelhardt LM (1991a) Biologically active metabolites from Xenorhabdus spp. Part 1. Dithiolopyrrolone derivatives with antibiotic activity. J Nat Prod 54:774–784
McInerney BV, Taylor WC, Lacey MJ, Akhurst RJ, Gregson RP (1991b) Biologically active metabolites from Xenorhabdus spp. Part 2 Benzopyran-1-one derivatives with gastroprotective activity. J Nat Prod 54:785–795
Paul VJ, Frautschy S, Fenical W, Nealson KH (1981) Antibiotics in microbial ecology, isolation and structure assignment of several new antibacterial compounds from the insect symbiotic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. J Chem Ecol 7:589–597
Prasad C (1995) Bioactive cyclic dipeptides. Peptides 16:151–164
Rhee KH (2004) Cyclic dipeptides exhibit synergistic, broad spectrum antimicrobial effects and have anti-mutagenic properties. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24:423–427
Rollas S, Kalyoncuoglu N, Sur-Altiner D, Yegenglu Y (1993) 5-(4-Aminophenyl)-4-substituted 2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiones: synthesis, antibacterial and antifungal activities. Pharmazie 48:308–309
Rosa SD, Mitova M, Tommonaro G (2003) Marine bacteria associated with sponge as source of cyclic peptides. Biomol Engineering 20:311–316
Rudi A, Kashman Y, Benayahu Y, Schleyer M (1994) Amino acid derivatives from the marine sponge Jaspis digonoxea. J Nat Prod 57:829
Shapiro-Ilan DI, Gouge GH, Piggott SJ, Patterson FJ (2006) Application technology and environmental considerations for use of entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. Biol Cont 38:124–133
Smaoui S, Mathieu F, Elleuch L, Coppel Y, Merlina G, Karray RI, Mellouli L (2012) Taxonomy, purification and chemical characterization of four bioactive compounds from new Streptomyces sp. TN256 strain. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:793–804
Ström K, Sjogren J, Broberg A, Schnurer J (2002) Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo(L-Phe-L-Pro) and cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-OH-L-pro) and 3-phenyllactic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4322–4327
Thaler JO, Duvic B, Givaudan A, Boemare N (1998) Isolation and entomotoxic properties of the Xenorhabdus nematophilus F1 lecithinase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2367–2373
Toubarro D, Lucena-Robles M, Nascimento G, Costa G, Montiel R, Coelho AV, Simões N (2009) An apoptosis-inducing serine protease secreted by the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. Int J Parasitol 39:1319–1320
Tullberg M, Luthman K, Grtli M (2006) Microwave assisted solid-phase synthesis of 2,5-diketopiperazines: solvent and resin dependence. J Comb Chem 8:915–922
Wang Y, Mueller UG, Clardy J (1999) Antifungal diketopiperazines from symbiotic fungus of fungus-growing ant Cyphomyrmex minutus. J Chem Ecol 25:935–941
Wang Y, Fang X, Cheng Y, Zhang X (2011) Manipulation of pH shift to enhance the growth and antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus nematophila. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:1–9
Yan PS, Song Y, Sakuno E, Nakajima H, Nakagawa H, Yabe K (2004) Cyclo(Leucyl- L-prolyl) produced by Achromobacter xylosoxidans inhibits aflatoxin production by Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7466–7473
Yang J, Zeng HM, Lin HF, Yang XF, Liu Z, Guo LH, Yuan JJ, Qiu DW (2012) An insecticidal protein from Xenorhabdus budapestensis that results in prophenoloxidase activation in the wax moth, Galleria mellonella. J Invertebr Pathol 110:60–67
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. R. Srinivas, HOD, NCMS, IICT, Hyderabad for HRMS analysis. This work was funded by Indian council of Medical Research (ICMR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11274_2012_1189_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary data includes HRMS of DKPs and HPLC profile of FDAA derivatives of the acid hydrolysates of DKPs 1–6 and respective derivatives of l and d standard amino acids. (DOC 1186 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Mohandas, C., Nambisan, B. et al. Isolation of proline-based cyclic dipeptides from Bacillus sp. N strain associated with rhabitid entomopathogenic nematode and its antimicrobial properties. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 355–364 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1189-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1189-9