Abstract
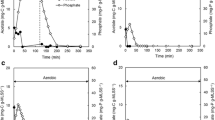
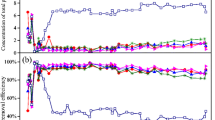
The microbial selection on an enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) system was investigated in a laboratory-scale sequencing batch reactor fed exclusively with glucose as the carbon source. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization analysis was performed to target two polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) (i.e., Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis and Microlunatus phosphovorus) and two glycogen accumulating organisms (GAOs) (i.e., Candidatus Competibacter phosphatis and Micropruina glycogenica). The results show that glucose might not select for Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis. However, Microlunatus phosphovorus, Candidatus Competibacter phosphatis, and Micropruina glycogenica might be selected. The highest percent relative abundance (% RA) of Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis was about 42%; this occurred at the beginning of the experimental period when phosphorus removal was efficient. However, the % RA of these bacteria decreased, reaching below 4% at the end of the run. The maximum % RA of Microlunatus phosphovorus, Candidatus Competibacter phosphatis, and Micropruina glycogenica was about 21, 37, 17%, respectively. It appears that a higher glucose concentration might be detrimental for Microlunatus phosphovorus and Micropruina glycogenica. Results also indicate a dominance of GAOs over PAOs when EBPR systems are fed with glucose. It is possible that the GAOs outcompete the PAOs at low pH values; it has been reported that at low pH, GAOs use glycogen as the energy source to uptake glucose. As a result, P-removal deteriorated. Therefore, glucose is not a strong candidate as a carbon source to supplement EBPR systems that do not contain sufficient volatile fatty acids.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Z, Lim B-R, Cho J, Song K-G, Kim K-P, Ahn K-H (2008) Biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal and changes in microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor: effect of different carbon sources. Water Res 42:198–210
Amann RI (1995) In situ identification of micro-organisms by whole cell hybridization with rRNA-targeted nucleic acid probes. In: Akkermans ADL, van Elsas JD, de Bruijn FJ (eds) Manual of molecular microbial ecology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1–15
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Beer M, Kong YH, Seviour RJ (2004) Are some putative glycogen accumulating organisms (GAO) in anaerobic: aerobic activated sludge systems members of the α-proteobacteria? Microbiol 150:2267–2275
Bond PL, Keller J, Blackall LL (1999) Bio-P, and non-bio-P bacteria identification by a novel microbial approach. Water Sci Technol 39:13–20
Burow LC, Kong Y, Nielsen JL, Blackall LL, Nielsen PH (2007) Abundance and ecophysiology of Defluvicoccus spp., glycogen-accumulating organisms in full-scale wastewater treatment processes. Microbiol 153:178–185
Cech JS, Hartman P (1993) Competition between polyphosphate and polysaccharide accumulating bacteria in enhanced biological phosphate removal system. Water Res 27:1219–1225
Chen Y, Gu G (2006) Effect of changes of pH on the anaerobic/aerobic transformations of biological phosphorus removal in wastewater fed with a mixture of propionic and acetic acids. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1021–1028
Chuang S-H, Chang W-C, Huang Y-H, Tseng C-C, Tai C-C (2011) Effects of different carbon supplements on phosphorus removal in low C/P ratio industrial wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102:5461–5465
Cokgor EU, Yagci NO, Randall CW, Artan N, Orhon D (2004) Effects of pH and substrate on the competition between glycogen and phosphorus accumulating organisms. J Environ Sci Health A39:1695–1704
Comeau Y, Hall KJ, Hancock REW, Oldham WK (1986) Biochemical model for enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Water Res 20:1511–1521
Crocetti GR, Hugenholtz P, Bond PL, Schuler A, Keller J, Jenkins D, Blackall LL (2000) Identification of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and design of 16S rRNA-directed probes for their detection and quantification. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1175–1182
Crocetti GR, Banfield JF, Keller J, Bond PL, Blackall LL (2002) Glycogen-accumulating organisms in laboratory-scale and full-scale wastewater treatment processes. Microbiol 148:3353–3364
Fang HHP, Zhang T, Liu Y (2002) Characterization of an acetate-degrading sludge without intracellular accumulation of polyphosphate and glycogen. Water Res 36:3211–3218
Filipe CDM, Daigger GT, Grady CPL (2001) Stoichiometry and kinetic of acetate uptake under anaerobic conditions by an enriched culture of phosphorus-accumulating organisms at different pHs. Biotech Bioeng 76:32–43
Grady CPL, Daigger GT, Lim HC (1999) Biological wastewater treatment, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Hollender J, van der Krol D, Kornberger L, Gierden E, Dott W (2002) Effect of different carbon sources on the enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:355–360
Jeon CO, Park JM (2000) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor supplied with glucose as a sole carbon source. Water Res 34:2160–2170
Jeon CO, Lee DS, Park JM (2001) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal in an anaerobic—aerobic sequencing batch reactor: characteristics of carbon metabolism. Water Environ Res 73:295–300
Kawaharasaki M, Tanaka H, Kanagawa T, Nakamura K (1999) In situ identification of polyphosphate-accumulating bacteria in activated sludge by dual staining with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes and 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindol (DAPI) at a polyphosphate-probing concentration. Water Res 33:257–265
Kong YH, Beer M, Seviour RJ, Lindrea KC, Rees GN (2001) Structure and functional analysis of the microbial community in an aerobic: anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (SBR) with no phosphors removal. Syst Appl Microbiol 24:597–609
Kong YH, Beer M, Seviour RJ, Lindrea KC, Rees GA (2002) Role of “G-bacteria” in anaerobic substrate uptake in a SBR with no phosphorus removal. Water Sci Technol 46:171–178
Kong Y, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2004) Microautoradiographic study of Rhodocyclus-related polyphosphate accumulating bacteria in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5383–5390
Kong Y, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2005) Identity and ecophysiology of uncultured actinobacterial polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Appl Environl Microbiol 71:4076–4085
Kong Y, Xia Y, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2006) Ecophysiology of a group of uncultured gammaproteobacterial glycogen-accumulating organisms in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal wastewater treatment plants. Environ Microbiol 8:479–489
Lu H, Oehmen A, Virdis B, Keller J, Yuan Z (2006) Obtaining highly enriched cultures of candidatus accumulibacter phosphates through alternating carbon sources. Water Res 40:3838–3848
Machado JC (2004) Impacts of different types of volatile fatty acids on the bacterial selection in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Dissertation, University of Nevada Las Vegas
Meyer RL, Saunders AM, Blackall LL (2006) Putative glycogen-accumulating organisms belonging to the alphaproteobacteria identified through rRNA-based stable isotope probing. Microbiol 152:419–429
Nakamura K, Ishikawa S, Kawaharasaki M (1995a) Phosphate uptake and release activity in immobilized polyphosphate-accumulating bacterium Microlunatus phosphovorus strain NM-1. J Ferment Bioeng 80:377–382
Nakamura K, Hiraishi A, Yoshimi Y, Kawaharasaki M, Masuda K, Kamagata Y (1995b) Microlunatus phosphovorus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new gram-positive polyphosphate-accumulating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:17–22
NIH (2008) Image J. http://rsbweb.nih.gov. Accessed 10 July 2008
NIH (2012) http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi. Accessed 1 Jan 2012
Oehmen A, Yuan Z, Blackall LL, Keller J (2004) Short-term effects of carbon source on the competition of polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Water Sci Technol 50:139–144
Oehmen A, Zeng RJ, Yuan Z, Keller J (2005a) Anaerobic metabolism of propionate by polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Biotech Bioeng 91:43–52
Oehmen A, Vives TM, Lu H, Yuan Z, Keller J (2005b) The effect of pH on the competition between polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and glycogen-accumulating organisms. Water Res 39:3727–3737
Oehmen A, Yuan Z, Blackall L, Keller J (2005c) Comparison of acetate and propionate uptake by polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Biotech Bioeng 91:162–168
Oehmen A, Saunders AM, Vives MT, Yuan Z, Keller J (2006) Competition between polyphosphate and glycogen accumulating organisms in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems with acetate and propionate as carbon sources. J Biotechnol 123:22–32
Pijuan M, Saunders AM, Guisasola A, Baeza JA, Casas C, Blackall LL (2004a) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor using propionate as the sole carbon source. Biotechnol Bioeng 5:56–67
Pijuan M, Baeza JA, Casas C, Lafuente J (2004b) Response of an EBPR population developed in an SBR with propionate to different carbon sources. Water Sci Technol 50:131–138
Santos MM, Lemos PC, Reis MAM, Santos H (1999) Glucose metabolism and kinetics of phosphorus removal by the fermentative bacterium Microlunatus Phosphovorus. Appl Environl Microbiol 65:3920–3928
Satoh H (1994) Deterioration of enhanced biological phosphorus removal by the domination of microorganisms without polyphosphate accumulation. Water Sci Technol 30:203–211
Saunders AM, Oehmen A, Blackall LL, Yuan Z, Keller J (2003) The effect of GAOs (glycogen accumulating organisms) on anaerobic carbon requirements in full-scale australian EBPR (enhanced biological phosphorus removal) plants. Water Sci Technol 47:37–43
Schuler AJ, Jenkins D (2002) Effects of pH on enhanced biological phosphorus removal metabolisms. Water Sci Technol 46:171–178
Serafim LS, Lemos PC, Reis MAM (2002) Effect of pH control of EBPR stability and efficiency. Water Sci Technol 46:179–184
Shintani T, Liu W-T, Hanada S, Kamagata Y, Miyaoka S, Suzuki T, Nakamura K (2000) Micropruina Glycogenica gen. nov., sp. nov., a new gram-positive glycogen-accumulating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:201–207
Smolders GJF, van der Meij J, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1994) Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process: stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:461–470
Tasli R, Artan N, Orhon D (1997) The influence of different substrates on enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 35:75–80
Wang N, Hill G, Peng J (2002) The role of glucose in developing enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Environ Eng Policy 3:45–54
Wong MT, Tan FM, Ng WJ, Liu WT (2004) Identification and occurrence of tetrad-forming Alphaproteobacteria in anaerobic-aerobic activated sludge processes. Microbiol 150:3741–3748
Wong MT, Mino T, Seviour RJ, Onuki M, Liu WT (2005) In situ identification and characterization of the microbial community structure of full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants in Japan. Water Res 39:2901–2914
Zengin GE, Artan N, Orhon D, Chua ASM, Satoh H, Mino T (2010) Population dynamics in a sequencing batch reactor fed with glucose and operated for enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Bioresour Technol 101:4000–4005
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Clark County Water Reclamation District (CCWRD) of Las Vegas, Nevada, and a grant from the Graduate Professional Student Association of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV). We would like to thank Mr. William Shepherd, Operations Manager of CCWRD for his full support to this research. We thank Dr. Richard F. Unz for reviewing this manuscript and for the invaluable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Begum, S.A., Batista, J.R. Microbial selection on enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems fed exclusively with glucose. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 2181–2193 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1024-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1024-3