Abstract
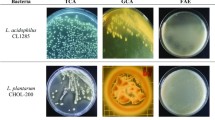
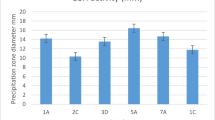
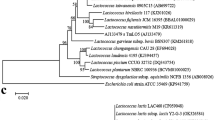
Hypercholesterolemia has been reported to be the main cause of cardiovascular diseases and the leading cause of death. Therefore, decreasing serum cholesterol level is very important for preventing the cardiovascular diseases. It has been supposed that probiotics in human gastrointestinal tract have the ability to decrease serum cholesterol level by reducing the absorption of cholesterol from the intestinal tract and the bile salt deconjugation. In this study, 28 strains of Lactobacillus spp., isolated from breast-fed infant’s feces, were identified and investigated for their bile salt deconjugation ability. The deconjugation ability of the strains was determined by the release of cholic acid resulting from the deconjugation of conjugated bile salts. Research results showed that four of the strains had bile salt deconjugation ability. The strains with deconjugation ability have been identified in species level by using biochemical test, and molecular techniques, API 50CHL test and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis respectively. LP1, E3, and E9 strains with deconjugation activity were identified as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and GD2 strain as Lactobacillus plantarum. Even if oxgall decreases the viability of bacteria, the highest amount of cholesterol precipitation (42%) was performed by GD2 strain in the presence of 0.3% (w/v) bile. This study demonstrated that the identified Lactobacillus strains had an excellent ability to survive at low pH, a high bile deconjugation ability, and hypocholesterolemic effect in in vitro conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JW, Gilliland SE (1999) Effect of fermented milk (Yogurt) containing Lactobacillus acidophilus L1 on serum cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic humans. J Am Coll Nutr 18:43–50
Bahar RJ, Andrew S (1999) Bile acid transport. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 28:27–58
Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CGM (2006) Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1729–1738
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1984) How LDL receptors influence cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Sci Am 251:52–60
Center SA (1993) Serum bile acid in companion animal medicine. In: Michael SL (ed) Gastroenterology: the 1990 s. Saunders Co. Ltd, Philadelphia, pp 625–657
Chiu C, Lu Z, Tseng Y, Pan T (2006) The effects of Lactobacillus-fermented milk on lipid metabolism in hamsters fed on high-cholesterol diet. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:238–245
Cocconcelli PS, Paris MG, Senini L, Bottazzi V (1997) Use of RAPD and 16S rRNA sequencing for the study of Lactobacillus population dynamics in natural whey culture. Lett Appl Microbiol 25:8–12
Coleman JP, Hudson LL (1995) Cloning and characterization of a conjugated bile acid hydrolase gene from Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2514–2520
Corzo G, Gilliland SE (1999) Bile salt hydrolase activity of three strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Dairy Sci 82:472–480
Dalezios I, Siebert KJ (2001) Comparison of pattern recognition techniques for the identification of lactic acid bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 91:225–236
De Smet I, De Boever P, Verstraete W (1998) Cholesterol lowering in pigs through enhanced bacterial bile salt hydrolase activity. Br J Nutr 79:185–194
Elkins CA, Moser SA, Savage DC (2001) Genes encoding bile salt hydrolases and conjugated bile salt transporters in Lactobacillus johnsonii 100–100 and other Lactobacillus species. Microbiology 147:3403–3412
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP-phylogeny inference package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fernandez ML, Roy S, Vergara-Jimenez M (2000) Resistant starch and cholestyramine have distinct effects on hepatic cholesterol metabolism in guinea pigs fed a hypercholesterolemic diet. Nutr Res 20:837–849
Fukushima M, Yamada A, Endo T, Nakano M (1999) Effects of a mixture of organisms, Lactobacillus acidophilus or Streptococcus faecalis on D6-desaturase activity in the livers of rats fed a fat- and cholesterol-enriched diet. Nutrients 15:373–378
Gilliland SE, Nelson CR, Maxwell C (1985) Assimilation of cholesterol by Lacobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(2):377–381
Haberer P, Du Toit M, Dicks LMT, Ahrens F, Holzapfel WH (2003) Effect of potentially probiotic lactobacilli on fecal enzyme activity in minipigs on a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet a preliminary in vivo trial. Int J Food Microbiol 87:287–291
Hammes WP, Hertel C (2006) The genera Lactobacillus and Carnobacterium. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds) The Prokaryotes, vol 4, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 320–403
Henriksson R, Bergstrom P, Franzen L, Lewin F, Wagenius G (1999) Aspects on reducing gastrointestinal adverse effects associated with radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 38(2):226–231
Hofmann AF (1999) Bile acids: the good, the bad and the ugly. News Physiol Sci 14:24–29
Irvin JL, Johnson CG, Kopala J (1944) A photometric method of the determination of cholates in bile and blood. J Biol Chem 153:439–457
Jones ML, Chen H, Ouyang W, Metz T, Prakash S (2004) Microencapsulated genetically engineered Lactobacillus plantarum 80 (pCBH1) for bile acid deconjugation and its ‘implication in lowering cholesterol. J Biomed Biotechnol 1:61–69
Kao YT, Liu Y, Shyu Y (2007) Identification of Lactobacillus spp. in probiotics products by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. Food Res Int 40:71–79
Kawamoto K, Horibe I, Uchida K (1989) Purification and characterization of a new hydrolase for conjugated bile acids, chenodeoxy- cholyltaurine hydrolase, from Bacteroides vulgatus. J Biochem 106:1049–1053
Kawase M, Hashimoto H, Hosoda M, Morita H, Hosono A (2000) Effect of administration of fermented milk containing whey protein concentrate to rats and healthy men on serum lipids and blood pressure. J Dairy Sci 83:255–263
Khedkar CD, Mantri JM, Garge RD (1993) Hypocholesterolemic effect of fermented milks: a review. Cult Dairy Prod J 28:15–18
Kim GB, Lee BH (2005) Biochemical and molecular insights into bile salt hydrolase in the gastrointestinal microflora: a review. Asian Aust J Anim Sci 18:1505–1512
Kim GB, Yi SH, Lee BH (2004) Purification and characterization of three different types of bile salt hydrolase from Bifidobacterium strains. J Dairy Sci 87:258–266
Klaver FAM, van der Meer R (1993) The assumed assimilation of cholesterol by lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium bifidum is due to their bile salt-deconjugating activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1120–1124
Klein G, Pack A, Bonaparte C, Reuter G (1998) Taxonomy and physiology of probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 41:103–125
Kumar R, Grover S, Batish VK (2010) Hypocholesterolaemic effect of dietary inclusion of two putative probiotic bile salt hydrolase-producing Lactobacillus plantarum strains in prague-Dawley rats. Br J Nutr 105:1–12
Lang GN, Binggeli C (2002) High-density lipoprotein restores endothelial function in hypercholesterolemia in men. Circulation 105:1399–1402
Law MR, Wald NJ, Wu T, Hackshaw A, Bailey A (1994) Systema tic underestimation of association between serum cholesterol concentration and ischaemic heart disease in observational studies: data from BUPA study. Br Med J 308:363–366
Lee YK, Salminen S (1995) The coming age of probiotics. Trends Food Sci Technol 6:241–245
Lim HJ, Kim SY, Lee WK (2004) Isolation of cholesterol-lowering lactic acid bacteria from human intestine for probiotic use. J Vet Sci 5:391–395
Liong MT, Shah NP (2006) Effects of Lactobacillus casei symbiotic on serum lipoprotein, intestinal microflora, and organic acids in rats. J Dairy Sci 89:1390–1399
Mc Auliffe O, Cano RJ, Klaenhammer TR (2005) Genetic analysis of two bile salt hydrolase activities in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4925–4929
Néron B, Ménager H, Maufrais C, Joly N, Maupetit J, Letort S, Carrere S, Tuffery P, Letondal C (2009) Mobyle: a new full web bioinformatics framework. Bioinformatics 25(22):3005–3011
Nguyen TDT, Kang JH, Lee MS (2007) Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum PH04, a potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. Int J Food Microbiol 113:358–361
Ooi LG, Liong MT (2010) Cholesterol lowering effects of probotics and prebiotics: A review of in vivo and vitro findings. Int J Mol Sci 11:2499–2522
Park YH, Jong GK, Young WS (2007) Effect of dietary inclusion of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 43121 on cholesterol metabolism in rats. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:655–662
Rodas AM, Ferrer S, Pardo I (2003) 16S-ARDRA, a tool for identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from grape must and wine. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:412–422
Rudel LL, Morris MD (1973) Determination of cholesterol using o-phthalaldehyde. J Lipid Res 14:364–366
Sato T, Hu JP, Ohki K, Yamaura M, Washio J, Matsuyama J, Takahashi N (2003) Identification of mutants streptococci by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified 16S ribosomal RNA genes. Oral Microbiol Immunol 18:323–326
Schuster H (2004) Improving lipid management: to titrate, combine, or switch. Int J Clin Pract 58:689–694
Shah NP (2007) Functional cultures and health benefits. Int Dairy J, doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.01.014
Song YL, Kato N, Liu CX, Matsumiya Y, Kato H, Watanabe K (2000) Rapid identification of 11 human intestinal Lactobacillus species by multiplex PCR assays using group- and species-specific primers derived from the 16S–23S rRNA intergenic spacer region and its flanking 23S rRNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:167–173
Stahl M, Molin G, Persson A, Ahrne S, Stahl S (1990) Restriction endonuclease patterns and multivariate analysis as a classification tool for Lactobacillus spp. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:189–193
Tanaka H, Doesburg K, Iwasaki T, Mierau I (1999) Screening of lactic acid bacteria for bile salt hydrolase activity. J Dairy Sci 82:2530–2535
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tok E, Aslım B (2010) Cholesterol removal by lactic acid bacteria that can be used as probiotic. Microbiol Immunol 54:257–264
Ulrich RL, Hughes TA (2001) A rapid procedure for isolating chromosomal DNA from Lactobacillus species and other gram-positive bacteria. Lett Appl Microbiol 32:52–56
Vandamme P, Pot B, Gillis M, De Vos P, Kersters K, Swings J (1996) Polyphasic taxonomy, a consensus approach to bacterial systematics. Microbiol Rev 60:407–438
Walker DK, Gilliland SE (1993) Relationships among bile tolerance, bile salt deconjugation, and assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Dairy Sci 76:956–961
Walter J, Tannock GW, Tilsala-Timisjärvin A, Rodtong S, Loach DM, Munro K, Alatossava T (2000) Detection and identification of gastrointestinal Lactobacillus species using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and species specific PCR primers. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:297–303
Wijaya A, Hermann A, Abriouel H, Specht I, Yousif NM, Holzapfel WH, Franz CM (2004) Cloning of the bile salt hydrolase (bsh) gene from Enterococcus faecium FAIR-E-345 and chromosomal location of bsh genes in food enterococci. J Food Prot 67:2772–2778
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51:221–271
Yeung PSM, Sanders ME, Kitts CL, Cano R, Tong PS (2002) Species specific identification of commercial probiotic strains. Am Dairy Sci Assoc 85:1039–1055
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigo J, Lishen A (2004) Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infraction in 52 countries (INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet 364:937–952
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Scientific Research Projects of Abant Izzet Baysal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yıldız, G.G., Öztürk, M. & Aslım, B. Identification of Lactobacillus strains from breast-fed infant and investigation of their cholesterol-reducing effects. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 2397–2406 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0710-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0710-x