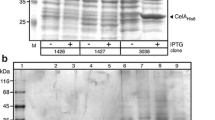
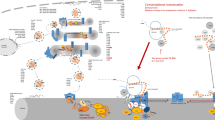
Abstract
In recent years much attention has been given to the identification and characterisation of the key elements of the secretory machinery of Streptomyces lividans, a non-pathogenic filamentous Gram-positive soil bacterium, whose metabolism is relatively well characterised and capable of secreting large amounts of proteins when grown in laboratory conditions. The relevance of S. lividans from a commercial standpoint is due to its potential usefulness for the overproduction of secretory homologous and heterologous proteins of interest. Therefore, this review focuses on the knowledge already obtained on the S. lividans secretion pathways.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anné J, Mellaert LV (1993) Streptomyces lividans as a host for heterologous protein production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 114:121–128
Beck K, Wu LF, Brunner J, Muller M (2000) Discrimination between SRP- and SecA/SecB-dependent substrates involves selective recognition of nascent chains by SRP and trigger factor. EMBO J 19:134–143
Beha D, Deitermann S, Müller M, Koch H-G (2003) Export of beta-lactamase is independent of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem 278:22161–22167
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, Widdick D, Palmer T, Brunak S (2005) Prediction of twin-arginine signal peptides. BMC Bioinf 6:167–175
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL et al (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Berks BC (1996) A common export pathway for proteins binding complex redox cofactors? Mol Microbiol 22:393–404
Berks BC, Sargent F, Palmer T (2000) The Tat protein export pathway. Mol Microbiol 35:260–274
Bibi E, Herskovits AA, Bochkareva E, Zelazny A (2001) Putative integral membrane SRP receptors. Trend Biochem Sci 26:15–16
Binnie C, Cossar JD, Stewart DI (1997) Heterologous biopharmaceutical protein expression in Streptomyces. Trend Biotechnol 15:315–320
Blanco J, Driessen AJ, Coque JJ, Martínn JF (1998) Biochemical characterization of the SecA protein of Streptomyces lividans interaction with nucleotides, binding to membrane vesicles and in vitro translocation of proAmy protein. Eur J Biochem 257:472–478
Böhni PC, Deshaies RJ, Schekman RW (1988) SEC11 is required for signal peptide processing and yeast cell growth. J Cell Biol 106:1035–1042
Bunai K, Takamatsu H, Horinaka T, Oguro A, Nakamura K, Yamane K (1996) Bacillus subtilis Ffh, a homologue of mammalian SRP54, can intrinsically bind to the precurssors of secretory proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:762–767
Bunai K, Yamada K, Hayashi K, Nakamura K, Yamane K (1999) Enhancing effect of Bacillus subtilis Ffh, a homologue of the SRP54 subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle, on the binding of SecA to precursors of secretory proteins in vitro. J Biochem 125:151–159
Cao T, Saier M (2003) The general protein secretory pathway: phylogenetic analyses leading to evolutionary conclusions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1609:115–125
Chater KF (1998) Taking a genetic scalpel to the Streptomyces colony. Microbiology 144:1465–1478
Chater KF, Biró S, Lee KJ, Palmer T, Schrempf H (2010) The complex extracellular biology of Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:171–198
Cregg KM, Wilding I, Black MT (1996) Molecular cloning and expression of the spsB gene encoding an essential type I signal peptidase from Staphylococus aureus. J Bacteriol 178:5712–5718
Dalbey RE, Wickner W (1985) Leader peptidase catalyzes the release of exported proteins from the outer surface of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 260:15925–15931
Dalbey RE, Lively MO, Bron S, van Dijl JM (1997) The chemistry and enzymology of the type I signal peptidases. Protein Sci 6:1129–1138
de Gier JW, Mansournia P, Valent QA, Phillips GJ, Luirink J, von Heijne G (1996) Assembly of a cytoplasmic membrane protein in Escherichia coli is dependent on the signal recognition particle. FEBS Lett 399:307–309
Dilks K, Rose RW, Hartmann E, Pohlschröder M (2003) Prokaryotic utilization of the twin-arginine translocation pathway: a genomic survey. J Bacteriol 185:478–1483
Dilks K, Giménez MI, Pohlschröder M (2005) Genetic and biochemical analysis of the twin-arginine translocation pathway in halophilic archaea. J Bacteriol 187:8013–8104
Driessen AJ, Nouwen N (2008) Protein translocation across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Annu Rev Biochem 77:643–667
Escutia MR, Val G, Palacín A, Geukens N, Anné J, Mellado RP (2006) Compensatory effect of the minor Streptomyces lividanstype I signal peptidases on the SipY major signal peptidase deficiency as determined by extracellular proteome analysis. Proteomics 6:4137–4146
Fekkes P, Driessen AJM (1999) Protein targeting to the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Microbiol Mol Rev 63:161–173
Gilbert M, Morosoli R, Shareck F, Kluepfel D (1995) Production and secretion of proteins by streptomycetes. Crit Rev Biotechnol 15:13–19
Herscovits AA, Bochkareva E, Bibi E (2000) New prospects in studying the bacterial signal recognition particle pathway. Mol Microbiol 38:927–939
Hirose I, Sano K, Shioda I, Kumano M, Nakamura K, Yamane K (2000) Proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis extracellular proteins: a two-dimensional protein electrophoretic study. Microbiology 146:65–75
Hoang V, Hofemeister J (1995) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens possesses a second type I signal peptidase with extensive sequence similarity to other Bacillus SPases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1269:64–68
Isiegas C, Parro V, Mellado RP (1999) Streptomyces lividansas a host to produce and secrete Escherichia coli TEM β-lactamase. Lett Appl Microbiol 28:321–326
Jongbloed JD, Grieger U, Antelmann H, Hecker M, Nijland R, Bron S, van Dijl JM (2004) Two minimal Tat translocases in Bacillus. Mol Microbiol 545:1319–1325
Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A et al (1996) Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions (supplement). DNA Res 3:185–209
Keenan RJ, Freymann DM, Stroud RM, Walter P (2001) The signal recognition particle. Annu Rev Biochem 70:755–775
Klenk HP, Clayton RA, Tomb JF, White O et al (1997) The complete genome sequence of the hyperthermophilic, sulphate-reducing archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Nature 390:364–370
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, et al. (1997) The complete genome sequence of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. 390:249–256
Lammertyn E, Mellaert LV, Schacht S, Dillen C, Sablon E, Broekhoven AV, Anné J (1997) Evaluation of a novel a novel subtilisin inhibitor gene and mutant derivative for the expression of mouse tumor necrosis factor alpha by Streptomyces lividans. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1808–1813
Meijer WJ, de Jong A, Bea G, Wisman A, Tjalsma H, Venema G, Bron S, van Dijl JM (1995) The endogenous Bacillus subtilis (natto) plasmids pTA1015 and pTA1040 contain signal peptidase-encoding genes: identification of a new structural module on cryptic plasmids. Mol Microbiol 17:621–631
Miller JD, Bernstein HD, Walter P (1994) Interaction of E.coli Ffh/4.5 Sribonucleoprotein and FtsY mimics that of mammalian signal recognition particle and its receptor. Nature 366:351–354
Millman JS, Andrews DW (1999) A site-specific, membrane-dependent cleavage event defines the membrane binding domain of FtsY. J Biol Chem 274:33227–33234
Oguro A, Kakeshita H, Takamatsu H, Nakamura K, Yamane K (1996) The effect of Srb, a homologue of the mammalian SRP receptor alpha-subunit, on Bacillus subtilis growth and protein translocation. Gene 172:17–24
Palacín A, Parro V, Geukens N, Anné J, Mellado RP (2002) SipY is the Streptomyces lividanstype I signal peptidase exerting a major effect on protein secretion. J Bacteriol 184:4875–4880
Palacín A, de la Fuente R, Valle I, Rivas LA, Mellado RP (2003) Streptomyces lividans contains a minimal functional signal recognition particle that is involved in protein secretion. Microbiology 149:2435–2442
Pallen MJ (2002) The ESAT-6/WXG100 superfamily and a new gram-positive secretion system? Trends Microbiol 10:209–212
Palomino C, Mellado RP (2005) The Streptomyces lividans signal recognition particle receptor FtsY is involved in protein secretion. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 9:57–62
Palomino C, Mellado RP (2008) Influence of a Streptomyces lividans SecG functional analogue on protein secretion. Int Microbiol 11:25–31
Parro V, Mellado RP (1994) Effect of glucose on agarase overproduction by Streptomyces. Gene 145:49–55
Parro V, Schacht S, Anné J, Mellado RP (1999) Four genes encoding different type I signal peptidases are organized in a cluster in Streptomyces lividans TK21. Microbiology 145:2255–2263
Pohlschöder M, Dilks K, Hand N, Wesley Rose R (2004) Translocation of proteins across archaeal cytoplasmic membranes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:3–24
Pop O, Martin U, Abel C, Muller JP (2002) The twin-arginine signal peptide of PhoD and the TatAd/Cd proteins of Bacillus subtilis form an autonomous Tat translocation system. J Biol Chem 277:3268–3273
Powers T, Walter P (1997) Co-translational protein targeting catalised by the Escherichia coli signal recognition particle and its receptor. EMBO J 16:4880–4886
Schaerlaekens K, Van Mellaert L, Lammertyn E, Geukens N, Anné J (2004) The importance of the Tat-dependent protein secretion pathway in Streptomyces as revealed by phenotypic changes in tat deletion mutants and genome análisis. Microbiology 150:21–31
Song W, Raden D, Mandon E, Gilmore R (2000) Role of Sec61α in the regulated transfer of the ribosome-nascent chain complex from the signal recognition particle to the translocation channel. Cell 100:333–343
Stanley NR, Palmer T, Berks BC (2000) The twin-arginine consensus motif of Tat signal peptides is involved in Sec-independent protein targeting in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 275:11591–11596
Tjalsma H, Bolhuis A, van Roosmalen ML, Wiegert T, Schumann W, Broekhizen CP, Quax WJ, Venema G, Bron S, van Dijl JM (1998) Functional analysis of the secretory precursor processing machinery of Bacillus subtilis: identification of a eubacterial homolog of archaeal and eukaryotic signal peptidases. Genes and Dev 12:2318–2331
Tschantz WR, Sung M, Delgado-Partin VM, Dalbey R (1993) A serine and a lysine residue implicated in the catalytic mechanims of the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. J Biol Chem 268:27349–27354
Ulbrandt ND, Newitt JA, Bernstein HD (1997) The E. coli signal recognition particle is required for the insertion of a subset of inner membrane proteins. Cell 88:187–196
van Dijl JM, de Jong A, Venema G, Bron S (1995) Identification of the potential active site of the SPase SipS of Bacillus subtilis: structural and functional similarities with LexA-like proteases. J Biol Chem 270:3611–3618
Van Mellaert L, Anné J (1994) Protein secretion in gram-positive bacteria with high GC- content. Recent Res Dev Microbiol 3:324–340
Van Welly KHM, Swaving J, Freudl A, Driessen AJM (2001) Translocation of proteins across the cell envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:437–454
Van Wely KHM, Swaving J, Broekhuizen CP, Rose M, Quax WJ, Driessen AJM (1999) Functional identification of the product of the Bacillus subtilis yvaL gene as a SecG homologue. J Bacteriol 181:1786–1792
Vrancken K, Anné J (2009) Secretory production of recombinant proteins by Streptomyces. Future Microbiol 4:181–188
Walter P, Johnson AE (1994) Signal sequence recognition and protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol 10:87–119
White O, Eisen JA, Heidelberg JF, Hickey EK et al (1999) Genome sequence of the radioresistant bacterium Deinococus radiodurans R1. Science 286:1571–1577
Widdick DA, Dilks K, Chandra G, Bottrill A, Naldrett M, Pohlschröder M, Palmer T (2006) The twin-arginine translocation pathway is a major route of protein export in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17927–17932
Wolin SL (1994) From the elephant to E. coli: SRP-dependent protein targeting. Cell 77:787–790
Wu CJ, Janssen GR (1996) Translation of vph mRNA in Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli after removal of 5′ untranslated leader. Mol Microbiol 22:339–355
Acknowledgments
Grants BIO2003-03948 and BIO2006-12762 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation have supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mellado, R.P. Summing up particular features of protein secretion in Streptomyces lividans . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 2231–2237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0709-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0709-3