Abstract
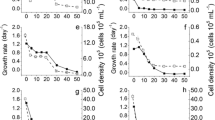
Vinasse is a highly colored effluent with a high pollutant potential when disposed in the environment. Assays for decolorization of vinasse were performed, selecting the fungus Pleurotus sajor-caju CCB 020. The discoloration was cocominant with the increase of the activities of laccase, manganese-peroxidase and peroxidases. P. sajor-caju demonstrated a rise in biomass production (1.06 g 100 ml−1), and the enzyme activities such as laccase (varying from 400 to 450 IU l−1) reached between the 9th and 10th day of growth and for MnP at the 12th day of cultivation (varying from 60 to 100 IU l−1). It was concluded that the system P. sajor-caju/vinasse can be utilized as a bioprocess for color removal and degradation of complex vinasse compounds. It was observed an improvement in the characteristics and detoxification allowing its utilization as reused water, laccase and manganese-peroxidase enzymes production and for fungal biomass production with a high nutritional value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar JM (2008) Análise enzimática de fungos lignocelulolíticos cultivados em vinhaça e bagaço de cana-de-açúcar. Dissertation, University of São Paulo – ESALQ
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Rai V (2009) Isolation and characterization of aerobic bacteria capable of the degradation of synthetic and natural melanoidins from distillery effluent. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:737–744
Chagas E, Durrant LR (2001) Decolorization of azo dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus sajor-caju. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:473–477
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Rai V (2008) Melanoidins as major colourant in sugarcane molasses based distillery effluent and its degradation. Bioresour Technol 99:4648–4660
Doerge DR, Divi RL, Churchwell MI (1997) Identification of the colored guaiacol oxidation product produced by peroxidases. Anal Biochem 250:10–17
Durán N, Esposito E (1997) Biodegradação de lignina e tratamento de efluentes por fungos lignolíticos. In: Melo IS, Azevedo JL (eds) Microbiologia ambiental. CNPM/EMBRAPA, Jaguariúna, pp 269–292
Eggen T (2000) Bioremediation of recalcitrant aromatic organic pollutants with white rot fungi. Dissertation, Agricultural University of Norway
Freire WJ, Cortez LA (2000) Vinhaça de cana-de-açúcar. ESALQ, Piracicaba
Fujian X, Hongzhang C, Zuohu L (2001) Solid-state production of lignin peroxidase (LiP) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium using steam-exploded straw as substrate. Bioresour Technol 80:149–151
Gokarn AN, Mayadevi S (2000) Active charcoal from agro-waste for colour removal of treated spentwash. In: Ann convention of D.S.T.A., Pune, proceedings, part 1, pp B1–B10
Gross D, Coombs J (1976) Enzymic colour formation in beet and cane juices. Int Sugar J 928:69–106
Hofrichter M, Vares T, Kalsi M, Galkin S, Scheibner K, Fritsche W, Hatakka A (1999) Production of manganese peroxidase and organic acids and mineralization of 14C labelled lignin (14C-DHP) during solidstate fermentation of wheat straw with the white rot fungus Nematoloma frowardii. App Environ Microbiol 65:1864–1870
Kerem Z, Friesem D, Hadar Y (1992) Lignocellulose degradation during solid-state fermentation: Pleurotus ostreatus versus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. App Environ Microbiol 58:1121–1127
Kumaran S, Sastry CA, Vikineswary S (1997) Laccase, cellulase and xylanase activities during growth of Pleurotus sajor-caju on sago hampas. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:43–49
Kuwahara M, Glenn JK, Morgan MA, Gold MH (1984) Separation and characterization of two extracellular H2O2 dependent oxidases from lignolytic cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. FEBS Microbiol Lett 169:247–250
Mane JD, Modi S, Nagawade S, Phadnis SP, Bhandari VM (2006) Treatment of spentwash using chemically modifed bagasse and colour removal studies. Bioresour Technol 97:1752–1755
Masaphy S, Levanon D (1992) The effect of lignocellulose on lignolellulolytic activity of Pleurotus pulmonaris in submerged culture. App Microbiol Biotechnol 36:828–832
Maziero R, Cavazzoni V, Bononi VLR (1999) Screening of Basidiomycetes for the production of exopolysaccharide and biomass in submerged culture. Rev Microbiol 30:77–84
Membrillo I, Sánchez C, Meneses M, Favela E, Loera O (2008) Effect of substrate particle size and additional nitrogen source on production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by Pleurotus ostreatus strains. Bioresour Technol 99:7842–7847
Miranda PM, Benito GG, Cristobal NS, Nieto CH (1996) Color elimination from molasses wastewater by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 57:229–235
Naik NM, Jagadeesh KS, Alagawadi AR (2008) Microbial decolorization of spentwash: a review. Indian J Microbiol 48:41–48
Ohmomo S, Kaneko Y, Sirianuntapiboon S, Somchal P, Atthasampunna P, Nakamura I (1987) Decolorization of molasses wastewater by a thermophilic strain, Aspergillus fumigatus G-2–6. Agric Bio Chem J 51:3339–3346
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007a) Biological approaches for treatment of distillery wastewater: a review. Biores Technol 98:2321–2334
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007b) Identification, ligninolytic enzyme activity and decolorization potential of two fungi isolated from a distillery effluent contaminated site. Water Air Soil Pollut 183:165–176
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007c) Enhanced production of ligninolytic enzymes and decolorization of molasses distillery wastewater by fungi under solid state fermentation. Biodegradation 18:647–659
Pant D, Adholeya A (2009) Concentration of fungal ligninolytic enzymes by ultrafiltration and their use in distillery effluent decolorization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1793–1800
Pascholatti SF, Stangarlin JR, Piccinin E (1998) Cogumelos–cultivo e comercialização: shiitake e cogumelo do sol. SEBRAE, Cuiabá
Pérez SR, Savón RC, Diaz MS, Kourouma A (2006) Selección de cepas de Pleurotus ostreatus para la decoloración de efluentes industriales. Rev Mex Micol 23:9–15
Putzke J, Putzke MT (1998) O reino dos fungos. EDUNISC, Santa Cruz do Sul
Raghukumar C, D’Souza-Ticlo D, Verma AK (2008) Treatment of colored effluents with lignin-degrading enzymes: an emerging role of marine-derived fungi. Critical Rev Microbiol 34:189–206
Rajarathnam S, Bano Z (1989) Pleurotus mushrooms: part III. Biotransformations of natural lignocellulosic wastes commercial applications and implications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 28:31–113
Rodríguez E, Pickard M, Vazquez-Duhalt R (1999) Industrial dye decolorization by laccases from ligninolytic fungi. Curr Microbiol 38:27–31
Rodríguez S, Fernández M, Bermúdez RC, Morris H (2003) Tratamiento de efluentes industriales coloreados com Pleurotus spp. Rev Iberoam Micol 20:164–168
Satyawali Y, Balakrishanan M (2008) Wastewater treatment in molasses based alcohol distilleries for COD and color removal: a review. J Environ Manag 86:481–497
Sayadi S, Ellouz R (1995) Roles of lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase from Phanerochaete crysosporium in the decolorization of olive mill wastewaters. App Environ Microbiol 61:1098–1103
Shayegan J, Pazouki M, Afshari A (2004) Continuous decolorization of anaerobically digested distillery wastewater. Process Biochem 40:1323–1329
Silva FAS, Azevedo CAV (2002) Versão do programa computacional Assistat para o sistema operacional Windows. Rev Bras Prod Agroind 4:71–78
Sirianuntapiboon S, Sihanonth P, Somchai P, Atthasampunna P, Hayashida S (1995) An adsorption mechanism for melanoidin decolorization by Rhizoctonia sp. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1185–1189
Stanbury PF, Whitake A, Hall SJ (2003) Principles of fermentation technology, 2nd edn. Tarrytown, Oxford
Szklarz G, Antibus RK, Sinsabaugh RL, Linkins AE (1989) Production of phenoloxidases and peroxidases by wood-rotting fungi. Mycologia 81:234–240
Tuor U, Winterhalter K, Fiechter A (1995) Enzymes of white-rot-fungi involved in lignin degradation and ecological determinants for wood decay. J Biotechnol 41:1–17
Wadt LC (2008) Cultivo de Pleurotus spp. Em vinhaça visando à produção de biomassa e exopolissacarídeos. Dissertation, University of São Paulo, CENA
Wesenberg D, Kyriakides I, Agathos SN (2003) White-rot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnol Adv 22:161–187
Zhao LH, Zhou JT, Zheng CL, Yang YS, Sun HJ, Zhang XH (2008) Decolorization of cotton pulp black liquor by Pleurotus ostreatus in a bubble-column reactor. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:44–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, L.F., Aguiar, M., Pompeu, G. et al. Selection of vinasse degrading microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1613–1621 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0337-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0337-3