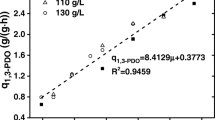
Abstract
Sustained oscillations have been observed in cell growth and glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae during long-term continuous cultivations under anaerobic conditions. However, the oscillation behavior of glucose–glycerol co-fermentation under micro-aerobic conditions has yet not been studied. In this study, the unclear mechanism of oscillation was investigated by using different substrates including glycerol, glucose, and mixtures of glycerol and glucose. A large perturbation of substrate concentration was operated to study the dynamic behavior of continuous fermentation by K. pneumoniae DSM 2026 under micro-aerobic conditions. Oscillations occurred when 80 g of glycerol l−1 was used as single carbon source or co-substrate with 35 g of glucose l−1, whereas no oscillation was observed when glucose was used alone. During the oscillation phases, parameters periodically passed maxima and minima at a relatively constant time interval, and the period of oscillation was 10–16 h. The comparison between glycerol and glucose metabolism revealed that a potential mechanism of oscillation lies in the accumulation of 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, which is toxic to cell growth.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbirato F, Grivet JP, Soucaille P, Bories A (1996) 3-Hydroxypropionaldehyde, an inhibitory metabolite of glycerol fermentation to 1,3-propanediol by Enterobacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1448–1451
Chen X, Xiu ZL, Wang JF, Zhang DJ, Xu P (2003) Stoichiometric analysis and experimental investigation of glycerol bioconversion to 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae under microaerobic conditions. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:386–394
Circle SJ, Stone L, Boruff CS (1945) Acrolein determination by means of tryptophan A colorimetric micrometric. Ind Eng Chem Res 17:259–262
Deckwer WD (1995) Microbial conversion of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol. FEMS Microbiol Rev 16:143–149
Du CY, Yan H, Zhang YP, Li Y, Cao ZA (2006) Use of oxidoreduction potential as an indicator to regulate 1,3-propanediol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:554–563
Homann T, Tag C, Biebl H, Deckwer WD, Schink B (1990) Fermentation of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol by klebsiella and Citrobacter strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:121–126
Lin RH, Liu HJ, Zhang J, Hao J, Cheng KK, Liu DH (2005) Effect of 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde on 1,3-propanediol fermentation by klebsiella pneumonae and regulation for it. Mod Chem Ind (Xian Dai Hua Gong) 25:47–51 (in Chinese)
Menzel K, Zeng AP, Biebl H, Dechwer WD (1996) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: I. The phenomena and characterization of oscillation and hysteresis. Biotechnol Bioeng 52:549–560
Rasch M (2002) The influence of temperature, salt and pH on the inhibitory effect of reuterin on Escherichia coli. Int J Food Microbiol 72:225–231
Richard P (2003) The rhythm of yeast. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:547–557
Slininger PJ, Bothast RJ (1985) Optimizing aerobic conversion of glycerol to 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:1444–1450
Wang JF, Xiu ZL, Fan SD (2001) Determination of glycerin concentration during the fermentation of glycerin to 1,3-propanediol. Ind Microbiol (Gong Ye Wei Sheng Wu) 31:33–35 (in Chinese)
Wang W, Sun JB, Hartlep M, Dechwer WD (2003) Combined use of proteomic analysis and enzyme activity assays for metabolic pathway analysis of glycerol fermentation by klebsiella pneumonae. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:525–536
Xiu ZL, Chen X, Sun YQ, Zhang DJ (2007) Stoichiometric analysis and experimental investigation of glycerol–glucose cofermentation in Klebsiella pneumoniae under microaerobic conditions. Biochem Eng J 33:42–52
Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1992) Utilization of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, a reactor design criterion for the microaerobic production of 2,3-butanediol. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:1078–1084
Zeng AP, Menzel K, Deckwer WD (1996) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: II. Analysis of metabolic rates and pathways under oscillation and steady-state conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 52:561–571
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20576018) and the grant from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2007CB714306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, LH., Song, ZY., Sun, YQ. et al. Dynamic behavior of glycerol–glucose co-fermentation for 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae DSM 2026 under micro-aerobic conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1401–1407 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0314-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0314-x