Abstract
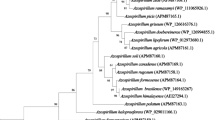
Arsenic (As) is a very toxic metalloid to a great number of organisms. It is one of the most important global environmental pollutants. To resist the arsenate invasion, some microorganisms have developed or acquired genes that permit the cell to neutralize the toxic effects of arsenic through the exclusion of arsenic from the cells. In this work, two arsenic resistance genes, arsA and arsC, were identified in three strains of Rhizobium isolated from nodules of legumes that grew in contaminated soils with effluents from the chemical and fertilizer industry containing heavy-metals, in the industrial area of Estarreja, Portugal. The arsC gene was identified in strains of Sinorhizobium loti [DQ398936], Rhizobium leguminosarum [DQ398938] and Mesorhizobium loti [DQ398939]. This is the first time that arsenic resistance genes, namely arsC, have been identified in Rhizobium leguminosarum strains. The search for the arsA gene revealed that not all the strains with the arsenate reductase gene had a positive result for ArsA, the ATPase for the arsenite-translocating system. Only in Mesorhizobium loti was the arsA gene amplified [DQ398940]. The presence of an arsenate reductase in these strains and the identification of the arsA gene in Mesorhizobium loti, confirm the presence of an ars operon and consequently arsenate resistance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman JD (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bruins MR, Kapil S, Oehme FW (2000) Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotox Environ Saf 45:198–207
Butcher BG, Deane SM, Rawlings DE (2000) The chromosomal arsenic resistance genes of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans have an unusual arrangement and confer increased arsenic and antimony resistance to Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(5):1826–1833
Castro IV, Ferreira E, McGrath SP (1997). Effectiveness and genetic diversity of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii strains in Portuguese soils polluted by industrial effluents. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1209–1213
Castro IV, Ferreira E, McGrath SP (2003) Survival and plasmid stability of rhizobia introduced into a contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35:49–54
Cervantes C, Ji G, Ramirez JL, Silver S (1994) Resistance to arsenic compounds in microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:355–367
Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1989) Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem Rev 89:713–764
Dey S, Dou D, Tisa LS, Rosen BP (1994) Interaction of the catalytic and the membrane subunits of an oxanion-translocating ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys 311:418–424
Diorio C, Cai J, Marmor J, Shinder R, DuBow MS (1995) An Escherichia coli chromosomal ars operon homolog is functional in arsenic detoxification and is conserved in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 177(8):2050–2056
Galibert F, Finan TM, Long SR, Puhler A, Abola P, Ampe F, Barloy-Hubler F, Barnett MJ, Becker A, Boistard P, Bothe G, Boutry M, Bowser L, Buhrmester J, Cadieu E, Capela D, Chain P, Cowie A, Davis RW, Dreano S, Federspiel NA, Fisher RF, Gloux S, Godrie T, Goffeau A, Golding B, Gouzy J, Gurjal M, Hernandez-Lucas I, Hong A, Huizar L, Hyman RW, Jones T, Kahn D, Kahn ML, Kalman S, Keating DH, Kiss E, Komp C, Lelaure V, Masuy D, Palm C, Peck MC, Pohl TM, Portetelle D, Purnelle B, Ramsperger U, Surzycki R, Thebault P, Vandenbol M, Vorholter FJ, Weidner S, Wells DH, Wong K, Yeh KC, Batut J (2001) The composite genome of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Sci 293(5530):668–672
Gihring TM, Bond PL, Peters SC, Banfield JF (2003) Arsenic resistance in the archaeon Ferroplasma acidarmanus: new insights into the structure and evolution of the ars genes. Extrem 7(2):123–130
Glockner FO, Kube M, Bauer M, Teeling H, Lombardot T, Ludwig W, Gade D, Beck A, Borzym K, Heitmann K, Rabus R, Schlesner H, Amann R, Reinhardt R (2003) Complete genome sequence of the marine planctomycete Pirellula sp strain 1. Proc Nat Acad Sci 100(14):8298–8303
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program
Henikoff S, Henikoff JG, Alford WJ, Pietrokovski S (1995) Automated construction and graphical presentation of protein blocks from unaligned sequences. Gene 163:GC17–GC26
Jackson CR, Jackson EF, Dugas SL, Gamble K, Williams SE (2003) Microbial transformations of arsenite and arsenate in natural environments. Rec Res Develop Microbiol 7:103–118
Ji G, Silver S (1992a) Regulation and expression of the arsenic resistance operon from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. J Bacteriol 174:3684–3694
Ji G, Silver S (1992b) Reduction of arsenate to arsenite by the ArsC protein of the arsenic resistance operon on Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. Proc Nat Acad Sci 89:9474–9478
Jones CA, Langner HW, Anderson K, McDermott TR, Inskeep WP (2000) Rates of microbially mediated arsenate reduction and solubilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:600–608
Leitão TE, Zungailia JE, Lobo-Ferreira JP (1992) Metodologias para a Recuperação de Águas Subterrâneas e Solos Contaminados. Partes A e B. Relatório Final. Lisboa, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil, Relatório LNEC/DGQA, Setembro
Lindstrom K, Terefework Z, Suominen L, Lortet G (2002) Signalling and development of Rhizobium–legume symbiosis. Biol Environ 102(1):61–64
Mergeay M (1991) Towards an understanding of the genetics of bacterial metal resistance. Tibtech 9:17–24
Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen BP, Phung LT, Silver S (2002) Microbial arsenic: from geocycles to genes and enzymes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:311–325
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:730–750
Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2003) The ecology of arsenic science 300:939–944
Rasko DA, Ravel J, Okstad OA, Helgason E, Cer RZ, Jiang L, Shores KA, Fouts DE, Tourasse NJ, Angiuoli SV, Kolonay J, Nelson WC, Kolsto AB, Fraser CM, Read TD (2004) The genome sequence of Bacillus cereus ATCC 10987 reveals metabolic adaptations and a large plasmid related to Bacillus anthracis pXO1. Nucleic Acid Res 32(3):977–988
Raven PH, Evert RF, Eichhorn SE (eds) (1999) Biology of plants, 6th edn. W H Freeman and Company Worth Publishers, 738–741
Rose TM, Schultz ER, Henikoff JG, Pietrokovski S, McCallum CM, Henikoff S (1998) Consensus-degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primers for amplification of distantly related sequences. Nucleic Acid Res 26:1628–1635
Rosen BP, Bhattacharjee H, Zhou T, Walmsley AR (1999) Mechanism of the ArsA ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1461:207–215
Rouch DA, Lee BTD, Morby AP (1995) Understanding cellular responses to toxic agents: a model for mechanism choice in bacterial metal resistance. J Indust Microbiol 14:132–141
Saltikov CW, Olson BH (2002) Homology of Escherichia coli R773 arsA, arsB, and arsC genes in arsenic-resistant bacteria isolated from raw sewage and arsenic-enriched Creek Waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):280–288
Saltikov CW, Cifuentes A, Venkateswaran K, Newman DK (2003) The ars detoxification system is advantageous but not required for As(V) respiration by the genetically tractable Shewanella species strain ANA-3. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(5):2800–2809
Silver D, Keach D (1982) Energy-dependent arsenate efflux: the mechanism of plasmid-mediated resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79:6114–6118
Silver S (1996) Bacterial resistances to toxic metal ions––a review. Gene 179:9–19
Silver S, Budd K, Leahy KM, Shaw WV, Hammond D, Novick RP, Willsky GR, Malamy MH, Rosenberg H (1981) Inducible plasmid-determined resistance to arsenate, arsenite, and antimony (III) in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 146(3):983–996
Stewart JWB, Bettany JR (1982) Mercury. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis Part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 367–384
Suzuki K, Wakao N, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (1998) Expression and Regulation of the Arsenic Resistance Operon of Acidiphilium multivorum AIU 301 Plasmid pKW301 in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(2):411–418
Taiz L, Zeiger E (1998) Plant physiology, 2nd Edn. Sinauer Associates Publishers, 330–335
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acid Res 22:4673–4680
Tsutomu S, Kobayashi Y (1998) The ars operon in the skin element of Bacillus subtilis confers resistance to arsenate and arsenite. J Bacteriol 180:1655–1661
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of the root-nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Vogelstein B, Gillespie D (1979) Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:615–619
Xu C, Zhou T, Kuroda M, Rosen BP (1998) Metalloid resistance mechanisms in prokaryotes. J Biochem 123(1):16–23
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Eng. Diogo Mendonça from Molecular Biology Group-INETI and Fátima Sobral from Direcção Geral de Veterinária, for DNA sequencing procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sá-Pereira, P., Rodrigues, M., e Castro, I.V. et al. Identification of an arsenic resistance mechanism in rhizobial strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 1351–1356 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9370-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9370-2