Abstract
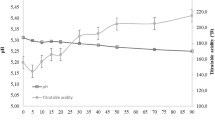
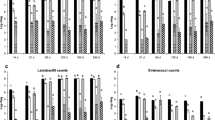
The effect of heat treatment and commercial starter culture utilization on the physicochemical and microbiological properties of Kulek cheese made from raw milk with or without starter culture and heated milk with starter culture were investigated during ripening. Titratable acidity (TA) was the highest in cheeses made from heated milk while total solids (TS), salt, and fat were the highest in cheeses made from raw milk. The heat treatment significantly decreased the counts of coliforms and Enterobacteriaceae in cheeses. At the beginning of the ripening period, cheeses manufactured from heated milk with starter exhibited significantly higher counts of lactococci and proteolytic organisms and lower counts of lactobacilli than the other cheeses. After the first day, raw milk cheeses without starter showed higher microbiological counts than the others. In fresh cheeses, Lactococcus was the main lactic acid bacterium, with Lc. lactis lactis being predominant. Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus paracasei paracasei dominated at the later stages of the ripening.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albenzio M, Corbo MR, Rehman SU, Fox PF, De Angelis M, Corsetti A, Sevi A, Gobbetti M (2001) Microbiological and biochemical characteristics of Canestrato Pugliese cheese made from raw milk, pasteurized milk or by heating the curd in hot whey. Int J Food Microbiol 67:35–48
Alonso-Calleja C, Carballo J, Capita R, Bernardo A, Garcia-López ML (2002) Changes in the microflora of Valdetaja raw goat’s milk cheese troughout manufacturing and ripening. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technologie 35:222–232
AOAC (1992) Official Methods of Analysis. Association of official analytical chemists. Washington, DC. ISBN 093558448X
Aran N (1998) A microbiological study of Kashar cheese. Milchwissenschaft 53(10):565–568
Arenas R, González L, Bernardo A, Fresno JM, Tornadijo ME (2004) Microbiological, and physico-chemical changes in Genestoso cheese, a Spanish acid curd variety, throughout ripening. Food Control 15:271–279
Badis A, Guetarni D, Moussa-Boudjemeâa B, Henni DE, Tornadijo ME, Kihal M (2004) Identification of cultivable lactic acid bacteria isolated from Algerian raw goat’s milk and evaluation of their technological properties. Food Microbiol 21:343–349
Ballesteros C, Poveda JM, González-Viñas MA, Cabezas L (2006) Microbiological, biochemical and sensory charecteristics of artisanal and industrial Manchego cheeses. Food Control 17:249–255
Beresford TP, Fitzsimons NA, Brennan NL, Cogan TM (2001) Recent advances in cheese microbiology. Int Dairy J 11:259–274
Beuvier E, Berthaud K, Cegarra S, Dasen A, Pochet S, Buchin S, Duboz G (1997) Ripening and quality of Swiss-type cheese made from raw, pasteurized or microfiltered milk. Int Dairy J 7:311–323
Bradley RL, Arnold E, Barbano DM, Semerad RG, Smith DE, Vines BK (1992) Chemical and physical methods. In: Marshall RT (ed) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products, 16th edn American Public Health Association. ISBN 087553208X
Caridi A (2003) Identification and first characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the artisanal ovine cheese Pecorino del Poro. Int J Dairy Technol 56:105–110
Christen GL, Davidson PM, McAllister JS, Roth LA (1992) Coliform and other indicator bacteria. In: Marshall RT (ed) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products, 16th edn American Public Health Association. ISBN 087553208X
Corroler D, Mangin L, Desmasures N, Gueguen M (1998) An ecological study of lactococci isolated from raw milk in the Camembert cheese registered designation of origin area. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4729–4735
Curk MC, Hubert JC, Bringel F (1996) Lactobacillus paracasei plantarum sp. nov., a new species related to Lactobacillus plantarum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:595–598
Dervisoglu M (1999) Changes in Kulek cheese throughout the ripening. Ph.D Thesis, Trakya University, Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences, Edirne, Turkey
Dervisoglu M, Yazici F (2001) Ripening changes of Kulek cheese in wooden and plastic containers. J Food Eng 48:243–249
Dias B, Weimer B (1998) Conversion of methionine to thiols by lactococci, lactobacilli, and Brevibacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3320–3326
Durlu-Özkaya F, Xanthopoulos V, Tunail N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E (2001) Technologically important properties of lactic acid bacteria isolates from Beyaz cheese made from raw ewes’ milk. J Appl Microbiol 91:861–870
Elortondo FJP, Echobarria PA, Albisu M, Barcina Y (1998) Indigenous lactic acid bacteria in Idiazábal ewes’ milk cheese. Int Dairy J 8:725–732
Ferrazza RE, Fresno JM, Ribeiro JI, Tornadijo ME, Mansur Furtado M (2004) Changes in the microbial flora of Zamorano cheese (P.D.O) by accelerated ripening. Food Res Int 37:149–155
Fortina MG, Ricci G, Acquati A, Zeppa G, Gandini A, Manachini PL (2003) Genetic characterization of some lactic acid bacteria occuring in an artisanal protected denomination origin (PDO) Italian cheese, the Toma piemontese. Food Microbiol 20:397–404
Frank JF, Christen GL, Bullerman LB (1992) Tests for groups of microorganisms. In: Marshall RT (ed) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products, 16th edn. American Public Health Association. ISBN 087553208X
Garcia-Fontan MC, Franco I, Prieto B, Tornadijo ME, Carballo J (2001) Microbial changes in ‘San Simon’ cheese throughout ripening and its relationship with physico-chemical parameters. Food Microbiol 18:25–33
Gerasi E, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Tzanetakis N (2003) Microbiological study of Manura, a hard cheese made from raw ovine milk in the Greek island Sifnos. Int J Dairy Technol 56:117–122
Gobbetti M, Morea M, Baruzzi F, Corbo MR, Matarante A, Considine T, Di Cagno R, Guinee T, Fox PF (2002) Microbiological, compositional, biochemical and textural characterisation of Caciocavallo Pugliese cheese during ripening. Int Dairy J 12:511–523
González-Crespo J, Mas M (1993) Estudio del empleo de fermentes iniciadores autóetones en la elaboración de queso de calsa de pasta prensada, con leche pasteurizade. Alimentaria 243:51–53
Grappin R, Beuvier E (1997) Possible implications of milk pasteurization on the manufacture and sensory quality of ripened cheese. Int Dairy J 7:751–761
Guinee TP, Fenelon MA, Mulholland EO, O’Kennedy BT, O’Brien N, Reville WJ (1998) The influence of milk pasteurization temperature and pH at curd milling on the composition, texture and maturation of reduced-fat Cheddar cheese. Int J Dairy Technol 51:1–10
Guven M, Konar A (1994) The microbiological qualities of Tulum cheeses which were made from cow’s milk and packed and ripened in different packing materials. Gida 19:(3)179–185
Hatzikamari M, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Tzanetakis N (1999) Microbiological characteristics of Anevato: a traditional Greek cheese. J Appl Microbiol 87:595–601
Houghtby GA, Maturin LJ, Koening EK (1992) Microbiological count methods. In: Marshall RT (ed) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products, 16th edn, American Public Health Association. ISBN 087553208X
Kelly M, Fox PF, McSweeney PLH (1996) Effect of salt-in-moisture on proteolysis in Cheddar-type cheese. Milchwissenschaft 51:498–501
Kelly AL (1999) The influence of heat treatment of milk on proteolysis in Cheddar cheese during ripening. Milchwissenschaft 54:682–684
Klijn N, Weerkamp AH, De Vos WM (1995) Detection and characterization of lactose-utilizing Lactococcus spp. in natural ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:788–792
Lebeuf Y, Lacroix C, Paquin P (1998) Effect of incorporation of denatured and microparticulated whey proteins in young Cheddar cheese. Le Lait 78:303–318
Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Tzanetakis N (1992) Microbiological study of white-brined cheese made from raw goat milk. Food Microbiol 9:13–19
Lopez-Dıaz TM, Alonso C, Roman C, Garcıa-Lopez ML, Moreno B (2000) Lactic acid bacteria isolated from a hand-made blue cheese. Food Microbiol 17:23–32
Macedo AC, Malcata FX, Hogg TA (1995) Microbiological profile in Serra ewe’s cheese during ripening. J Appl Bacteriol 79:1–11
Marino M, Maifreni M, Rondinini G (2003) Microbiological charecterization of artisanal Montasio cheese analysis of its indigenous lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 229:133–140
Martley FG, Crow WL (1993) Interactions between non-starter microorganisms during cheese manufacture and ripening. Int Dairy J 3:461–483
Martley FG, Crow VL (1996) Open texture in cheese: the contributions of gas production by microorganisms and cheese manufacturing practices. J Dairy Res 63:489–507
Medina M, Fernandez Del Pozo B, Rodriguez-Marin MA, Gaya P, Nunez M (1991) Effect of lactic starter inoculation on chemical, microbiological, rheological and sensory characteristics of La Serena cheese. J Dairy Res 58:355–361
Menéndez S, Godinez R, Hermida M, Centeno JA, Rodriguez-Otero JL (2004) Characteristics of ‘‘Tetilla’’ pasteurized milk cheese manufactured with the addition of autochthonous cultures. Food Microbiol 21:97–104
Minitab (1996) Minitab Reference Manual. Minitab, Inc.
Mor-Mur M, Carretero C, Pla R, Guamis B (1992) A survey on the microbiological quality of a semi-soft on-farm manufactured goat cheese. Food Microbiol 9:345–352
Nuňez M, Medina M (1979) La flore lactique du fromage bleu de Cabrales. Le Lait 59:497–513
Nuňez M, Gaya P, Medina M (1985) Influence of manufacturing and ripening conditions on the survival of Enterobacteriaceae in Manchego cheese. J Dairy Sci 68:794–800
Olarte C, Sanz S, Gonzalez-Fandos E, Torre P (2000) The effect of a commercial starter culture addition on the ripening of an artisanal goat’s cheese (Cameros cheese). J Appl Microbiol 88:421–429
O’Mahony M (1986) Sensory evaluation of food. Statistical methods and procedures. Marcel Dekker, Inc. ISBN 0585158401
Ortigosa M, Barcenas P, Arizcun C, Perez-Elortondo F, Albisu M, Torre P (1999) Influence of the starter culture on the microbiological and sensory characteristics of ewe’s cheese. Food Microbiol 16:237–247
Papademas P, Robinson RK (2000) A comparison of the chemical, microbiological and sensory charecteristic of bovine and ovine Halloumi cheese. Int Dairy J 10:761–768
Poznanski E, Cavazza A, Cappa F, Cocconcelli PS (2004) Indigenous raw milk microbiota influences the bacterial development in traditional cheese from an alpine natural park. Int J Food Microbiol 92:141–151
Psoni L, Tzanetakis N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E (2003) Microbiological characteristics of Batzos, a traditional Greek cheese from raw goat’s milk. Food Microbiol 20:575–582
Psoni L, Tzanetakis N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E (2006) Characteristics of Batzos cheese made from raw, pasteurized and/or pasteurized standardized goat milk and a native culture. Food Control 17:533–539
Ramesh CC, Shahani KM (1992) Yogurt. In: Hui YH (ed) Dairy science and technology handbook. 2 product manufacturing. VCH Publishers Inc., New York. ISBN 1560810785
Rondinini G, Bortolussi G (1994) Importance of Leuconostoc in Montasio cheesemaking and setting up of quantification rapid method in milk. Annali di Microbiologia ed Enzimologia 44:277–281
Skeie S, Ardö Y (2000) Influence from raw milk flora on cheese ripening studied by different treatments of milk to model cheese. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technologie 33:499–505
Somers JM, Kelly AL (2002) Contribution of plasmin to primary proteolysis during ripening of cheese: effect of milk heat treatment and cheese cooking temperature. Le Lait 82:181–191
Tamime AY, Robinson RK (2001) Yoghurt: Science and technology, 2nd edn. Woodhead Publishing Limited, CRC Press, Cambridge. ISBN 1855733994
Wood BJB, Holzapfel WH (1995) The genera of lactic acid bacteria. Blackic Academic and Professional, London. ISBN 075140215X
Wouters JTM, Ayad EHE, Hugenholtz J, Smit G (2002) Microbes from raw milk for fermented dairy products. Int Dairy J 12:91–109
Yazici F, Dervisoglu M, Temiz H (1998) Sensory, physical, chemical, and microbiological properties of Kulek cheese. In: Demirci M (ed) Traditional dairy products. May 21–22, 1998, Tekirdag, Turkey, 621, MPM, pp.133–144
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported by Ondokuz Mayis University Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dervisoglu, M., Aydemir, O. Physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of Kulek cheese made from raw and heat-treated milk. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 451–460 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9246-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9246-x