Summary
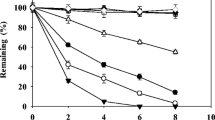
Four strains of bacteria, 9 strains of fungi and 20 strains of actinomycetes capable of utilizing metsulfuron-methyl as sole carbon and energy source were isolated from a metsulfuron-methyl-treated soil by the enrichment culture method. A fungus named DS11F was selected as the most highly effective one according to the maximum tolerance concentration of 1,200 mg l−1 and metsulfuron-methyl-degrading rate of 0.0716 g g−1 cells h−1, and was identified as an unknown strain of Penicillium sp. on the basis of colony growth, morphology and biochemical characteristics.␣Through liquid pure culture, the optimal metsulfuron-methyl-degrading conditions of DS11F were determined to be metsulfuron-methyl concentration 22.6 mg l−1, inoculum concentration 12.25 mg l−1, pH 7.0 and temperature 30°C. As additional C sources, supernatant of soaked compost could increase metsulfuron-methyl degradation by 8%, but glucose was ineffective. DS11F inoculation was found to significantly enhance the degradation of metsulfuron-methyl in soil, with the reduction of the concentration reaching 50% in 6 days. Admixture of compost could promote metsulfuron-methyl degradation to some extent. The growth of the inocula in the soils remained dominant and degradation resumed immediately when metsulfuron-methyl was applied again. The results show that addition of the isolated Penicillium sp. enhances the degradation of metsulfuron-methyl in water and soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen SM, Hertz PB, Holst T, Bossi R, Jacobsen CS (2001) Mineralisation studies of 14C-labelled metsulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron and thifensulfuron-methyl in one Danish soil and groundwater sediment profile. Chemosphere 45:775–782
Barnett HL, Hunter BB (1972) Illustrated genera of imperfect fungi. Third edn. Burgess Publishing Company, Minneapolis, MN, pp 67–75, ISBN 0808702661
Barriuso E (1997) Influence of compost addition to soil on the behaviour of herbicides. Pestic Sci 49:65–75
Berger BM, Wolfe NL (1996) Hydrolysis and biodegradation of sulfonylurea herbicides in aqueous buffers and anaerobic water-sediment systems: assessing fate pathways using molecular descriptors. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1500–1507
Boschin G, Agostina AD, Arnoldi A, Marotta E, Zanardini E, Negri M, Valle A, Sorlini C (2003) Biodegradation of chlorsulfuron and metsulfuron-methyl by Aspergillus niger in laboratory conditions. J Environ Sci Health B38:737–746
Braschi I, Pusino A, Gessa C, Bollag JM (2000) Degradation of primisulfuron by a combination of chemical and microbiological process. J Agric Food Chem 48:2565–2571
Brown HM (1990) Modes of action, crop selectivity and soil relations of the sulfonylurea herbicides. Pestic Sci 29:263–281
Dinelli G, Vicari A, Bonetti A (1997) Separation of sulfonylurea metabolites in water by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 700:195–200
Ghani A, Wardle DA (2001) Fate of 14C from glucose and the herbicide metsulfuron-methyl in a plant-soil microcosm system. Soil Biol Biochem 33:777–785
Hammamda S, Calmon JP (1994) Kinetics and hydrolysis mechanism of chlorsulfuron and metsulfuron-methyl. Pestic Sci 40:71–76
Joshi MM, Brown HM, Romesser JA (1985) Degradation of chlorsulfuron by soil microorganisms. Weed Sci 33:888–893
Kotoula SE, Eleftherohorinos IG, Gagianas AA, Sficas AG (1993) Phytotoxicity and persistence of chlorsulfuron, metsulfuronmethyl, triasulfuron and tribenuron-methyl in three soils. Weed Res 33:355–367
Li Y, Zimmerman WT, Gorman MK, Reiser RW, Fogiel AJ, Haney PE (1999) Aerobic soil metabolism of metsulfuron-methyl. Pesticide Sci 55:434–445
Perkovich BS, Anderson TA, Kruger EL, Koats JR (1996) Enhanced mineralization of 14C-atrazine in Kochia scoparia rhizosphere soil from pesticide contaminated site. Pestic Sci 46:391–396
Pons N, Barriuso E (1998) Fate of metsulfuron-methyl in soils in relation to pedo-climatic conditons. Pestic Sci 53:311–323
Sabadie J (1993) Degradation of chlorsulfuron and metsulfuron-methyl in the presence of humic acids. Weed Res 33:397–407
Si Y, Wang S, Zhou J, Hua R, Zhou D (2005) Leaching and degradation of ethametsulfuron-methyl in soil. Chemosphere 60:601–609
Spliid NH, Kopper B (1998) Occurrence of pesticides in Danish shallow ground water. Chemosphere 37:1307–1316
Walker A, Welch SJ (1989) The relative movement and persistence in soil of chlorsulfuron, metsulfuron-methyl and triasulfuron. Weed Res 29:375–383
Wehtje GR, Spading RF, Burnside OC, Lowry SR, Leavitt JCR (1983) Biological significance and fate of atrazine under acquifer conditions. Weed Sci 31:610–618
Wei JC (1979) Identification manual of fungi. Shanghai Science & Technology Press, Shanghai, pp 132–134
Yu YL, Wang X, Luo YM, Yang JF, Yu JQ, Fan DF (2005) Fungal degradation of metsulfuron-methyl in pure cultures and soil. Chemosphere 60:460–466
Zanardini E, Arnoldi A, Boschin G, D’Agostina A, Negri M, Sorlini C (2002) Degradation pathways of chlorsulfuron and metsulfuron-methyl by a Pseudomonas fluorescens strain. Ann Microbiol 52:25–37
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Fundation of P.R. China (20077024)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y.H., Shen, D.S., Fang, C.R. et al. Rapid biodegradation of metsulfuron-methyl by a soil fungus in pure cultures and soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 1095–1104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9148-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9148-y