Summary
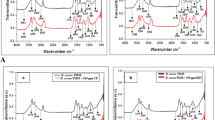
Five strains of the Rhodococcus and Gordonia genera were evaluated for their potential use in bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) with or without another substrate (co-substrate). Their ability to produce biosurfactants or to degrade phenanthrene when growing on glucose, hexadecane and rapeseed oil was tested in liquid medium at 30 °C. All strains showed biosurfactant activity. The highest reduction in surface tension was recorded in whole cultures of Rhodococcus sp. DSM 44126 (23.1%) and R. erythropolis DSM 1069 (21.1%) grown on hexadecane and Gordonia sp. APB (20.4%) and R. erythropolis TA57 (18.2%) grown on rapeseed oil. Cultures of Gordonia sp. APB and G. rubripertincta formed emulsions when grown on rapeseed oil. After 14 days of incubation, Rhodococcus sp. DSM 44126 degraded phenanthrene (initial concentration 100 μg ml−1) as sole carbon source (79.4%) and in the presence of hexadecane (80.6%), rapeseed oil (96.8%) and glucose (below the limit of detection). The other strains degraded less than 20%, and then with a co-substrate only. Rhodococcus sp. DSM 44126 was selected and its performance evaluated in soil spiked with a mixture of PAH (200 mg kg−1). The effect of the addition of 0, 0.1 and 1% rapeseed oil as co-substrate was also tested. Inoculation enhanced the degradation of phenanthrene (55.7% and 95.2% with 0.1% oil and without oil respectively) and of anthracene (29.2% with 0.1% oil). Approximately 96% of anthracene and 62% of benzo(a)pyrene disappeared from the soil (inoculated and control) after 14 days and anthraquinone was detected as a metabolite. Rhodococcus sp. DSM 44126 was identified as Rhodococcus wratislaviensis by 16S rRNA sequencing and was able to degrade anthracene as sole carbon source in liquid culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen S.M., Mortensen H.S., Bossi R., Jacobsen C.S.. 2001 Isolation and characterization of Rhodococcus erythropolis TA57 able to degrade the triazine amine product from hydrolysis of sulfonylurea pesticides in soilsSystematic and Applied Microbiology 24:262–266
April T.M., Foght J.M., Currah R.S.. 2000 Hydrocarbon-degrading filamentous fungi isolated from flare pit soils in northern and western CanadaCanadian Journal of Microbiology 46:38–49
Atagana H.I., Haynes R.J., Wallis F.M.. 2003 The use of surfactants as possible enhancers in bioremediation of creosote contaminated soil. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 142:137–149
Barkay T., Navon-Venezia S., Ron E., Rosenberg E.. 1999 Enhancement of solubilization and biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons by the bioemulsifier AlasanApplied and Environmental Microbiology 65:2697–2702
Behki R., Topp E., Dick W., Germon P.. 1993 Metabolism of the herbicide atrazine by Rhodococcus strainsApplied and Environmental Microbiology 59:1955–1959
Bezalel L., Hadar Y., Fu P.P., Freeman J.P., Cerniglia C.E.. 1996 Initial oxidation products in the metabolism of pyrene, anthracene, fluorene and dibenzothiophene by the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatusApplied and Environmental Microbiology 62:2554–2559
Berg Schuur J.H., Mattiasson B.. 2003 Separation of coal-tar constituents from soil particles in a two-liquid-phase slurry systemEnvironmental Technology 24:755–765
Bogan B.W., Trbovic V., Paterek J.R.. 2003 Inclusion of vegetable oils in Fenton’s chemistry for remediation of PAH-contaminated soilsChemosphere 50:15–21
Bouchez M., Blanchet D., Vandecasteele J.-P.. 1997 An interfacial uptake mechanism for the degradation of pyrene by a Rhodococcus strainMicrobiology 143:1087–1093
Brinch U., Ekelund F., Jacobsen C. 2002 Method for spiking soil samples with organic compoundsApplied and Environmental Microbiology 68:1808–1816
Cajthaml T., Möder M., Kačer P., Šašek V., Popp P.. 2002 Study of fungal degradation products of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using gas chromatography with ion trap mass spectrometry detectionJournal of Chromatography A 974:213–222
Cerniglia C.E., Heitkamp M.A.. 1990 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by MycobacteriumMethods in Enzymology 188:148–153
Christofi N., Ivshina I.B.. 2002 Microbial surfactants and their use in field studies of soil remediationJournal of Applied Microbiology 93:915–929
Dean-Roos D., Moody J., Freeman J, Doerge D., Cerniglia C.. 2001 Metabolism of anthracene by a Rhodococcus speciesFEMS Microbiology Letters 204:205–211
Dean-Roos D., Moody J., Cerniglia C.. 2002 Utilization of mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria isolated from contaminated sedimentFEMS Microbiology Ecology 41:1–7
Eggeling L., Sahm H.. 1980 Degradation of coniferyl alcohol and other lignin-related aromatic compounds by Nocardia sp. DSM 1069Archives of Microbiology 126:141–148
Gemini V.L., Gallego A., de Oliveira V.M., Gomez C.E., Manfio G.P., Korol S.E.. 2005 Biodegradation and detoxification of p-nitrophenol byRhodococcus wratislaviensis International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 55:103–108
Georgiou G., Lin S.C., Sharma M.M.. 1992 Surface-active compounds from microorganismsBiotechnology 10:60–65
Guerra-Santos L., Käppeli O., Fiethter A.. 1984 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon sourceApplied and Environmental Microbiology 48:301–305
Grund E., Denecke B., Eichenlaub R.. 1992 Naphthalene degradation via salicylate and gentisate by Rhodococcus sp. strain B4Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58:1874–1877
Hatzinger P.B., Alexander M.. 1995 Effect of aging chemicals in soil on their biodegradability and extractabilityEnvironmental Science and Technology 29:537–545
Hwang S., Cutright T.J.. 2002 Biodegradability of aged pyrene and phenanthrene in a natural soilChemosphere 47:891–899
Iqbal S., Khalid Z.M., Malik K.A.. 1995 Enhanced biodegradation and emulsification of crude oil and hyperproduction of biosurfactants by a gamma ray-induced mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosaLetters in Applied Microbiology 21:176–179
Iwahori K., Tokutomi T., Miyata N., Fujita M.. 2001 Formation of stable foam by the cells and culture supernatant of Gordonia (Nocardia) amaraeJournal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 92:77–79
Kanaly R.A., Harayama S.. 2000 Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteriaJournal of Bacteriology 182:2059–2067
Kanaly R., Bartha R., Watanabe K., Harayama S.. 2000 Rapid mineralization of benzo(a)pyrene by a microbial consortium growing on diesel fuelApplied and Environmental Microbiology 66:4205–4211
Karstensen K.H. 1996 Analysis of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. In Nordic guidelines for chemical analysis of contaminated soil samples, pp. 126–130. Nordtest Report. ISSN 0283-7234
Kästner M., Breuer-Jammali M., Mahro B.. 1994 Enumeration and characterization of the soil microflora from hydrocarbon-contaminated soil sites able to mineralize polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 41:267–273
Kim S.B., Falconer C., Williams E., Goodfellow M.. 1998 Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans sp. Nov. and Streptomyces thermocarboxydus sp. Nov., two moderately thermophilic carboxydotrophic species from soilInternational Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 48:59–68
Kraus J.J., Munir I.Z., McEldoon J.P., Clark D.S., Dordick J.S.. 1999 Oxidation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons catalyzed by soybean peroxidaseApplied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 80:221–230
Lang S., Philp J.C.. 1998 Surface-active lipids in rhodococciAntonie van Leeuwenhoek 74:59–70
Larkin M., Kulakov L., Allen C.. 2005 Biodegradation and Rhodococcus – masters of catabolic versatilityCurrent Opinion in Biotechnology 16:282–290
Lin T., Young C., Ho M., Yeh M., Chou C., Wei Y., Chang J.. 2005 Characterization of floating activity of indigenous diesel-assimilating bacterial isolatesJournal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 99:466–472
Mallakin A., Dixon D.G., Greenberg B.M.. 2000 Pathway of anthracene modification under simulated solar radiationChemosphere 40:1435–1441
Mandelbaum R.T., Wackett L.P., Allan D.L.. 1993 Mineralization of the s-triazine ring of atrazine by stable bacterial mixed culturesApplied and Environmental Microbiology 59:1695–1701
McCarthy A.J., Williams S.T.. 1992 Actinomycetes as agents of biodegradation in the environment – a reviewGene 115:189–192
Mil’ko E., Egorov N.. 1994 Hydrophilic-hydrophobic and adhesive properties of Rhodococcus rubropertinctus dissociantsMicrobiology 63:214–215
Moody J.D., Freeman J.P., Doerge D.R., Cerniglia C.E.. 2001 Degradation of phenanthrene and anthracene by cell suspensions of Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67:1476–1483
Navrátilová J., Tvrzová L., Durnová E., Spöer C., Sedláček I., Neča J., Němec M.. 2005 Characterization of Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain J3 that degrades 4-nitrocatechol and other nitroaromatic compoundsAntonie van Leeuwenhoek 87:149–153
Nazina T., Sokolova D., Grigor’yan A., Xue Y., Belyaev S., Ivanov M.. 2003 Production of oil-releasing compounds by microorganisms from the Daqing oil field, ChinaMicrobiology 72:206–211
Pannu J.K., Singh A., Ward O.P.. 2003 Influence of peanut oil on microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonsCanadian Journal of Microbiology 49:508–513
Pérez-Bercoff, Å. 2003 Evolutionary changes in soil bacterial communities due to 3- or 4-chlorophenol enrichment and inoculation with the 4-chlorophenol degrading strain Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus. Master Thesis, Södertörns Högskola, Sweden
Pirog T.P., Shevchuk T.A., Voloshina I.N., Karpenko E.V.. 2004 Production of surfactants by Rhodococcus erythropolis strain EK-1, grown on hydrophilic and hydrophobic substratesApplied Biochemistry and Microbiology 40:544–550
Ramsay B., McCarthy J., Guerra-Santos L., Kappeli O., Fiechter A., Margaritis A.. 1988 Biosurfactant production and diauxic growth of Rhodococcus aurantiacus when using n-alkanes as the carbon sourceCanadian Journal of Microbiology 34:1209–1212
Singer M.E., Finnerty W.R.. 1990 Physiology of biosurfactant synthesis by Rhodococcus species H13-ACanadian Journal of Microbiology 36:741–745
Tiehm A., 1994 Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of synthetic surfactantsApplied and Environmental Microbiology 60:258–263
Trojanowski J., Haider K., Sundman V.. 1977 Decomposition of 14C-labelled lignin and phenols by a Nocardia spArchives of Microbiology 114:149–153
Walter U., Beyer M., Klein J., Rehm H.J.. 1991 Degradation of pyrene by Rhodococcus sp. UW1Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 34:671–676
Wattiau P., 2002 Microbial aspects in bioremediation of soils polluted by polyaromatic hydrocarbonsFocus on Biotechnology 3A:2–22
Weissenfels W.D., Beyer M., Klein J.. 1990 Degradation of phenanthrene, fluorene and fluoranthene by pure bacterial culturesApplied Microbiology and Biotechnology 32:479–484
Whyte L., Slagman S., Pietrantonio F., Bourbonnière L., Koval S., Lawrence J., Inniss W., Greer C.. 1999 Physiological adaptations involved in alkane assimilation at a low temperature by Rhodococcus sp. Strain Q15Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65:2961–2968
Wick L.Y., de Munain A.R., Springael D., Harms H.. 2002 Responses of Mycobacterium sp. LB501T to the low bioavailability of solid anthraceneApplied Microbiology and Biotechnology 58:378–385
Willumsen P., Karlson U.. 1997 Screening of bacteria, isolated from PAH-contaminated soils, for production of biosurfactants and bioemulsifiersBiodegradation 7:415–423
Wilson S.C., Jones K.C.. 1993 Bioremediation of soil contaminated with polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a reviewEnvironmental Pollution 81:229–249
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Michael Goodfellow and his group for their technical help in the identification of Rhodococcus wrastislaviensis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pizzul, L., Pilar Castillo, M.d. & Stenström, J. Characterization of selected actinomycetes degrading polyaromatic hydrocarbons in liquid culture and spiked soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 745–752 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9100-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9100-6