Abstract
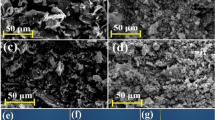
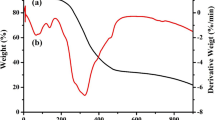
The dissemination of bismuth (Bi) into the environment has become a significant concern due to its wide application. The low-cost orange peel was used as a bio-sorbent to remove Bi from water. Influence of pH (4 ~ 12), biochar dosage (5 ~ 12.5 g L–1), temperature (25 ~ 55 °C), and coexisting ions (Mg2+ and Zn2+) on Bi adsorption were investigated. The removal rate was 91.90% when 10 g L–1 adsorbent was added at 25 °C in 40 mL Bi solution with an initial concentration of 50 mg L–1. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model could better describe the adsorption process than pseudo-first-order model, demonstrating that the adsorption of Bi by the orange peel biochar was predominantly chemisorption. Analytical techniques such as SEM, FTIR, XRD, and XPS indicated that the adsorption mechanism concerned electrostatic attraction, ion exchange, π-π electron donor–acceptor interaction, – OH and – COOH complexation, and pore filling. Orange peel biochar demonstrated a sustained performance, maintaining over 65% removal efficiency for Bi after three regeneration cycles. Orange peel biochar has a good application prospect as a cost-effective bio-sorbent for the treatment of Bi removal from water.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Abdelhafez, A. A., & Li, J. (2016). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by using biochars derived from sugar cane bagasse and orange peel. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 61, 367–375.
Ahmad, Z., Gao, B., Mosa, A., Yu, H., Yin, X., Bashir, A., Ghoveisi, H., & Wang, S. (2018). Removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by biochars derived from potassium-rich biomass. Journal of Cleaner Production, 180, 437–449.
Al-Saidi, H. M., Abdel-Fadeel, M. A., El-Sonbati, A. Z., & El-Bindary, A. A. (2016). Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as an adsorbent material for the solid phase extraction of bismuth from aqueous media: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies and analytical applications. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 216, 693–698.
Alizadeh, T., Hamidi, N., Ganjali, M. R., & Nourozi, P. (2017). Development of a highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor for Bi3+ determination based on nano-structured bismuth-imprinted polymer modified carbon/carbon nanotube paste electrode. Sensors and Actuators b: Chemical, 245, 605–614.
Amin, M. T., Alazba, A. A., & Shafiq, M. (2019). Comparative study for adsorption of methylene blue dye on biochar derived from orange peel and banana biomass in aqueous solutions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 735.
Amneklev, J., Augustsson, A., Sörme, L., & Bergbäck, B. (2016). Bismuth and silver in cosmetic products: A source of environmental and resource concern? Journal of Industrial Ecology, 20, 99–106.
Arami, M., Limaee, N., & Mahmoodi, N. (2008). Evaluation of the adsorption kinetics and equilibrium for the potential removal of acid dyes using a biosorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 139, 2–10.
Bakircioglu, Y., Bakircioglu, D., & Akman, S. (2003). Solid phase extraction of bismuth and chromium by rice husk. Journal of Trace and Microprobe Techniques, 21, 467–478.
Barakat, M. A. (2011). New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 4, 361–377.
Bonales-Revuelta, J., Musule, R., Navarro-Pineda, F. S., & García, C. A. (2022). Evaluating the environmental performance of orange production in Veracruz, Mexico: A life cycle assessment approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 343, 131002.
Chen, L., Wang, Y., Cao, C., Liu, C., & Zhu, L. (2017). Response of anaerobic membrane bioreactor to the presence of nano-Bi2WO6: Reactor performance, supernatant characteristics, and microbial community. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 24261–24271.
Gao, L.-Y., Deng, J.-H., Huang, G.-F., Li, K., Cai, K.-Z., Liu, Y., & Huang, F. (2019). Relative distribution of Cd2+ adsorption mechanisms on biochars derived from rice straw and sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 272, 114–122.
Gao, L., Li, Z., Yi, W., Wang, L., Zhang, P., Wan, Z., & Li, Y. (2021). Quantitative contribution of minerals and organics in biochar to Pb(II) adsorption: Considering the increase of oxygen-containing functional groups. Journal of Cleaner Production, 325, 129328.
He, R., Peng, Z., Lyu, H., Huang, H., Nan, Q., & Tang, J. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of an iron-impregnated biochar for aqueous arsenic removal. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 1177–1186.
Hu, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, Y., Lin, T., Zeng, G., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., He, W., Zhang, M., & Long, H. (2019). An efficient adsorbent: Simultaneous activated and magnetic ZnO doped biochar derived from camphor leaves for ciprofloxacin adsorption. Bioresource Technology, 288, 121511.
Ibrahim, W. A., Nodeh, H. R., & Sanagi, M. M. (2016). Graphene-based materials as solid phase extraction sorbent for trace metal ions, organic compounds, and biological sample preparation. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 46, 267–283.
Lam, S. S., Liew, R. K., Cheng, C. K., Rasit, N., Ooi, C. K., Ma, N. L., Ng, J.-H., Lam, W. H., Chong, C. T., & Chase, H. A. (2018). Pyrolysis production of fruit peel biochar for potential use in treatment of palm oil mill effluent. Journal of Environmental Management, 213, 400–408.
Li, J., Duan, Y., Zhou, S., Rong, L., Liu, Y., Chu, L., Li, Q., & Yang, L. (2021). Immobilization of uranium soil by geopolymer coupled with nHAP. Ceramics International, 47, 30815–30825.
Lian, F., Xing, B., & Zhu, L. (2011). Comparative study on composition, structure, and adsorption behavior of activated carbons derived from different synthetic waste polymers. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 360, 725–730.
Liu, J., Huang, Z., Chen, Z., Sun, J., Gao, Y., & Wu, E. (2020). Resource utilization of swine sludge to prepare modified biochar adsorbent for the efficient removal of Pb(II) from water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120322.
Mehmood, T., Khan, A. U., Dandamudi, K. P. R., Deng, S., Helal, M. H., Ali, H. M., & Ahmad, Z. (2022). Oil tea shell synthesized biochar adsorptive utilization for the nitrate removal from aqueous media. Chemosphere, 307, 136045.
Mo, G., Xiao, J., & Gao, X. (2023). To enhance the Cd2+ adsorption capacity on coconut shell-derived biochar by chitosan modifying: Performance and mechanism. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 13, 16737–16752.
Moawed, E. A., El-Hagrasy, M. A., & Embaby, N. E. M. (2017). Substitution influence of halo polyurethane foam on the removal of bismuth, cobalt, iron and molybdenum ions from environmental samples. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 70, 382–390.
Mukherjee, S., Sarkar, B., Aralappanavar, V. K., Mukhopadhyay, R., Basak, B. B., Srivastava, P., Marchut-Mikołajczyk, O., Bhatnagar, A., Semple, K. T., & Bolan, N. (2022). Biochar-microorganism interactions for organic pollutant remediation: Challenges and perspectives. Environmental Pollution, 308, 119609.
Osman, A. I., Fawzy, S., Farghali, M., El-Azazy, M., Elgarahy, A. M., Fahim, R. A., Maksoud, M. I. A. A., Ajlan, A. A., Yousry, M., Saleem, Y., & Rooney, D. W. (2022). Biochar for agronomy, animal farming, anaerobic digestion, composting, water treatment, soil remediation, construction, energy storage, and carbon sequestration: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 20, 2385–2485.
Pan, J., Deng, H., Du, Z., Tian, K., & Zhang, J. (2022). Design of nitrogen-phosphorus-doped biochar and its lead adsorption performance. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 28984–28994.
Rashidi Nodeh, H., & Sereshti, H. (2016). Synthesis of magnetic graphene oxide doped with strontium titanium trioxide nanoparticles as a nanocomposite for the removal of antibiotics from aqueous media. RSC Advances, 6, 89953–89965.
Rashidi Nodeh, H., Sereshti, H., Zamiri Afsharian, E., & Nouri, N. (2017). Enhanced removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous media using nanosized lanthanum hydrous doped on magnetic graphene nanocomposite. Journal of Environmental Management, 197, 265–274.
Ratova, M., Tosheva, L., Kelly, P. J., & Ohtani, B. (2019). Characterisation and properties of visible light-active bismuth oxide-titania composite photocatalysts. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 22, e00112.
Renner, R. (2004). Arsenic and lead leach out of popular fertilizer. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 382A-383A.
Saleh, T. A., Mustaqeem, M. & Khaled, M. (2022). ‘Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review’, Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Management, 100617–100617.
Sartape, A., Mandhare, A., Salvi, P., Pawar, D., Raut, P., Anuse, M., & Kolekar, S. (2012). Removal of Bi (III) with adsorption technique using coconut shell activated carbon. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 20, 768–775.
Shakya, A., Vithanage, M., & Agarwal, T. (2022). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar properties and Cr(VI) adsorption from water with groundnut shell biochars: Mechanistic approach. Environmental Research, 215, 114243.
Sireesha, S., Upadhyay, U. & Sreedhar, I. (2022). ‘Comparative studies of heavy metal removal from aqueous solution using novel biomass and biochar-based adsorbents: Characterization, process optimization, and regeneration’, Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery.
Sivaraj, R., Kadirvelu, K., & Namasivayam, C. (2001). Orange peel as an adsorbent in the removal of acid violet 17 (acid dye) from aqueous solutions. Waste Management, 21, 105–110.
Song, Z., Lian, F., Yu, Z., Zhu, L., Xing, B., & Qiu, W. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, 36–42.
Swiatkowski, A., Pakula, M., Biniak, S., & Walczyk, M. (2004). Influence of the surface chemistry of modified activated carbon on its electrochemical behaviour in the presence of lead(II) ions. Carbon, 42, 3057–3069.
Tan, Z., Yuan, S., Hong, M., Zhang, L., & Huang, Q. (2020). Mechanism of negative surface charge formation on biochar and its effect on the fixation of soil Cd. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121370.
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., & Chao, H. P. (2016). Effect of pyrolysis temperatures and times on the adsorption of cadmium onto orange peel derived biochar. Waste Management & Research, 34, 129–138.
Vengosh, A., Wang, Z., Williams, G., Hill, R., Coyte, M., & R. & Dwyer, G. S. (2022). The strontium isotope fingerprint of phosphate rocks mining. Science of the Total Environment, 850, 157971.
Wallace, A. R., Su, C., Sexton, M. & Sun, W. (2022). ‘Evaluation of the immobilization of coexisting heavy metal ions of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ from water by dairy manure-derived biochar: Performance and reusability’, Journal of Environmental Engineering 148.
Wang, L., Chang, G., Ai, M., Chen, G., Zhao, Y., & Wang, S. (2023). Quantitative analysis on the adsorption mechanism of Cd (II) by silicon-modified biochar in aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 43, 160–170. (in chinese).
Wang, X., & Xing, B. (2007). Sorption of organic contaminants by biopolymer-derived chars. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 8342–8348.
Weng, C.-H., & Huang, C. P. (2004). Adsorption characteristics of Zn(II) from dilute aqueous solution by fly ash. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 247, 137–143.
Wiriyathamcharoen, S., Sarkar, S., Jiemvarangkul, P., Nguyen, T. T., Klysubun, W., & Padungthon, S. (2020). Synthesis optimization of hybrid anion exchanger containing triethylamine functional groups and hydrated Fe(III) oxide nanoparticles for simultaneous nitrate and phosphate removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 381, 122671.
Wu, M., Liu, B., Li, J., Su, X., Liu, W., & Li, X. (2023). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on sludge biochar: The ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and the adsorption of Cd(II). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 12608–12617.
Xiao, Z., Wu, X., Tan, H., & Hao, S. (2022). CeO2@C synthesized from orange peel as carbon source and its removal performance for acid dyes. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 38, 407–414. (in Chinese).
Xing, Y., Luo, X., Liu, S., Wan, W., Huang, Q., & Chen, W. (2021). A novel eco-friendly recycling of food waste for preparing biofilm-attached biochar to remove Cd and Pb in wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 311, 127514.
Xue, F., Xia, B., Ying, R., Shen, S., & Zhao, P. (2013). Removal of Zn2+ from aqueous solution by biomass of Agaricus bisporus. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 7, 531–538.
Yan, J., Zuo, X., Yang, S., Chen, R., Cai, T., & Ding, D. (2022a). Evaluation of potassium ferrate activated biochar for the simultaneous adsorption of copper and sulfadiazine: Competitive versus synergistic. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424, 127435.
Yan, Y., Qi, F., Zhang, L., Zhang, P., & Li, Q. (2022b). Enhanced Cd adsorption by red mud modified bean-worm skin biochars in weakly alkali environment. Separation and Purification Technology, 297, 121533.
Yan, Y., Sarkar, B., Zhou, L., Zhang, L., Li, Q., Yang, J., & Bolan, N. (2020a). Phosphorus-rich biochar produced through bean-worm skin waste pyrolysis enhances the adsorption of aqueous lead. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115177.
Yan, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Wang, S., Li, Q., Liu, X., Xu, Y., Yang, J., & Bolan, N. (2020b). Clanis bilineata larvae skin-derived biochars for immobilization of lead: Sorption isotherm and molecular mechanism. Science of the Total Environment, 704, 135251.
Yang, T., Xu, Y., Huang, Q., Sun, Y., Liang, X., & Wang, L. (2022). Removal mechanisms of Cd from water and soil using Fe–Mn oxides modified biochar. Environmental Research, 212, 113406.
Yao, Y., Gao, B., Inyang, M., Zimmerman, A. R., Cao, X., Pullammanappallil, P., & Yang, L. (2011). Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 501–507.
Yin, Q., Wang, R., & Zhao, Z. (2018). Application of Mg–Al-modified biochar for simultaneous removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate from eutrophic water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 176, 230–240.
Yu, C. (2022a). ‘Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by nZVI-loaded sludge-derived biochar: Performance and mechanism’, Water Sci. Technol, 86, 2089–2105.
Yu, C. (2022b). ‘Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by nZVI-loaded sludge-derived biochar: performance and mechanism’, Water Science and Technology.
Zahedi, R., Dabbagh, R., Ghafourian, H., & Behbahanini, A. (2015). Nickel removal by Nymphaea alba leaves and effect of leaves treatment on the sorption capacity: A kinetic and thermodynamic study. Water Resources, 42, 690–698.
Zainal, N. H., Aziz, A. A., Idris, J., Jalani, N. F., Mamat, R., Ibrahim, M. F., Hassan, M. A., & Abd-Aziz, S. (2018). Reduction of POME final discharge residual using activated bioadsorbent from oil palm kernel shell. Journal of Cleaner Production, 182, 830–837.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the State Key Laboratory of Vanadium and Titanium Resources Comprehensive Utilization [2021P4FZG06A] and Sichuan Science and Technology Program [2022YFS0495].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kareem, A.A., Liao, Yl., Yu, Yq. et al. Removal of Bismuth from Water by Orange Peel Biochar. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 190 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06998-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06998-6