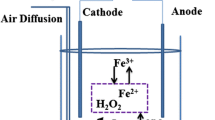
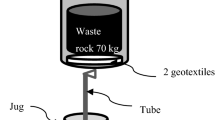
Abstract
A study was conducted to examine the impact of moderate thermophiles (Sulphobacillus thermosulphidooxidans, Acidithiobacillus caldus, Leptospirillum ferriphilum, Sulphobacillus spp.) on four different sulfide minerals, namely pyrite, marcasite, pyrrhotite, and arsenopyrite. The study was conducted with and without the addition of iron(II) sulfate and sulfur, and the results were analyzed in terms of the dissolution of iron, nickel, and zinc. These elements play a crucial role in the formation of acid mine drainage (AMD). During the 30-day incubation period, marcasite showed the highest iron dissolution level, with the iron concentration reaching 18.81 g/L at a pH range of 1.4 to 1.6. The dissolution rates of nickel and zinc were found to be high at 87% and 74%, respectively. The addition of external iron(II) sulfate (FeSO4⋅7H2O) and sulfur (S) did not have any effect on the dissolution of nickel and zinc. It was observed that marcasite and pyrite with high iron dissolution had a higher potential for acid mine drainage (AMD) formation. On the other hand, pyrrhotite with low iron dissolution had a lower potential for AMD formation. Despite the presence of additives, arsenopyrite had little effect on AMD production. The formation of passivation layers such as ammoniojarosite and hydronium jarosite effectively suppresses the continuous extraction of iron from pyrrhotite and arsenopyrite. Based on the surface analysis of feeds and residues of samples using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), it was concluded that the surface structures had been partially disrupted due to biochemical oxidation.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data underlying the results are available as part of the article, and no additional source data are required.
References
Abdollahi, H., Shafaei, S. Z., Noaparast, M., & Manafi, Z. (2017). Mixed moderate thermophilic bioleaching of Cu, Mo and Re from molybdenite concentrate: Effects of silver ion, medium and energy sources. International Journal of Mining and Geo-Engineering, 51(2), 151–159.
Aksoy, T., Cetin, M., Cabuk, S. N., Senyel Kurkcuoglu, M. A., Bilge Ozturk, G., & Cabuk, A. (2023). Impacts of wind turbines on vegetation and soil cover: A case study of Urla, Cesme, and Karaburun Peninsulas, Turkey. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 25(1), 51–68.
Alakangas, L., & Öhlander, B. (2006). Formation and composition of cemented layers in low-sulphide mine tailings, Laver, northern Sweden. Environmental Geology, 50, 809–819.
Baker, B. J., & Banfield, J. F. (2003). Microbial communities in acid mine drainage. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 44(2), 139–152.
Barron, J. L., & Lueking, D. R. (1990). Growth and maintenance of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56(9), 2801–2806.
Bosecker, K. (1997). Bioleaching: Metal solubilization by microorganisms. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 20(3–4), 591–604.
Cesur, A., Zeren Cetin, I., Cetin, M., Sevik, H., & Ozel, H. B. (2022). The use of Cupressus arizonica as a biomonitor of Li, Fe, and Cr pollution in Kastamonu. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(6), 193.
Cetin, M., Aljama, A. M. O., Alrabiti, O. B. M., Adiguzel, F., Sevik, H., & Zeren Cetin, I. (2022a). Determination and mapping of regional change of Pb and Cr pollution in Ankara city center. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(5), 163.
Cetin, M., Isik Pekkan, O., Bilge Ozturk, G., Senyel Kurkcuoglu, M. A., Kucukpehlivan, T., & Cabuk, A. (2022b). Examination of the change in the vegetation around the Kirka Boron mine site by using remote sensing techniques. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(7), 254.
Cetin, M. (2013). Landscape engineering, protecting soil, and runoff storm water. In Advances in landscape architecture.
Cicek, N., Erdogan, M., Yucedag, C., & Cetin, M. (2022). Improving the detrimental aspects of salinity in salinized soils of arid and semi-arid areas for effects of vermicompost leachate on salt stress in seedlings. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(6), 197.
Córdoba, E. M., Muñoz, J. A., Blázquez, M. L., González, F., & Ballester, A. (2008). Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. Part I: General aspects. Hydrometallurgy, 93(3–4), 81–87.
Deveci, H. A. C. I., Akcil, A., & Alp, I. (2004). Bioleaching of complex zinc sulphides using mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: Comparative importance of pH and iron. Hydrometallurgy, 73(3–4), 293–303.
Ding, J. N., Jian, G. A. O., Wu, X. L., Zhang, C. G., Wang, D. Z., & Qiu, G. Z. (2007). Jarosite-type precipitates mediated by YN22, Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, and their influences on strain. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 17(5), 1038–1044.
Dutrizac, J. E. (2004). The behaviour of the rare earths during the precipitation of sodium, potassium and lead jarosites. Hydrometallurgy, 73(1–2), 11–30.
Dutrizac, J. E., & Jambor, J. L. (2000). Jarosites and their application in hydrometallurgy. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 40(1), 405–452.
Figueiredo, M. O., & da Silva, T. P. (2011). The positive environmental contribution of jarosite by retaining lead in acid mine drainage areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8(5), 1575–1582.
Garcia, O., Jr., Bigham, J. M., & Tuovinen, O. H. (2007). Oxidation of isochemical FeS2 (marcasite–pyrite) by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals Engineering, 20(1), 98–101.
Grishin, S. I., Bigham, J. M., & Tuovinen, O. H. (1988). Characterization of jarosite formed upon bacterial oxidation of ferrous sulfate in a packed-bed reactor. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54(12), 3101–3106.
Gu, G. H., Hu, K. T., & Li, S. K. (2013). Bioleaching and electrochemical properties of chalcopyrite by pure and mixed culture of Leptospirillum ferriphilum and Acidthiobacillus thiooxidans. Journal of Central South University, 20(1), 178–183.
Holmes, D. S. (2008). Review of international biohydrometallurgy symposium, Frankfurt, 2007. Hydrometallurgy, 92(1–2), 69–72.
Jia, R., Unsal, T., Xu, D., Lekbach, Y., & Gu, T. (2019). Microbiologically influenced corrosion and current mitigation strategies: A state of the art review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 137, 42–58.
Kazemi, M. J., Kargar, M., Nowroozi, J., Sepahi, A. A., Doosti, A., & Manafi, Z. (2019). The wide distribution of an extremely thermoacidophilic microorganism in the copper mine at ambient temperature and under acidic condition and its significance in bioleaching of a chalcopyrite concentrate. Revista Argentina De Microbiologia, 51(1), 56–65.
King, P. L., & McSween, H. Y., Jr. (2005). Effects of H2O, pH, and oxidation state on the stability of Fe minerals on Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 110(12), 12–22.
Klauber, C. (2008). A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 86(1–4), 1–17.
Kocaman, A. T., Cemek, M., & Edwards, K. J. (2016). Kinetics of pyrite, pyrrhotite, and chalcopyrite dissolution by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 62(8), 629–642.
Kravkaz Kuscu, I. S., Cetin, M., Yigit, N., Savaci, G., & Sevik, H. (2018). Relationship between enzyme activity (Urease-Catalase) and nutrient element in soil use. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 27(5).
Kravkaz-Kuscu, I. S., Sariyildiz, T., Cetin, M., Yigit, N., Sevik, H., & Savaci, G. (2018). Evaluation of the soil properties and primary forest tree species in Taskopru (Kastamonu) district. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 27(3), 1613–1617.
Lee, E., Han, Y., Park, J., Hong, J., Silva, R. A., Kim, S., & Kim, H. (2015). Bioleaching of arsenic from highly contaminated mine tailings using Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Journal of Environmental Management, 147, 124–131.
Leng, F., Li, K., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Lu, J., & Li, H. (2009). Comparative study of inorganic arsenic resistance of several strains of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy, 98(3–4), 235–240.
Matusiewicz, H. (2017). Sample preparation for inorganic trace element analysis. Physical Sciences Reviews, 2(5), 20178001.
Milojevic, T., Kölbl, D., Ferrière, L., Albu, M., Kish, A., Flemming, R. L., & Rupert, A. N. (2019). Exploring the microbial biotransformation of extraterrestrial material on nanometer scale. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 18028.
Nazari, B., Jorjani, E., Hani, H., Manafi, Z., & Riahi, A. (2014). Formation of jarosite and its effect on important ions for Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans bacteria. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 24(4), 1152–1160.
Nordstrom, D. K. (2009). Acid rock drainage and climate change. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 100(2–3), 97–104.
Qiu, M. Q., Xiong, S. Y., Zhang, W. M., & Wang, G. X. (2005). A comparison of bioleaching of chalcopyrite using pure culture or a mixed culture. Minerals Engineering, 18(9), 987–990.
Rawlings, D. E. (2001). The molecular genetics of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and other mesophilic, acidophilic, chemolithotrophic, iron-or sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Hydrometallurgy, 59(2–3), 187–201.
Rawlings, D. E. (2011). Biomining (mineral bioleaching, mineral biooxidation).In Encyclopedia of geobiology, 182–185.
Sajjad, W., Zheng, G., Din, G., Ma, X., Rafiq, M., & Xu, W. (2019). Metals extraction from sulfide ores with microorganisms: The bioleaching technology and recent developments. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 72, 559–579.
Shu, X., Dang, Z., Zhang, Q., Yi, X., Lu, G., Guo, C., & Yang, C. (2013). Passivation of metal-sulfide tailings by covalent coating. Minerals Engineering, 42, 36–42.
Silverman, M. P., & Lundgren, D. G. (1959). Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans: I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. Journal of Bacteriology, 77(5), 642–647.
Skousen, J., Rose, A., Geidel, G., Foreman, J., Evans, R., & Hellier, W. (1998). Handbook of technologies for avoidance and remediation of acid mine drainage (p. 131). National Mine Land Reclamation Center.
Sracek, O., Choquette, M., Gélinas, P., Lefebvre, R., & Nicholson, R. V. (2004). Geochemical characterization of acid mine drainage from a waste rock pile, Mine Doyon, Quebec Canada. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 69(1–2), 45–71.
Sreekrishnan, T. R., Tyagi, R. D., Blais, J. F., & Campbell, P. G. (1993). Kinetics of heavy metal bioleaching from sewage sludge—I. Effects of process parameters. Water Research, 27(11), 1641–1651.
Tekin, O., Cetin, M., Varol, T., Ozel, H. B., Sevik, H., & Zeren Cetin, I. (2022). Altitudinal migration of species of Fir (Abies spp.) in adaptation to climate change. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(9), 385.
Third, K. A., Cord-Ruwisch, R., & Watling, H. R. (2000). The role of iron-oxidizing bacteria in stimulation or inhibition of chalcopyrite bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy, 57(3), 225–233.
Ubaldini, S., Veglio, F., Beolchini, F., Toro, L., & Abbruzzese, C. (2000). Gold recovery from a refractory pyrrhotite ore by biooxidation. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 60(3–4), 247–262.
Varol, T., Emir, T., Akgul, M., Ozel, H. B., Acar, H. H., & Cetin, M. (2020). Impacts of small-scale mechanized logging equipment on soil compaction in forests. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 20, 953–963.
Varol, T., Ozel, H. B., Ertugrul, M., Emir, T., Tunay, M., Cetin, M., & Sevik, H. (2021). Prediction of soil-bearing capacity on forest roads by statistical approaches. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193, 1–13.
Wang, H., Bigham, J. M., & Tuovinen, O. H. (2007). Oxidation of marcasite and pyrite by iron-oxidizing bacteria and archaea. Hydrometallurgy, 88(1–4), 127–131.
Wang, G., Xie, S., Liu, X., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., & Zeng, T. (2018). Bio-oxidation of a high-sulfur and high-arsenic refractory gold concentrate using a two-stage process. Minerals Engineering, 120, 94–101.
Watling, H. R. (2006). The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—a review. Hydrometallurgy, 84(1–2), 81–108.
Watling, H. R. (2008). The bioleaching of nickel-copper sulfides. Hydrometallurgy, 91(1–4), 70–88.
Xingyu, L., Rongbo, S., Bowei, C., Biao, W., & Jiankang, W. (2009). Bacterial community structure change during pyrite bioleaching process: Effect of pH and aeration. Hydrometallurgy, 95(3–4), 267–272.
Yadollahi, A., Abdollahi, H., Ardejani, F. D., Mirmohammadi, M., & Magdouli, S. (2021). Bio-oxidation behavior of pyrite, marcasite, pyrrhotite, and arsenopyrite by sulfur-and iron-oxidizing acidophiles. Bioresource Technology Reports, 15, 100699.
Yin, S. H., Wu, A. X., & Qiu, G. Z. (2008). Bioleaching of low-grade copper sulphides. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 18(3), 707–713.
Zhao, K., Gu, G., Wang, X., Yan, ; Wu, and Qiu, G. (2017). Study on the jarosite mediated by bioleaching of pyrrhotite using Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans. Bioscience Journal, 3, 721–729.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the staff of the Mineral Processing, Mine Environment and Hydrogeology Research (MEHR), and Geochemistry Laboratory of the University of Tehran for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ali Yadollahi: investigation, methodology, software, formal analysis, validation, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and visualization. Hadi Abdollahi: conceptualization, methodology, validation, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. Faramarz Doulati Ardejani: supervision, funding acquisition, resources, and writing—review and editing. Mirsaleh Mirmohammadi: resources and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Biooxidation of sulfide minerals was used to evaluate AMD production.
• Dissolution of marcasite and pyrite produces AMD.
• Moderately thermophilic microorganisms dissolve Fe, Ni, and Zn.
• Jarosite precipitation can affect the biooxidation process of pyrrhotite.
• Arsenopyrite has a low iron dissolution rate due to its toxicity to bacteria.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadollahi, A., Abdollahi, H., Ardejani, F.D. et al. The Impact of Moderate Thermophiles on the Production of Acid Mine Drainage and the Dissolution of Ni and Zn from Iron-Bearing Sulfide Minerals. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 203 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06997-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06997-7