Abstract
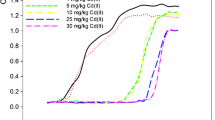
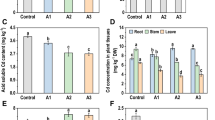
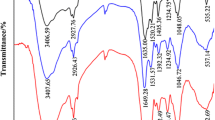
The concentrated heavy metal in plant biomass, following successful phytoremediation of contaminated soil, needs to be disposed of sustainably. In this study, Bidens pilosa biomass harvested after phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil was incinerated to ash and was further stabilized through a biocalcification process using a novel ureolytic strain Advenella sp. AV1. The changes in pH, ammonium ion (NH4+) concentration, and residual calcium ions (Ca2+) were measured for 3 days in biocalcification experiments. The increase in pH (from 7.8 to 9.6), NH4+ ions, and concomitant reduction in soluble Ca2+ in microbial “treatment” set containing B. pilosa biomass ash suggest the production of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which was further confirmed through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersion X-ray analysis. Sequential extraction of bio-calcified ash revealed a decrease in easily available cadmium (Cd) fractions, while an increase in more stable oxide and organic matter bound fractions in comparison to that from non-calcified biomass ash. The results suggest a reduced risk of heavy metals leaching following the biocalcification of phytoremediated biomass ash.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Date will be made available on request.
References
Achal, V., Pan, X., Zhang, D., & Fu, Q. (2012). Bioremediation of Pb-contaminated soil based on microbially induced calcite precipitation. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22(2), 244–247. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1108.08033
Ahmad, S. S., Reshi, Z. A., Shah, M. A., Rashid, I., & Ara, R. (2023). Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Trapa natans in Hokersar Wetland, a Ramsar Site of Kashmir Himalayas. In: Newman, L., Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Naeem, M., Gill, R. (eds) Phytoremediation, 147–154. Springer International Publishing, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17988-4_8
Anbu, P., Kang, C. H., Shin, Y. J., & So, J. S. (2016). Formations of calcium carbonate minerals by bacteria and its multiple applications. Springerplus, 5(1), 250. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-1869-2
Bhattacharya, A., Naik, S. N., & Khare, S. K. (2018). Harnessing the bio-mineralization ability of urease producing Serratia marcescens and Enterobacter cloacae EMB19 for remediation of heavy metal cadmium (II). Journal of Environmental Management, 215, 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.055
Cui, X., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Pan, M., Lin, Q., Khan, K. Y., Yan, B., Li, T., He, Z., Yang, X., & Chen, G. (2021). A review on the thermal treatment of heavy metal hyperaccumulator: Fates of heavy metals and generation of products. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 405, 123832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123832
Dineshbabu, G., Uma, V. S., Mathimani, T., Deviram, G., Arul Ananth, D., Prabaharan, D., & Uma, L. (2017). On-site concurrent carbon dioxide sequestration from flue gas and calcite formation in ossein effluent by a marine cyanobacterium Phormidium valderianum BDU 20041. Energy Conversion and Management, 141, 315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.040
Feng, J., Jia, W., Lv, S., Bao, H., Miao, F., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Li, J., Li, D., Zhu, C., Li, S., & Li, Y. (2018). Comparative transcriptome combined with morpho-physiological analyses revealed key factors for differential cadmium accumulation in two contrasting sweet sorghum genotypes. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 16(2), 558–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12795
García-Reyes, S., Yáñez-Ocampo, G., Wong-Villarreal, A., Rajaretinam, R. K., Thavasimuthu, C., Patiño, R., & Ortiz-Hernández, M. L. (2018). Partial characterization of a biosurfactant extracted from Pseudomonas sp. B0406 that enhances the solubility of pesticides. Environmental Technology (United Kingdom), 39(20), 2622–2631. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2017.1363295
Ghorbanzadeh, N., Abduolrahimi, S., Forghani, A., & Farhangi, M. B. (2020). Bioremediation of cadmium in a sandy and a clay soil by microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation after one week incubation. Arid Land Research and Management, 34(3), 319–335. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2020.1720866
Gong, Y., Zhao, D., & Wang, Q. (2018). An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Research, 147, 440–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.024
Gupta, S., Thapliyal, P., Shah, V., & Daverey, A. (2022). Optimization of Bio-Calcification Process for a Newly Isolated Urease Producing Bacterial Strain Advenelle sp AV1. Geomicrobiology Journal, 39(3–5), 242–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2021.1980920
Ha, J., Jai, K., & Lee, Y. (2019). An optimum condition of MICP indigenous bacteria with contaminated wastes of heavy metal. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21(2), 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0779-5
Houzelot, V., Ranc, B., Laubie, B., & Simonnot, M. O. (2018). Agromining of hyperaccumulator biomass: Study of leaching kinetics of extraction of nickel, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, iron, and manganese from Alyssum murale ashes by sulfuric acid. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 129, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.10.030
Jalilvand, N., Akhgar, A., Alikhani, H. A., Rahmani, H. A., & Rejali, F. (2020). Removal of heavy metals zinc, lead, and cadmium by biomineralization of urease-producing bacteria isolated from Iranian mine calcareous soils. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 20(1), 206–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00121-z
Kang, C. H., Han, S. H., Shin, Y., Oh, S. J., & So, J. S. (2014). Bioremediation of Cd by microbially induced calcite precipitation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172(4), 1929–1937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0626-z
Kim, J.-H., & Lee, J.-Y. (2019). An optimum condition of MICP indigenous bacteria with contaminated wastes of heavy metal. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21(2), 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0779-5
Kovacs, H., & Szemmelveisz, K. (2017). Disposal options for polluted plants grown on heavy metal contaminated brownfield lands – A review. Chemosphere, 166, 8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.076
Li, X., Luo, K., Ren, J., Wang, X., Mu, Q., & Fan, W. (2017). Characterisation of extracellular polymeric substances from different cyanobacterial species and their influence on biocalcification processes. Environmental Chemistry, 14(4), 254. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN17068
Li, Q., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, L., Tang, M., Hu, W., Chen, L., & Ai, S. (2022). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Science of the Total Environment, 825, 153862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153862
Liu, Z., & Tran, K. Q. (2021). A review on disposal and utilization of phytoremediation plants containing heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 226, 112821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112821
Liu, L., Li, W., Song, W., & Guo, M. (2018). Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: Principles and applicability. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
Liu, J., Xue, J., Yuan, D., Wei, X., & Su, H. (2019). Surfactant washing to remove heavy metal pollution in soil: A review. Recent Innovations in Chemical Engineering (formerly Recent Patents on Chemical Engineering), 13(1), 3–16. https://doi.org/10.2174/2405520412666190912151737
Mahanty, B., Kim, S., & Kim, C. G. (2013). Assessment of a Biostimulated or Bioaugmented Calcification System with Bacillus pasteurii in a Simulated Soil Environment. Microbial Ecology, 65, 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0137-4
Mahar, A., Wang, P., Ali, A., Awasthi, M. K., Lahori, A. H., Wang, Q., Li, R., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. In Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Mitchell, A. C., & Ferris, F. G. (2005). The coprecipitation of Sr into calcite precipitates induced by bacterial ureolysis in artificial groundwater: Temperature and kinetic dependence. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(17), 4199–4210. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703705002486
Phillips, A. J., Gerlach, R., Lauchnor, E., Mitchell, A. C., Cunningham, A. B., & Spangler, L. (2013). Engineered applications of ureolytic biomineralization: a review. Biofouling, 29(6), 715–733. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.796550
Rajasekar, A., Wilkinson, S., & Moy, C. K. S. (2021). MICP as a potential sustainable technique to treat or entrap contaminants in the natural environment: A review. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 6, 100096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2021.100096
Rautela, R., & Rawat, S. (2020). Analysis and optimization of process parameters for: In vitro biomineralization of CaCO3 by Klebsiella pneumoniae, isolated from a stalactite from the Sahastradhara cave. RSC Advances, 10(14), 8470–8479. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00090f
Sarfaraz, Q., da Silva, L. S., Drescher, G. L., Zafar, M., Severo, F. F., Kokkonen, A., Dal Molin, G., Shafi, M. I., Shafique, Q., & Solaiman, Z. M. (2020). Characterization and carbon mineralization of biochars produced from different animal manures and plant residues. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 955. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57987-8
Saxena, G., Purchase, D., Mulla, S. I., Saratale, G. D., & Bharagava, R. N. (2019). Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Sites: Eco-environmental Concerns, Field Studies, Sustainability Issues, and Future Prospects. In How to Recruit Voluntary Donors in the Third World?, 238, 71–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2019_24
Shah, V., & Daverey, A. (2020). Phytoremediation: A multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 18, 100774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100774
Shah, V., & Daverey, A. (2021). Effects of sophorolipids augmentation on the plant growth and phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 280, 124406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124406
Singh, J., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2013). Chemical speciation of heavy metals in compost and compost amended soil -a review. International Journal of Environmental Engineering Research, 2(2), 27–37.
Tabla-Hernandez, J., Rodriguez-Espinosa, P. F., Mendoza-Pérez, J. A., Sánchez-Ortíz, E., Martinez-Tavera, E., & Hernandez-Ramirez, A. G. (2019). Assessment of potential toxic metals in a Ramsar Wetland, Central Mexico and its Self-Depuration through Eichhornia crassipes. Water, 11(6), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061248
Tamayo-Figueroa, D. P., Castillo, E., & Brandão, P. F. B. (2019). Metal and metalloid immobilization by microbiologically induced carbonates precipitation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 35(4), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2626-9
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a017
Uma, V. S., Dineshbabu, G., Subramanian, G., Uma, L., & Prabaharan, D. (2014). Biocalcification mediated remediation of calcium rich ossein effluent by filamentous marine cyanobacteria. Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation, 05, 07. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000257
Vocciante, M., Caretta, A., Bua, L., Bagatin, R., Franchi, E., Petruzzelli, G., & Ferro, S. (2019). Enhancements in phytoremediation technology: Environmental assessment including different options of biomass disposal and comparison with a consolidated approach. Journal of Environmental Management, 237, 560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.104
Wang, X., Zhang, L., Zhu, K., Li, C., Zhang, Y., & Li, A. (2021). Efficiently sintering of MSWI fly ash at a low temperature enhanced by in-situ pressure assistant: Process performance and product characterization. Waste Management, 134, 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.07.036
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) of India (Grant no. EEQ/2017/ 000641). Mr. Vijendra received the fellowship from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), India under the project Grant no. EEQ/2017/ 000641.
Funding
This study is financially supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) of India (Grant no. EEQ/2017/ 000641).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V. Shah: Conducted Experiments, Formal Analysis, Writing: First draft, review and editing. B. Mahanty: Conceptualization; Writing: review and editing. A. Daverey: Conceptualization; Supervision; Writing: First draft, Review and Editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, and Resources. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, V., Mahanty, B. & Daverey, A. Biocalcification-Based Stabilization of Cadmium-Enriched Phytoremediation Biomass Using Advenella sp. AV1. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 185 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06994-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06994-w