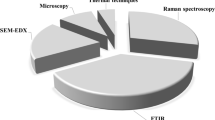
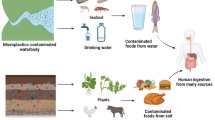
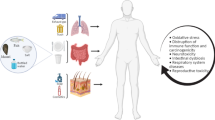
Abstract
Plastic is a widely used material in the food area; it is used in the crop field and water pipes for the growth of plants, in food processing, packaging, and distribution of products and beverages, as well as in preparation and consumption at home. However, plastic wears down when used in all these processes, releasing tiny particles, denominate microplastics (MP), that mix with food, drinkable water, and other beverages before or during consumption. This review discusses recent findings of MP contamination in non–processed and processed food, and water, as well as the possible sources. The risks to human health associated with the consumption of MP and their effect on its metabolism are detailed. Some recommendations are made to reduce exposure to MP related to food practices, and some social behavior patterns that influence food–buying decisions are analyzed. The consumption of MP from food and water affects the entire population since a large part of the products and water contain them due to the practices used for their production and processing. However, the number of MP ingested daily can be reduced if consumption and behavior patterns are considered and modified at home when preparing food. Awareness of the health problems that MP consumption can cause is essential for the entire population since, unfortunately, no one is exempt from MP; infants and young children are the most at risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Afrin, S., Rahman, M. M., Hossain, M. N., Uddin, M. K., & Malafaia, G. (2022). Are there plastic particles in my sugar? A pioneering study on the characterization of microplastics in commercial sugars and risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 837, 155849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155849
Akhbarizadeh, R., Dobaradaran, S., Nabipour, I., Tajbakhsh, S., Darabi, A. H., & Spitz, J. (2020). Abundance, composition, and potential intake of microplastics in canned fish. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 160, 111633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111633
Allen, S., Allen, D., Phoenix, V. R., Le Roux, G., Durántez Jiménez, P., Simonneau, A., . . . Galop, D. (2019). Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nature Geoscience, 12(5), 339–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0335-5
ALPLA México, C. y. e. C., & P&G-México. (2023). El reciclaje de plásticos entre los mexicanos. Encuesta nacional de hábitos de reciclaje de plásticos 2023. www.vidacircular.lat. Accessed 5 Dec 2023
Altunışık, A. (2023). Prevalence of microplastics in commercially sold soft drinks and human risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 336, 117720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117720
Amato-Lourenço, L. F., Carvalho-Oliveira, R., Júnior, G. R., dos Santos Galvão, L., Ando, R. A., & Mauad, T. (2021). Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 416, 126124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126124
Aydın, R. B., Yozukmaz, A., Şener, İ., Temiz, F., & Giannetto, D. (2023). Occurrence of microplastics in most consumed fruits and vegetables from Turkey and public risk assessment for consumers. Life, 13(8), 1686. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/13/8/1686
Bai, C.-L., Liu, L.-Y., Guo, J.-L., Zeng, L.-X., & Guo, Y. (2022). Microplastics in take-out food: Are we over taking it? Environmental Research, 215, 114390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114390
Barker, H., Shaw, P. J., Richards, B., Clegg, Z., & Smith, D. M. (2023). Towards sustainable food systems: Exploring household food waste by photographic diary in relation to unprocessed, processed and ultra-processed food. Sustainability, 15(3), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032051
Betts, K. (2008). Why small plastic particles may pose a big problem in the oceans. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(24), 8995–8995. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802970v
Bilal, M., Taj, M., Ul Hassan, H., Yaqub, A., Shah, M. I. A., Sohail, M., . . . Arai, T. (2023). First report on microplastics quantification in poultry chicken and potential human health risks in Pakistan. Toxics, 11(7), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070612
Bindon, K. A., Carew, A. L., Mierczynska-Vasilev, A., Kassara, S., Kerslake, F., & Smith, P. A. (2016). Characterization of macromolecular complexes in red wine: Composition, molecular mass distribution and particle size. Food Chemistry, 199, 838–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.12.079
Bohdan, K. (2022). Estimating global marine surface microplastic abundance: Systematic literature review. Science of the Total Environment, 832, 155064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155064
Borges-Ramírez, M. M., Mendoza-Franco, E. F., Escalona-Segura, G., & Osten, J.R.-V. (2020). Plastic density as a key factor in the presence of microplastic in the gastrointestinal tract of commercial fishes from Campeche Bay, Mexico. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115659
Brown, D. M., Wilson, M. R., MacNee, W., Stone, V., & Donaldson, K. (2001). Size-dependent proinflammatory effects of ultrafine polystyrene particles: A role for surface area and oxidative stress in the enhanced activity of ultrafines. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 175(3), 191–199. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.2001.9240
Carpenter, E. J., & Smith, K. L. (1972). Plastics on the Sargasso Sea Surface. Science, 175(4027), 1240–1241. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.175.4027.1240
Chen, Y., Xu, H., Luo, Y., Ding, Y., Huang, J., Wu, H., . . . Yang, Z. (2023). Plastic bottles for chilled carbonated beverages as a source of microplastics and nanoplastics. Water Research, 242, 120243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120243
Çobanoğlu, H., Belivermiş, M., Sıkdokur, E., Kılıç, Ö., & Çayır, A. (2021). Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of polyethylene microplastics on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Chemosphere, 272, 129805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129805
Conti, G. O., Ferrante, M., Banni, M., Favara, C., Nicolosi, I., Cristaldi, A., . . . Zuccarello, P. (2020). Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables. The first diet risks assessment for the general population. Environmental Research, 187, 109677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109677
Daniel, D. B., Ashraf, P. M., Thomas, S. N., & Thomson, K. T. (2021). Microplastics in the edible tissues of shellfishes sold for human consumption. Chemosphere, 264, 128554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128554
de Araújo, T. P., & de Moraes, M. M. (2022). Food processing: comparison of different food classification systems. Nutrients, 14(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040729
Deng, Y., Jiang, X., Zhao, H., Yang, S., Gao, J., Wu, Y., . . . Hou, C. (2021). Microplastic polystyrene ingestion promotes the susceptibility of honeybee to viral infection. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(17), 11680–11692. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01619
Dessì, C., Okoffo, E. D., O’Brien, J. W., Gallen, M., Samanipour, S., Kaserzon, S., . . . Thomas, K. V. (2021). Plastics contamination of store-bought rice. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 416, 125778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125778
Diaz-Basantes, M. F., Conesa, J. A., & Fullana, A. (2020). Microplastics in honey, beer, milk and refreshments in Ecuador as emerging contaminants. Sustainability, 12(14), 5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145514
Djouina, M., Vignal, C., Dehaut, A., Caboche, S., Hirt, N., Waxin, C., . . . Body-Malapel, M. (2022). Oral exposure to polyethylene microplastics alters gut morphology, immune response, and microbiota composition in mice. Environmental Research, 212, 113230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113230
Dong, C. D., Chen, C. W., Chen, Y. C., Chen, H. H., Lee, J. S., & Lin, C. H. (2020). Polystyrene microplastic particles: In vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, 121575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121575
Du, F., Cai, H., Zhang, Q., Chen, Q., & Shi, H. (2020). Microplastics in take-out food containers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 399, 122969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122969
Edo, C., Fernández-Alba, A. R., Vejsnæs, F., van der Steen, J. J. M., Fernández-Piñas, F., & Rosal, R. (2021). Honeybees as active samplers for microplastics. Science of the Total Environment, 767, 144481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144481
Enste, K., Borchers, L. J., & Fischer, E. K. (2022, November, 17). Microplastic contamination in croplands: Investigation of microplastics at asparagus and strawberries comparing conventional and organic farming systems. MICRO 2022,
Enyoh, C. E., Verla, A. W., Verla, E. N., Ibe, F. C., & Amaobi, C. E. (2019). Airborne microplastics: A review study on method for analysis, occurrence, movement and risks. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(11), 668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7842-0
Etxabide, A., Young, B., Bremer, P. J., & Kilmartin, P. A. (2022). Non-permanent primary food packaging materials assessment: Identification, migration, toxicity, and consumption of substances. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 21(5), 4130–4145. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.13001
Evode, N., Qamar, S. A., Bilal, M., Barceló, D., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2021). Plastic waste and its management strategies for environmental sustainability. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 4, 100142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100142
Fadare, O. O., Okoffo, E. D., & Olasehinde, E. F. (2021). Microparticles and microplastics contamination in African table salts. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 164, 112006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112006
FAO. (2016). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016. Contributing to food security and nutrition for all. FAO.
FAO. (2022). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc0461en
Geyer, R. (2020). Chapter 2 - Production, use, and fate of synthetic polymers. In T. M. Letcher (Ed.), Plastic Waste and Recycling (pp. 13–32). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817880-5.00002-5
Giwa, A., Ahmed, M., & Hasan, S. W. (2019). Polymers for membrane filtration in water purification. In R. Das (Ed.), Polymeric Materials for Clean Water (pp. 167–190). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00743-0_8
González-Pleiter, M., Edo, C., Aguilera, Á., Viúdez-Moreiras, D., Pulido-Reyes, G., González-Toril, E., . . . Rosal, R. (2021). Occurrence and transport of microplastics sampled within and above the planetary boundary layer. Science of The Total Environment, 761, 143213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143213
Gregory, M. R., & Ryan, P. G. (1997). Pelagic plastics and other seaborne persistent synthetic debris: a review of Southern Hemisphere perspectives. In J. M. Coe & D. B. Rogers (Eds.), Marine Debris: Sources, Impacts, and Solutions (pp. 49–66). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8486-1_6
Gundala, R. R., Nawaz, N., R M, H., Boobalan, K., & Gajenderan, V. K. (2022). Does gender moderate the purchase intention of organic foods? Theory of reasoned action. Heliyon, 8(9), e10478 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10478
Guo, Y., Xia, X., Ruan, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., LeBlanc, G. A., & An, L. (2022). Ignored microplastic sources from plastic bottle recycling. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156038
Hee, Y. Y., Weston, K., & Suratman, S. (2022). The effect of storage conditions and washing on microplastic release from food and drink containers. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 32, 100826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100826
Hossain, M. S., Rahman, M. S., Uddin, M. N., Sharifuzzaman, S. M., Chowdhury, S. R., Sarker, S., & Nawaz Chowdhury, M. S. (2020). Microplastic contamination in Penaeid shrimp from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere, 238, 124688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124688
Hu, J., Qin, X., Zhang, J., Zhu, Y., Zeng, W., Lin, Y., & Liu, X. (2021). Polystyrene microplastics disturb maternal-fetal immune balance and cause reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice. Reproductive Toxicology, 106, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.10.002
Huerta Lwanga, E., Mendoza Vega, J., Ku Quej, V., Chi, J. d. l. A., Sanchez del Cid, L., Chi, C., . . . Geissen, V. (2017). Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 14071https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14588-2
Hussain, K. A., Romanova, S., Okur, I., Zhang, D., Kuebler, J., Huang, X., . . . Li, Y. (2023). Assessing the release of microplastics and nanoplastics from plastic containers and reusable food pouches: implications for human health. Environmental Science & Technology, 57(26), 9782–9792. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c01942
Imasha, H. U. E., & Babel, S. (2021). Microplastics contamination in commercial green mussels from selected wet markets in Thailand. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81(3), 449–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-021-00886-4
Kadac-Czapska, K., Knez, E., Gierszewska, M., Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E., & Grembecka, M. (2023). Microplastics derived from food packaging waste—their origin and health risks. Materials, 16(2), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020674
Karami, A., Golieskardi, A., Choo, C. K., Larat, V., Karbalaei, S., & Salamatinia, B. (2018). Microplastic and mesoplastic contamination in canned sardines and sprats. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 1380–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.005
Kedzierski, M., Lechat, B., Sire, O., Le Maguer, G., Le Tilly, V., & Bruzaud, S. (2020). Microplastic contamination of packaged meat: Occurrence and associated risks. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 24, 100489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100489
Kiefer, I., Rathmanner, T., & Kunze, M. (2005). Eating and dieting differences in men and women. The Journal of Men’s Health & Gender, 2(2), 194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmhg.2005.04.010
Kosuth, M., Mason, S. A., & Wattenberg, E. V. (2018). Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE, 13(4), e0194970. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194970
Krapivin, V. F., Varotsos, C. A., & Soldatov, V. Y. (2017). The Earth’s population can reach 14 billion in the 23rd century without significant adverse effects on survivability. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), 885. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/14/8/885
Krasucka, P., Bogusz, A., Baranowska-Wójcik, E., Czech, B., Szwajgier, D., Rek, M., . . . Oleszczuk, P. (2022). Digestion of plastics using in vitro human gastrointestinal tract and their potential to adsorb emerging organic pollutants. Science of The Total Environment, 843, 157108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157108
Kurtuluş, E. M., & Çöl, B. G. (2023). Micro to nano plastics and its link to human health. International Journal of Medical Biochemistry, 6(1), 51–56. https://doi.org/10.14744/ijmb.2022.64326
Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Pérez-Guevara, F., Elizalde-Martínez, I., & Shruti, V. C. (2020). Branded milks — are they immune from microplastics contamination? Science of the Total Environment, 714, 136823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136823
Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Shruti, V. C., Pérez-Guevara, F., & Roy, P. D. (2023a). Microplastic diagnostics in humans: “The 3Ps” progress, problems, and prospects. Science of the Total Environment, 856, 159164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159164
Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Shruti, V. C., Pérez-Guevara, F., Roy, P. D., & Martínez, I. E. (2023b). Consumption of commercially sold dried fish snack “Charales” contaminated with microplastics in Mexico. Environmental Pollution, 332, 121961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121961
Kye, H., Kim, J., Ju, S., Lee, J., Lim, C., & Yoon, Y. (2023). Microplastics in water systems: A review of their impacts on the environment and their potential hazards. Heliyon, 9(3), e14359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14359
Le, V.-R., Nguyen, M.-K., Nguyen, H.-L., Lin, C., Rakib, M. R. J., Thai, V.-A., . . . Idris, A. M. (2023). Organic composts as A vehicle for the entry of microplastics into the environment: a comprehensive review. Science of The Total Environment, 892, 164758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164758
Li, Q., Feng, Z., Zhang, T., Ma, C., & Shi, H. (2020). Microplastics in the commercial seaweed nori. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388, 122060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122060
Li, H., Zhu, L., Ma, M., Wu, H., An, L., & Yang, Z. (2023). Occurrence of microplastics in commercially sold bottled water. Science of the Total Environment, 867, 161553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161553
Liebezeit, G., & Liebezeit, E. (2015). Origin of synthetic particles in honeys. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 65(2), 143–147. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjfns-2015-0025
Liu, Q., Chen, Z., Chen, Y., Yang, F., Yao, W., & Xie, Y. (2021). Microplastics and nanoplastics: Emerging contaminants in food. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 69(36), 10450–10468. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04199
Liu, Q., Chen, Z., Chen, Y., Yang, F., Yao, W., & Xie, Y. (2022). Microplastics contamination in eggs: Detection, occurrence and status. Food Chemistry, 397, 133771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133771
Liu, Z., Sokratian, A., Duda, A. M., Xu, E., Stanhope, C., Fu, A., . . . West, A. B. (2023). Anionic nanoplastic contaminants promote Parkinson’s disease–associated α-synuclein aggregation. Science Advances, 9(46), eadi8716. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi8716
López-Espinoza, A., Martínez Moreno, A. G., Aguilera Cervantes, V. G., de la Torre-Ibarra, C., Cárdenas-Villalvazo, A., Valdés Miramontes, E., . . . Barragán Carmona, M. d. C. (2011). Género, Interacción Social y Consumo de Alimento: “El Efecto Eva.” Revista mexicana de trastornos alimentarios, 2(1), 10–23. https://doi.org/10.22201/fesi.20071523e.2011.1.166
Lorge Rogers, B. (1996). The implications of female household headship for food consumption and nutritional status in the Dominican Republic. World Development, 24(1), 113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(95)00122-S
Luo, Y., Chuah, C., Amin, M. A., Khoshyan, A., Gibson, C. T., Tang, Y., . . . Fang, C. (2022). Assessment of microplastics and nanoplastics released from a chopping board using Raman imaging in combination with three algorithms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 431, 128636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128636
Makhdoumi, P., Naghshbandi, M., Ghaderzadeh, K., Mirzabeigi, M., Yazdanbakhsh, A., & Hossini, H. (2021). Micro-plastic occurrence in bottled vinegar: Qualification, quantification and human risk exposure. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 152, 404–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.06.022
Mariano, S., Tacconi, S., Fidaleo, M., Rossi, M., & Dini, L. (2021). Micro and nanoplastics identification: classic methods and innovative detection techniques. Frontiers in Toxicology, 3, 636640. https://doi.org/10.3389/ftox.2021.636640
Mas, A., Puig, J., Lladoa, N., & Zamora, F. (2002). Sealing and storage position effects on wine evolution. Journal of Food Science, 67(4), 1374–1378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb10292.x
Mason, S. A., Welch, V. G., & Neratko, J. (2018). Synthetic polymer contamination in bottled water. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6, 407. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00407
Mathalon, A., & Hill, P. (2014). Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding Halifax Harbor. Nova Scotia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 81(1), 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.018
Maurizi, L., Simon-Sánchez, L., Vianello, A., Nielsen, A. H., & Vollertsen, J. (2023). Every breath you take: high concentration of breathable microplastics in indoor environments. Preprint available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4524559. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4524559 (Posted: 3 Aug 2023)
Mohsen, M., Lin, C., Abdalla, M., Liu, S., & Yang, H. (2023). Microplastics in canned, salt-dried, and instant sea cucumbers sold for human consumption. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 192, 115040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115040
Monteiro, C. A., Cannon, G., Lawrence, M., Costa Louzada, M. D., & Pereira Machado, P. (2019). Ultra-processed foods, diet quality, and health using the NOVA classification system (p. 48). Rome: FAO.
Mortensen, N. P., Fennell, T. R., & Johnson, L. M. (2021). Unintended human ingestion of nanoplastics and small microplastics through drinking water, beverages, and food sources. NanoImpact, 21, 100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2021.100302
Naji, A., Nuri, M., & Vethaak, A. D. (2018). Microplastics contamination in molluscs from the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Environmental Pollution, 235, 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.046
Pérez-Reverón, R., González-Sálamo, J., Hernández-Sánchez, C., González-Pleiter, M., Hernández-Borges, J., & Díaz-Peña, F. J. (2022). Recycled wastewater as a potential source of microplastics in irrigated soils from an arid-insular territory (Fuerteventura, Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 817, 152830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152830
Pham, D. T., Kim, J., Lee, S.-H., Kim, J., Kim, D., Hong, S., . . . Kwon, J.-H. (2023). Analysis of microplastics in various foods and assessment of aggregate human exposure via food consumption in Korea. Environmental Pollution, 322, 121153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121153
Pickers, S., & Yamada, R. (2022). Estudio de Consciencia de Compra en Piso de Venta. GS1 México and Psyma Latina.
Piehl, S., Leibner, A., Löder, M. G. J., Dris, R., Bogner, C., & Laforsch, C. (2018). Identification and quantification of macro- and microplastics on an agricultural farmland. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 17950. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36172-y
Prata, J. C., Paço, A., Reis, V., da Costa, J. P., Fernandes, A. J. S., da Costa, F. M., . . . Rocha-Santos, T. (2020). Identification of microplastics in white wines capped with polyethylene stoppers using micro-Raman spectroscopy. Food Chemistry, 331, 127323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127323
Ragusa, A., Svelato, A., Santacroce, C., Catalano, P., Notarstefano, V., Carnevali, O., . . . Giorgini, E. (2021). Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environment International, 146, 106274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274
Ranjan, V. P., Joseph, A., & Goel, S. (2021). Microplastics and other harmful substances released from disposable paper cups into hot water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 404, 124118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124118
Renzi, M., & Blašković, A. (2018). Litter & microplastics features in table salts from marine origin: Italian versus Croatian brands. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 135, 62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.065
Reynolds®. (2023). Ideas para sorprender a tu familia. Retrieved August 16, 2023 from http://reynolds.pautacreativatemporales.com.mx/2015/entrada-tips/para-cocinar-chayotes-con-tu-microondas/
Saeed, M. S., Fahd, F., Khan, F., Chen, B., & Sadiq, R. (2023). Human health risk model for microplastic exposure in the Arctic region. Science of the Total Environment, 895, 165150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165150
Samandra, S., Mescall, O. J., Plaisted, K., Symons, B., Xie, S., Ellis, A. V., & Clarke, B. O. (2022). Assessing exposure of the Australian population to microplastics through bottled water consumption. Science of the Total Environment, 837, 155329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155329
Sanchez, J. (2018). Out of home, Out of mind? Understanding food and drink habits. Report. Kantar Worldpanel.
Schymanski, D., Goldbeck, C., Humpf, H.-U., & Fürst, P. (2018). Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Research, 129, 154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.11.011
Senathirajah, K., Attwood, S., Bhagwat, G., Carbery, M., Wilson, S., & Palanisami, T. (2021). Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested — a pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 404, 124004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124004
Shabbir, S., Faheem, M., Ali, N., Kerr, P. G., Wang, L.-F., Kuppusamy, S., & Li, Y. (2020). Periphytic biofilm: An innovative approach for biodegradation of microplastics. Science of the Total Environment, 717, 137064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137064
Shams, M., Alam, I., & Mahbub, M. S. (2021). Plastic pollution during COVID-19: Plastic waste directives and its long-term impact on the environment. Environmental Advances, 5, 100119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100119
Shruti, V. C., Pérez-Guevara, F., Elizalde-Martínez, I., & Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. (2020). First study of its kind on the microplastic contamination of soft drinks, cold tea and energy drinks — future research and environmental considerations. Science of the Total Environment, 726, 138580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138580
Shruti, V. C., Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Pérez-Guevara, F., Roy, P. D., & Elizalde-Martínez, I. (2022). Free, but not microplastic-free, drinking water from outdoor refill kiosks: A challenge and a wake-up call for urban management. Environmental Pollution, 309, 119800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119800
Shruti, V. C., Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Pérez-Guevara, F., Roy, P. D., & Elizalde-Martínez, I. (2023). First evidence of microplastic contamination in ready-to-use packaged food ice cubes. Environmental Pollution, 318, 120905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120905
Tamargo, A., Molinero, N., Reinosa, J. J., Alcolea-Rodriguez, V., Portela, R., Bañares, M. A., . . . Moreno-Arribas, M. V. (2022). PET microplastics affect human gut microbiota communities during simulated gastrointestinal digestion, first evidence of plausible polymer biodegradation during human digestion. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 528. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04489-w
UN. (2016). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. United Nations. https://sdgs.un.org/goals. Accessed 10 Dec 2023
Van Cauwenberghe, L., & Janssen, C. R. (2014). Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environmental Pollution, 193, 65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.010
Varotsos, C. A., & Cracknell, A. P. (2020). Remote sensing letters contribution to the success of the Sustainable Development Goals - UN 2030 agenda. Remote Sensing Letters, 11(8), 715–719. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2020.1753338
Wagoner, J. K. (1983). Toxicity of vinyl chloride and poly(vinyl chloride): A critical review. Environmental Health Perspectives, 52, 61–66. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.835261
Wang, H.-P., Huang, X.-H., Chen, J.-N., Dong, M., Zhang, Y.-Y., & Qin, L. (2023). Pouring hot water through drip bags releases thousands of microplastics into coffee. Food Chemistry, 415, 135717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135717
WHO. (2019). Microplastics in drinking-water. World Health Organization.
Yang, D., Shi, H., Li, L., Li, J., Jabeen, K., & Kolandhasamy, P. (2015). Microplastic pollution in table salts from China. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(22), 13622–13627. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03163
Zakeri, M., Naji, A., Akbarzadeh, A., & Uddin, S. (2020). Microplastic ingestion in important commercial fish in the southern Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 160, 111598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111598
Zhang, J., Wang, L., Trasande, L., & Kannan, K. (2021). Occurrence of polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate microplastics in infant and adult feces. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 8(11), 989–994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00559
Zhang, Q., Liu, L., Jiang, Y., Zhang, Y., Fan, Y., Rao, W., & Qian, X. (2023). Microplastics in infant milk powder. Environmental Pollution, 323, 121225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121225
Acknowledgements
The authors Jasso–Salcedo and Aguirre–Loredo thank CONAHCYT for the support of the program Investigadoras e Investigadores por México.
Funding
This work was supported by the project “Efecto de microplasticos generados durante la desintegración de productos de un solo uso en la germinación de semillas y desarrollo de especies vegetales” funded by FONCYT (COAH–2022–C19–C029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, A. B. J.–S. and R. Y. A.–L.; literature search, A. B. J.–S., C. A. D.–C., C. C. R.–V., E. J. J.–R., and R. Y. A.–L.; data analysis, A. B. J.–S., C. A. D.–C., C. C. R.–V., E. J. J.–R., and R. Y. A.–L.; visualization, A. B. J.–S., C. C. R.–V., and R. Y. A.–L.; supervision, A. B. J.–S. and R. Y. A.–L.; funding acquisition, R. Y. A.–L.; project administration, R. Y. A.–L; writing–original draft preparation, A. B. J.–S., C. A. D.–C., C. C. R.–V., E. J. J.–R., and R. Y. A.–L.; writing–review and editing, A. B. J.–S., C. A. D.–C., C. C. R.–V., E. J. J.–R., and R. Y. A.–L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jasso–Salcedo, A.B., Díaz–Cruz, C.A., Rivera–Vallejo, C.C. et al. Human Consumption of Microplastics via Food Type and Habits: Recent Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 139 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06920-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06920-0