Abstract
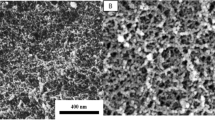
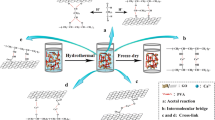
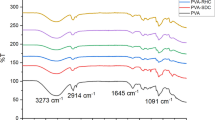
In this study, the influence of oxyranylmethanol over physiochemical properties and Pb (II) adsorption potential of RF aerogels was investigated. Three variants of RF aerogels were catalyzed with 1 mL (RF-1), 2 mL (RF-2), and 3 mL (RF-3) of oxyranylmethanol respectively. The color of the aerogels changed from light orange, dark orange, and reddish brown as the catalyst concentration increased from 1 to 3 mL. Similarly, higher catalyst concentration resulted in higher surface area, pore volume, and porosity; however, the pore size and density decreased. The best morphological and structural properties were indicated by the sample (RF-3) that was catalyzed with 3 mL of oxyranylmethanol with surface area of 290 m2/g, pore volume of 0.7 cm3/g, pore size of 4.8 nm, and density of 90 mg/cm3 respectively. The synthesized oxyranylmethanol catalyzed RF aerogels were investigated for Pb (II) adsorption from synthetic solutions. As per results, RF-3 indicated highest removal % than RF-2 and RF-1 with maximum adsorption capacity (Qm) of 210 mg/g. On the other hand, RF-2 indicated second highest removal with Qm of 153 mg/g followed by RF-1 with Qm of 112 mg/g respectively. When compared with 15 relevant studies that used other agents as catalysts/functionalizing agents for aerogel synthesis, RF-3 indicated the second highest maximum adsorption capacity (Qm). Overall, the present investigation confirmed that the higher catalyst concentration (oxyranylmethanol) in RF aerogel promotes higher degree of polymerization between R and F; hence, results in lower density, higher surface area, higher pore volume, smaller pore size, and enhanced Pb (II) adsorption from synthetic wastewater.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data and Code Availability
The data presented in this manuscript is available with the corresponding author and can be provided on reasonable request.
References
Aguado, J., Arsuaga, J. M., Arencibia, A., Lindo, N., & Gascón, V. (2009). Aqueous heavy metals removal by adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.080
Akhter, F., Ahmed, S., Ahmed, J., Ahsan, M. J., Arain, H. J., & Lakhmir, M. A. (2023). Evaluating Pb (II) adsorption performance by amine-modified resorcinol formaldehyde aerogel and organically modified silica aerogel: Comparative study of adsorption, synthesis, characterization, and isotherms. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2023, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13399-023-04845-Y
Akhter, F., Anees-u-Rehman, H., Ahmed, J., Ahsan, M. J., & Arain, H. J. (2024). Highly enhanced Pb(II) removal by mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane (MPTMS) surface-modified silica aerogel: Synthesis, characterization and isotherm studies. Physical Chemistry Research, 12(1), 219–227. https://doi.org/10.22036/PCR.2023.401363.2353
Akhter, F., Khan, W., & Jamali, A. R. (2024). Efficient lead(II) adsorption onto mesoporous silica aerogels synthesized via green method, organic solvents, and modified aging. Physical Chemistry Research, 12(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.22036/PCR.2023.374387.2246
Bakhori, N. M., Ismail, Z., Hassan, M. Z., & Dolah, R. (2023). Emerging trends in nanotechnology: Aerogel-based materials for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials, 13(6), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO13061063
Behzadi, A., Hashemi Motlagh, G., Rezvani Ghomi, E., Neisiany, R. E., Jafari, I., Chinnappan, A., et al. (2022). Synthesis and characterization of modified resorcinol formaldehyde aerogel as a novel absorbent to remove oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline antibiotics from wastewater. Polymer Bulletin, 79(8), 6309–6341. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00289-021-03812-9//7
Deniz, S., Tasci, N., Yetimoglu, E. K., & Kahraman, M. V. (2017). New thiamine functionalized silica microparticles as a sorbent for the removal of lead, mercury and cadmium ions from aqueous media. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 82(2). https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC160816098D
Fan, H. T., Sun, X. T., Zhang, Z. G., & Li, W. X. (2014). Selective removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution by an ion-imprinted silica sorbent functionalized with chelating N-donor atoms. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 59(6), 2106–2114. https://doi.org/10.1021/JE500328T
Gao, C., Dong, Z., Hao, X., Yao, Y., & Guo, S. (2020). Preparation of reduced graphene oxide aerogel and its adsorption for Pb(II). ACS Omega, 5(17), 9903–9911. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00183
Ghoul, M., Bacquet, M., & Morcellet, M. (2003). Uptake of heavy metals from synthetic aqueous solutions using modified PEI—silica gels. Water Research, 37(4), 729–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00410-4
Huang, X., Wang, L., Chen, J., Jiang, C., Wu, S., & Wang, H. (2020). Effective removal of heavy metals with amino-functionalized silica gel in tea polyphenol extracts. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 14(4), 2134–2144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00460-x
Joshi, S., & Srivastava, R. K. (2019). Adsorptive removal of lead (Pb), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni) and mercury (Hg) ions from water using chitosan silica gel composite. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7777-5
Kushwaha, A. K., Gupta, N., & Chattopadhyaya, M. C. (2017). Adsorption behavior of lead onto a new class of functionalized silica gel. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.06.010
Leventis, N. (2011). Interpenetrating organic/inorganic networks of resorcinol-formaldehyde/metal oxide aerogels. In Aerogels Handbook (pp. 287–313). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7589-8_14
Pranudta, A., El-Moselhy, M. M., Kamal, S. M., Chanlek, N., Nguyen, T. T., & Padungthon, S. (2021). Silica gel modified with a novel sulfur-containing organic ligand (2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-3,3-dimercapto acrylonitrile) for enhance Hg and Pb removal. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2021.100110
Radi, S., ell Massaoudi, M., Bacquet, M., Degoutin, S., Adarsh, N. N., Robeyns, K., & Garcia, Y. (2017). A novel environment-friendly hybrid material based on a modified silica gel with a bispyrazole derivative for the removal of ZnII, PbII, CdII and CuII traces from aqueous solutions. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 4(11). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7qi00322f
Schwan, M., & Ratke, L. (2013). Flexibilisation of resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1(43), 13462–13468. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13172f
Shajesh, P., Smitha, S., Aravind, P. R., & Warrier, K. G. K. (2009). Effect of 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane precursor on the properties of ambient pressure dried silica aerogels. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 50(3), 353–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-1926-1
Sunaja Devi, K. R., Prasanna, V., D’Sa, F., Shetty, K. R., Miranda, J. R., Pinheiro, D., & Shanbhag, G. V. (2020). Response surface optimization and process design for glycidol synthesis using potassium modified rice husk silica. Materials Today: Proceedings, 41, 506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.234
Wang, X., Lu, L. L., Yu, Z. L., Xu, X. W., Zheng, Y. R., & Yu, S. H. (2015). Scalable template synthesis of resorcinol-formaldehyde/graphene oxide composite aerogels with tunable densities and mechanical properties. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 54(8), 2397–2401. https://doi.org/10.1002/ANIE.201410668
Xiang, Y., Dai, D., Bai, W., Xu, L., & Liu, G. (2023). Layered aerogel embedded with thiourea-resorcinol-formaldehyde resin for efficient adsorption of Au(III). Separation and Purification Technology, 314, 123528. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2023.123528
Yang, M., Cai, X., Chen, X., Guan, S., Yan, K., An, L., & Xing, J. (2023). Shape recovery aerogels from wheat straw-based cellulose nanofibrils for dynamic removal of Cr (VI). Cellulose, 30(9), 5777–5793. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-023-05228-2/TABLES/4
Zhang, Y., Qu, R., Sun, C., Chen, H., Wang, C., Ji, C., et al. (2009). Comparison of synthesis of chelating resin silica-gel-supported diethylenetriamine and its removal properties for transition metal ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.070
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Faheem Akhter, Abdul Rauf Jamali, Jawad Ahmed: introduction, materials and methods; Faheem Akhter, Haris Jawad Arain, Muhammad Junaid Ahsan, Muhammad Naeem Akhtar: results and discussion, discussion, conclusion.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhter, F., Jamali, A.R., Ahmed, J. et al. Influence of Oxyranylmethanol as a Catalytic Cross-linking Agent over Physiochemical Properties and Pb (II) Adsorption Performance of Resorcinol Formaldehyde Aerogels: a Comparative Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 769 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06777-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06777-9