Abstract
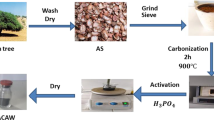
In this study, construction and demolition waste (CDW) were selected as raw material to prepare chabazite by alkali fusion hydrothermal method. The obtained chabazite was utilized in adsorbing methylene blue from high-salt wastewater. The physical and chemical properties of the chabazite were characterized by XRD, FTIR, and N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms. The synthesized chabazite possessed typical phase structure and functional groups. Its specific surface area (111.97 m2/g) and total pore volume (0.488 cm3/g) increased by about 8.26 and 6.78 times than that of CDW, respectively. The adsorption capacity on the chabazite at c(NaCl) = 7000 mg/L reduced to 77.28% of that at c(NaCl) = 0 mg/L, indicating that salinity had a negative effect on the adsorption. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic model could describe the adsorption process of methylene blue on the synthesized chabazite. The saturated adsorption capacity of chabazite for methylene blue reached up to 80.61 mg/g under c(NaCl) = 5000 mg/L at 25 °C, which was about 4 times that of CDW, showing the remarkable adsorption performance at high salinity. The adsorption process at high-salt condition was spontaneous, exothermic, and tended to be ordered. This study indicates that it is feasible to prepare chabazite from CDW, and the obtained chabazite is a novel and effective adsorbent in treating high-salt wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelrahman, E. A., El-Reash, Y. G. A., Youssef, H. M., Kotp, Y. H., & Hegazey, R. M. (2021). Utilization of rice husk and waste aluminum cans for the synthesis of some nanosized zeolite, zeolite/zeolite, and geopolymer/zeolite products for the efficient removal of Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous media. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 401, 123813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123813
Aguiar, J. E., Bezerra, B. T. C., Siqueira, A. C. A., Barrera, D., Sapag, K., Azevedo, D. C. S., Lucena, S. M. P., & Silva, I. J., Jr. (2014). Improvement in the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solutions: A comparative study using aluminium pillared clays and activated carbon. Separation Science and Technology, 49(5), 741–751. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.862720
Ahmad, A., Khan, N., Giri, B. S., Chowdhary, P., & Chaturvedi, P. (2020). Removal of methylene blue dye using rice husk, cow dung and sludge biochar: Characterization, application, and kinetic studies. Bioresource Technology, 306, 123202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123202
Akter, T., Bañuelos, J. L., Andrade, D., Bañuelos, D. I., & Saupe, G. B. (2022). Rapid adsorption mechanism of methylene blue onto a porous mixed Ti-Nb oxide. Materials Chemistry Horizons, 1(1), 49–67. https://doi.org/10.22128/MCH.2022.555.1006
Alver, E., & Metin, A. Ü. (2012). Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200-202, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.038
Aysan, H., Edebali, S., Ozdemir, C., Karakaya, M. C., & Karakaya, N. (2016). Use of chabazite, a naturally abundant zeolite, for the investigation of the adsorption kinetics and mechanism of methylene blue dye. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 235, 78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.08.007
Bedin, K. C., Martins, A. C., Cazetta, A. L., Pezoti, O., & Almeida, V. C. (2016). KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for methylene blue removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 286, 476–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.099
Bu, J., Yuan, L., Zhang, N., Liu, D., Meng, Y., & Peng, X. (2020). High-efficiency adsorption of methylene blue dye from wastewater by a thiosemicarbazide functionalized graphene oxide composite. Diamond and Related Materials, 101, 107604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2019.107604
Chen, B., Cao, Y., Zhao, H., Long, F., Feng, X., Li, J., & Pan, X. (2020). A novel Fe3+-stabilized magnetic polydopamine composite for enhanced selective adsorption and separation of methylene blue from complex wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 392, 122263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122263
Chen, X., Zhang, P., Wang, Y., Peng, W., Ren, Z., Li, Y., Chu, B., & Zhu, Q. (2023). Research progress on synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash and environmental applications. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 17(12), 149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-023-1749-2
Chen, Y., He, H., Liu, H., Li, H., Zeng, G., Xia, X., & Yang, C. (2018). Effect of salinity on removal performance and activated sludge characteristics in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresource Technology, 249, 890–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.092
Deniz, F., & Ersanli, E. T. (2022). A novel biowaste-based biosorbent material for effective purification of methylene blue from water environment. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 24(12), 1243–1250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.2025039
Ebadollahzadeh, H., & Zabihi, M. (2020). Competitive adsorption of methylene blue and Pb(II) ions on the nano-magnetic activated carbon and alumina. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 248, 122893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122893
Eren, M. Ş. A., Hasan Arslanoğlu, H., & Çiftçi, H. (2020). Production of microporous Cu-doped BTC (Cu-BTC) metal-organic framework composite materials, superior adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue (Basic Blue 9). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8, 104247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104247
Feng, Y., Yang, F., Wang, Y., Ma, L., Wu, Y., Kerr, P. G., & Yang, L. (2011). Basic dye adsorption onto an agro-based waste material - Sesame hull (Sesamum indicum L.). Bioresource Technology, 102, 10280–10285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.090
Ganguly, P., Sarkhel, R., & Das, P. (2020). Synthesis of pyrolyzed biochar and its application for dye removal: Batch, kinetic and isotherm with linear and non-linear mathematical analysis. Surfaces and Interfaces, 20, 100616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100616
Gao, J., Lin, Q., Yang, T., Bao, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). Preparation and characterization of ZSM-5 molecular sieve using coal gangue as a raw material via solvent-free method: Adsorption performance tests for heavy metal ions and methylene blue. Chemosphere, 139741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139741
Gelves, J. F., Gallego, G. S., & Marquez, M. A. (2016). Mineralogical characterization of zeolites present on basaltic rocks from Combia geological formation, La Pintada (Colombia). Microporous and Mezoporous Materials, 235, 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.07.035
Ghasemi, M., Khataee, A., Gholami, P., & Soltani, R. D. C. (2019). Template-free microspheres decorated with Cu-Fe-NLDH for catalytic removal of gentamicin in heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.07.007
Gong, H., Liu, W., Liu, L., Goyal, N., Xiao, P., Li, G., Wei, Y., & Du, T. (2019). In-situ synthesis of an excellent CO2 capture material chabazite. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 103, 160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.07.006
González-Crisostomo, J. C., López-Juárez, R., Yocupicio-Gaxiola, R. I., Villanueva, E., Zavala-Flores, E., & Petranovskii, V. (2022). Chabazite synthesis and its exchange with Ti, Zn, Cu, Ag and Au for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031730
Han, R., Zhang, J., Han, P., Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., & Tang, M. (2009). Study of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters about methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 145, 496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.003
He, H., Chen, Y., Li, X., Cheng, Y., Yang, C., & Zeng, G. (2017). Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: A review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 119, 520–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.10.007
Hor, K. Y., Chee, J. M. C., Chong, M. N., Jin, B., Saint, C., Poh, P. E., & Aryal, R. (2016). Evaluation of physicochemical methods in enhancing the adsorption performance of natural zeolite as low-cost adsorbent of methylene blue dye from wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 13, 197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.056
Hosseini, J., Zare, E. N., & Ajloo, D. (2019). Experimental and theoretical calculation investigation on effecyive adsorption of lead(II) onto poly (aniline-co-pyrrole) nanospheres. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 111789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111789
Hu, Y., Guo, T., Ye, X., Li, Q., Guo, M., Liu, H., & Wu, Z. (2013). Dye adsorption by resins: Effect of ionic strength on hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 228, 392–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.116
Kassim, T. A., Simoneit, B. R. T., & Williamson, K. J. (2005). Recycling solid wastes as road construction materials: An environmentally sustainable approach. Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, 5, 59–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/b98264
Kong, L. J., & Ma, B. (2020). Evaluation of environmental impact of construction waste disposal based on fuzzy set analysis. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 19, 100877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100877
Le, T. M., Nguyen, T. N., Dat, N. D., & Tran, N. T. (2023). An innovative approach based on microwave radiation for synthesis of zeolite 4A and porosity enhancement. Results in Engineering, 19, 101235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101235
Li, Z., Guo, H., Zhang, L., Liang, D., Zhu, Q., Liu, X., & Zhou, H. (2022). Time-series monitoring of dust-proof nets covering urban construction waste by multispectral images in Zhengzhou, China. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153805
Li, Z., Liu, D., Huang, W., Wei, X., & Huang, W. (2020). Biochar supported CuO composites used as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator for highly saline organic wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 721, 137764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137764
Liang, J., Li, J., Li, X., Liu, K., Wu, L., & Shan, G. (2020). The sorption behavior of CHA-type zeolite for removing radioactive strontium from aqueous solutions. Separation and Purification Technology, 230, 115874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115874
Liu, J. Y., Chen, F. J., Li, C. Z., Lu, L. Z., Hu, C. W., Wei, Y., Raymer, P., & Huang, Q. G. (2019). Characterization and utilization of industrial microbial waste as novel adsorbent to remove single and mixed dyes from water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, 552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.136
Liu, X. J., Li, M. F., Ma, J. F., Bian, J., & Peng, F. (2022). Chitosan crosslinked composite based on corncob lignin biochar to adsorb methylene blue: Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 642, 128621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128621
Liu, X. J., Li, M. F., & Singh, S. K. (2021). Manganese-modified lignin biochar as adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 12, 1434–1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.076
Mamedova, G. A., & Aliyew, T. A. (2020). Synthesis and research of the chabazite-type zeolite on the basis of natural mineral of nakhchivan. Journal of Chemistry and Technologies, 28(1), 42–50. https://doi.org/10.15421/082006
Mehdizadeh, A., Moghadam, P. N., Ehsanimehr, S., & Fareghi, A. R. (2022). Preparation of a new magnetic nanocomposite for the removal of dye pollutions from aqueous solutions: Synthesis and characterization. Materials Chemistry Horizons, 1(1), 23–34. https://doi.org/10.22128/MCH.2022.544.1003
Ndlovu, N. Z. N., Ameh, A. E., Petrik, L. F., & Ojumu, T. V. (2023). Synthesis and characterisation of pure phase ZSM-5 and sodalite zeolites from coal fly ash. Materials Today Communications, 34, 105436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105436
Nyankson, E., Mensah, R. Q., Kumafle, L., Gblerkpor, W. N., Aboagye, S. O., Asimeng, B. O., & Tiburu, E. K. (2020). Dual application of natural clay material for decolorization and adsorption of methylene blue dye. Cogent Chemistry, 6(1), 1788291. https://doi.org/10.1080/23312009.2020.1788291
Osias, J. M., Chen, Y. C., Lin, D. Y., Shih, Y. C., Caparanga, A. R., & Chen, B. H. (2019). Degradation of methylene blue utilizing cobalt-impregnated zeolite beta via sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation process. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 344(1), 012041. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/344/1/012041
Raghavendra, Y., Bera, S., Spinivasan, M. P., & Rangarajan, S. (2021). Mechanism of formation of chabazite-K by fusion of fly ash with KOH followed by hydrothermal reaction and its Cs+ sorption properties. JOM, 73, 2111–2121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04594-1
Sakızcı, M., & Özer, M. (2019). The characterization and methane adsorption of Ag-, Cu-, Fe-, and H-exchanged chabazite-rich tuff from Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 16616–16627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04996-4
Silva, E. O. D., Santos, V. D. D., Araujo, E. B. D., Guterres, F. P., Zottis, R., Flores, W. H., & Almeida, A. R. F. D. (2020). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by ryegrass Straw. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17, 3723–3740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02718-9
Song, X., Zhang, Y., Cui, X., Liu, F., & Zhao, H. (2021). Preparation and characterization of chabazite from construction waste and application as an adsorbent for methylene blue. Adsorption Science & Technology, 9994079. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9994079
Srivastava, V., Zare, E. N., Pooyan Makvandi, P., Zheng, X., Iftekhar, S., Wu, A., Padil, V. V. T., Mokhtari, B., Varma, R. S., Tay, F. R., & Sillanpaa, M. (2020). Cytotoxic aquatic pollutants and their removal by nanocomposite-based sorbents. Chemosphere, 258, 127324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127324
Sun, Y., Wang, T., Han, C., Lv, X., Bai, L., Sun, X., & Zhang, P. (2022). Facile synthesis of Fe-modified lignin-based biochar for ultra-fast adsorption of methylene blue: Selective adsorption and mechanism studies. Bioresource Technology, 344, 126186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126186
Supelano, G. I., Gómez Cuaspud, J. A., Moreno-Aldana, L. C., Ortiz, C., Trujillo, C. A., Palacio, C. A., Parra Vargas, C. A., & Mejía Gómez, J. A. (2020). Synthesis of magnetic zeolites from recycled fly ash for adsorption of methylene blue. Fuel, 263, 116800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116800
Uddin, M. J., Ampiaw, R. E., & Lee, W. (2021). Adsorptive removal of dyes from wastewater using a metal-organic framework: A review. Chemosphere, 284, 131314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131314
Wang, J., Ma, J., & Sun, Y. (2022). Adsorption of methylene blue by coal-based activated carbon in high-salt wastewater. Water, 14(21), 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213576
Wu, Z., Zhong, H., Yuan, X., Wang, H., Wang, L., Chen, X., Zeng, G., & Wu, Y. (2014). Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by rhamnolipid-functionalized graphene oxide from wastewater. Water Research, 67, 330–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.026
Yin, X., Zeng, L., Wang, C., Li, Z., Zhao, M., & Yang, S. (2019). A time- and cost-effective synthesis of CHA zeolite with small size using ultrasonic-assisted method. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 58, 104679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104679
Yu, H., Gu, L., Chen, L. U., Wen, H., Zhang, D., & Tao, H. (2020). Activation of grapefruit derived biochar by its peel extracts and its performance for tetracycline removal. Bioresource Technology, 316, 123971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.12397
Zare, E. N., Lakouraj, M. M., & Kasirian, N. (2018). Development of effective nano-biosorbent based on poly m-phenylenediamine grafted dextrin for removal of Pb (II) and methylene blue from water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 201(1), 539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.091
Zeng, Z., Ye, S., Wu, H., Xiao, R., Zeng, G., Liang, J., Zhang, C., Yu, J., Fang, Y., & Song, B. (2019). Research on the sustainable efficacy of g-MoS2 decorated biochar nanocomposites for removing tetracycline hydrochloride from antibiotic-polluted aqueous solution. Science of the Total Environment, 648, 206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.108
Zhang, H., Song, X., Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Zhao, H., Hu, J., & Zhao, J. (2022a). Performance and mechanism of sycamore flock based biochar in removing oxytetracycline hydrochloride. Bioresource Technology, 350, 126884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126884
Zhang, J., Deng, F., Yin, X., Song, X., Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Sun, R., & Zhang, L. (2022b). Adsorption of oxytetracycline hydrochloride and chloramphenicol in single and binary component systems by loofah sponge-based biochar. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 233, 427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05891-4
Zhao, Y. P., Guo, D. X., Li, S. F., Cao, J. P., & Wei, X. Y. (2020). Removal of methylene blue by NaX zeolites synthesized from coal gasification fly ash using an alkali fusion-hydrothermal method. Desalination and Water Treatment, 185, 355–363. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25424
Zheng, X., He, X., Peng, H., Wen, J., & Lv, S. (2021). Efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin using Ga2S3/S-modified biochar via the high-temperature sulfurization. Bioresource Technology, 334, 125238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125238
Zhu, B., Li, Y., Yan, Z., Yang, Z., Wu, X., Gui, T., Li, Y., Zhang, F., Chen, X., & Kita, H. (2022). Formation process of organic template-free chabazite zeolite membrane and its separation perfofmance of water-rich mixtures. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 341, 112085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.112085
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the “Science and Technology Key Project Foundation of Henan Provincial Education Department” (22A610001), the “Key Science and Technology Program of Henan Province” (232102321136), the “Innovative Funds Plan of Henan University of Technology” (2022ZKCJ09), the “Henan University of Technology” (2018BS046), and the “Student’s Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Henan Province” (202210463046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xue Song: Resources, Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing review and editing. Yi Ding: Validation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization. Yingming Zhang: Data curation, Formal analysis. Fangfang Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing review and editing. Feiyue Wang: Data curation, Formal analysis, Supervision. Yongde Liu: Conceptualization, Resources, Data curation, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Ding, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Adsorption of Methylene Blue from High-Salt Wastewater by Construction and Demolition Waste-Based Chabazite. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 607 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06625-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06625-w