Abstract
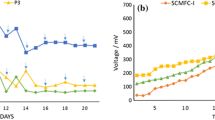
The effects of different oxytetracycline (OTC) acclimation strategies on the electricity generation performance of microbial fuel cells (MFCs), the microbial community composition, and functional groups of biofilms were investigated by using low-dose stepwise acclimation (L-MFC) and high-dose direct acclimation (H-MFC). The results showed that H-MFC could effectively shorten the acclimation period by 10 days while achieving 94.93% OTC removal efficiency, which was 1.31% higher than that of L-MFC. Based on a higher response current and lower internal resistance, the maximum power output of the L-MFC (690.28 mV) was better than that of the H-MFC (670.26 mV). High-throughput sequencing results showed that the species diversity and richness of the bioanode in L-MFC were higher, and the main dominant groups were Geobacter (26.48%), Aquamicrobium (10.31%), and other electroactive microorganisms involved in extracellular electron transfer, while Cupriavidus (21.46%), Rhodopseudomonas (10.38%), Acidovorax (7.62%), and other OTC degradation groups were further enriched in H-MFC. The KEGG manifested that the biological process was mainly controlled by genes of the metabolism pathway. Among them, except for the up-regulation of xenobiotics biometabolism and metabolism functional genes in H-MFC by 0.46%, the other metabolism-related genes were highly expressed in L-MFC. Different OTC acclimation strategies have an effect on the electricity generation, microbial structure, and function of MFCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files.
References
Ben, W., Zhu, B., Yuan, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., & Qiang, Z. (2018). Occurrence, removal and risk of organic micropollutants in wastewater treatment plants across China: Comparison of wastewater treatment processes. Water Research, 130, 38–46.
Cai, C., Huang, X., & Dai, X. (2022). Differential variations of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes between treatment units in centralized sewage sludge treatment plants. Water Research, 222, 118893.
Chatterjee, P., Dessì, P., Kokko, M., Lakaniemi, A., & Lens, P. (2019). Selective enrichment of biocatalysts for bioelectrochemical systems: A critical review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 109, 10–23.
Chen, J., Hu, Y., Huang, W., Liu, Y., Tang, M., Zhang, L., & Sun, J. (2018). Biodegradation of oxytetracycline and electricity generation in microbial fuel cell with in situ dual graphene modified bioelectrode. Bioresource Technol., 270, 482–488.
Cui, H., Zhu, D., Ding, L., Wang, Y., Su, J., Duan, G., & Zhu, Y. (2023). Co-occurrence of genes for antibiotic resistance and arsenic biotransformation in paddy soils. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 125, 701–711.
Danner, M., Robertson, A., Behrends, V., & Reiss, J. (2019). Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Science of the Total Environment, 664, 793–804.
Deng, Q., Su, C., Chen, Z., Gong, T., Lu, X., Chen, Z., & Lin, X. (2021). Effect of hydraulic retention time on the denitrification performance and metabolic mechanism of a multi-chambered bio-electrochemical system. Journal of Environmental Management, 299, 113575.
Deng, Q., Su, C., Lu, X., Chen, W., Guan, X., Chen, S., & Chen, M. (2020). Performance and functional microbial communities of denitrification process of a novel MFC-granular sludge coupling system. Bioresource Technology, 306, 123173.
Fang, H., Cai, L., Yu, Y., & Zhang, T. (2013). Metagenomic analysis reveals the prevalence of biodegradation genes for organic pollutants in activated sludge. Bioresource Technology, 129, 209–218.
He, C., Ding, R., Chen, J., Li, W., Li, Q., & Mu, Y. (2020). Interactions between nanoscale zero valent iron and extracellular polymeric substances of anaerobic sludge. Water Research, 178, 115817.
Huang, X., Feng, Y., Hu, C., Xiao, X., Yu, D., & Zou, X. (2016). Mechanistic model for interpreting the toxic effects of sulfonamides on nitrification. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 305, 123–129.
Karatay, S., & Dönmez, G. (2014). An economical phenol bioremoval method using Aspergillus versicolor and agricultural wastes as a carbon source. Ecological Engineering, 73, 224–228.
Li, W., Quan, X., Chen, L., & Zheng, Y. (2020). Application of slow-release carbon sources embedded in polymer for stable and extended power generation in microbial fuel cells. Chemosphere, 244, 125515.
Liu, C., Chen, J., Shan, X., Yang, Y., Song, L., Teng, Y., & Chen, H. (2023). Meta-analysis addressing the characterization and risk identification of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global groundwater. Science of the Total Environment, 860, 160513.
Long, S., Zhao, L., Chen, J., Kim, J., Huang, C., & Pavlostathis, S. G. (2021). Tetracycline inhibition and transformation in microbial fuel cell systems: Performance, transformation intermediates, and microbial community structure. Bioresource Technology, 322, 124534.
Luo, J., Xu, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Jiang, X., & Shen, J. (2021). Coupled biodegradation of p-nitrophenol and p-aminophenol in bioelectrochemical system: Mechanism and microbial functional diversity. Journal of Environmental Sciences (china), 108, 134–144.
Qin, S., Hou, Y., Yuan, G., Yu, Z., Tu, L., Yan, Y., Chen, S., Sun, J., Lan, D., & Wang, S. (2020). Different refractory organic substances degradation and microbial community shift in the single-chamber bio-photoelectrochemical system. Bioresource Technology, 307, 123176.
Raju, D., Nagarajan, A., Pandit, S., Nag, M., Lahiri, D., & Upadhye, V. (2022). Effect of bacterial quorum sensing and mechanism of antimicrobial resistance. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 43, 102409.
Shen, J., Du, Z., Li, J., & Cheng, F. (2020). Co-metabolism for enhanced phenol degradation and bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cell. Bioelectrochemistry, 134, 107527.
Slate, A., Whitehead, K., Brownson, D., & Banks, C. (2019). Microbial fuel cells: An overview of current technology. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 101, 60–81.
Sogani, M., Pankan, A., Dongre, A., Yunus, K., & Fisher, A. (2021). Augmenting the biodegradation of recalcitrant ethinylestradiol using Rhodopseudomonas palustris in a hybrid photo-assisted microbial fuel cell with enhanced bio-hydrogen production. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408, 124421.
Song, Z., Zhang, X., Ngo, H., Guo, W., Wen, H., & Li, C. (2019). Occurrence, fate and health risk assessment of 10 common antibiotics in two drinking water plants with different treatment processes. Science of the Total Environment, 674, 316–326.
Sun, D., Cheng, S., Wang, A., Li, F., Logan, B. E., & Cen, K. (2015). Temporal-spatial changes in viabilities and electrochemical properties of anode biofilms. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 5227–5235.
Wang, L., You, L., Zhang, J., Yang, T., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, P., Wu, S., Zhao, F., & Ma, J. (2018a). Biodegradation of sulfadiazine in microbial fuel cells: Reaction mechanism, biotoxicity removal and the correlation with reactor microbes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 360, 402–411.
Wang, Z., Zhang, B., Jiang, Y., Li, Y., & He, C. (2018b). Spontaneous thallium (I) oxidation with electricity generation in single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Applied Energy, 209, 33–42.
Wu, X., Chen, Z., Lv, Z., Zhang, L., Xin, F., Li, Y., Liu, G., Dong, W., Wei, P., & Jia, H. (2021). Enhanced chloramphenicol-degrading biofilm formation in microbial fuel cells through a novel synchronous acclimation strategy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 317, 128376.
Xue, W., Li, F., & Zhou, Q. (2019). Degradation mechanisms of sulfamethoxazole and its induction of bacterial community changes and antibiotic resistance genes in a microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 289, 121632.
Yan, W., Guo, Y., Xiao, Y., Wang, S., Ding, R., Jiang, J., Gang, H., Wang, H., Yang, J., & Zhao, F. (2018). The changes of bacterial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in microbial fuel cells during long-term oxytetracycline processing. Water Research, 142, 105–114.
Yan, W., Wang, S., Ding, R., Tian, X., Bai, R., Gang, H., Yan, W., Xiao, Y., & Zhao, F. (2019). Long-term operation of electroactive biofilms for enhanced ciprofloxacin removal capacity and anti-shock capabilities. Bioresource Technology, 275, 192–199.
Zhang, B., Cheng, Y., Shi, J., Xuan, X., Zhu, Y., Nan, X., Xia, J., & Borthwick, A. (2019). Insights into interactions between vanadium (V) bio-reduction and pentachlorophenol dechlorination in synthetic groundwater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 375, 121965.
Zhang, J., Chen, R., Du, C., Dong, S., & Sun, J. (2021a). Effects of continuous sulfamonomethoxine shock on the power generation performance and microbial community structure of MFCs under seasonal temperature variation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 167, 107909.
Zhang, J., Chu, L., Wang, Z., Guo, W., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Chen, R., Dong, S., & Sun, J. (2020). Dynamic evolution of electrochemical and biological features in microbial fuel cells upon chronic exposure to increasing oxytetracycline dosage. Bioelectrochemistry, 136, 107623.
Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Chu, L., Chen, R., Zhang, C., Toan, S., Bagley, D. M., Sun, J., Dong, S., & Fan, M. (2021b). Unified photoelectrocatalytic microbial fuel cell harnessing 3D binder-free photocathode for simultaneous power generation and dual pollutant removal. Journal of Power Sources, 481, 229133.
Zhang, Q., Ying, G., Pan, C., Liu, Y., & Zhao, J. (2015). Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 6772–6782.
Zheng, J., Wang, S., Zhou, A., Zhao, B., Dong, J., Zhao, X., Li, P., & Yue, X. (2020). Efficient elimination of sulfadiazine in an anaerobic denitrifying circumstance: Biodegradation characteristics, biotoxicity removal and microbial community analysis. Chemosphere, 252, 126472.
Zhuang, M., Achmon, Y., Cao, Y., Liang, X., Chen, L., Wang, H., Siame, B., & Leung, K. (2021). Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environmental Pollution, 285, 117402.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities of Henan Province (22A610011), the Special Fund for High-level Talents of Sanmenxia Polytechnic (SZYGCCRC-2021–004), and the Key Research Project of Sanmenxia City (2022002097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Huang, B. et al. Effects of Different Oxytetracycline Acclimation Strategies on Microbial Community Composition and Functional Characteristics of MFC. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 603 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06619-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06619-8