Abstract
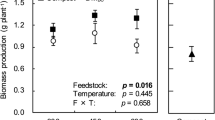
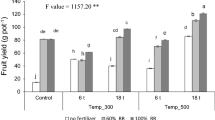
Alfalfa is a fodder food widely demanded by breeders; their classic cultural practice is characterized by the disrespect for the environment and the destruction of the soil. Several sustainable and environmentally friendly fertilizer alternatives, including biochar, have already been proposed. Numerous studies have investigated the effects of biochar on various physiological and productivity parameters of plants. However, there is a notable scarcity of research comparing the impacts of biochar derived from multiple biomasses at different doses, with and without other organic fertilizers with conventional fertilizers. To accurately characterize our substrates, we conducted physicochemical and morphological analyses of biochar, biocompost, manure, and soils. Subsequently, a pot study was conducted to assess the impact of biochar from various sources and doses on alfalfa’s productivity and physiological parameters. To this end, the various productivity and photosynthesis parameters were continuously monitored during this study. These tests showed biochars were very different in terms of chemical and organic compositions depending on the origin of the starting biomass. The combination of biochar sewage sludge and argan shell displayed exceptionally high levels of heavy metal content, with iron (Fe) exceeding 7000 mg/L. Biochar obtained by the pyrolysis of argan shells has on its surface just the basic elements C, Ca, and K with O which was barely detected on the surface. The biocompost exhibited a nitrogen content of less than 0.9% and demonstrated elevated levels of heavy metals, indicating its inferior quality. The comparison of the two agricultural practices under investigation demonstrated that conventional methods utilizing manure, with or without chemical fertilizers, remain the most effective approach for alfalfa productivity. However, certain types of biochar exhibited comparable levels of productivity, specifically the biochar derived from industrial agro-food sewage sludge. Notably, when this biochar was combined with biocompost at a 6% concentration for both of them, it resulted in an initial harvest with a fresh weight of approximately 17 g. Conversely, some biochar, such as the one composed of 6% tomato waste mixed with 3 and 6% biocompost, completely hindered germination at specific doses. Additionally, our study revealed that photosynthesis primarily relies on the plant’s physiological response at a specific time, rather than being influenced by growing conditions or substrate composition. In conclusion, this study has demonstrated that each treatment carries its own set of advantages and disadvantages across one or more productivity parameters. The optimal selection among these treatments hinges solely on the intended purpose and sought objectives. Despite all these conclusions, a long-term field study can approve or abrogate these results.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abdel-Fattah, T. M., Mahmoud, M. E., Ahmed, S. B., Huff, M. D., Lee, J. W., & Kumar, S. (2015). Biochar from woody biomass for removing metal contaminants and carbon sequestration. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 22, 103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.06.030
Agegnehu, G., Bass, A. M., Nelson, P. N., & Bird, M. I. (2016). Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar-compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Science of the Total Environment, 543, 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.054
Al-Lawati, A., Al-Waihibi, H., Al-Rawahy, S. A., Al-Dhuhli, H., Al-Rashdi, M., & Al-Habsi, S. S. (2010). In A. Mushtaque, S. A. Al-Rawahi, & N. Hussain (Eds.), Production and water-use efficiency of alfalfa under different water quantity and quality levels (pp. 61–65). Published in the Monograph on Management of Salt-Affected Soils and Water for Sustainable Agriculture.
Ameta, S. K., Sharma, S., Ameta, R., & Ameta, S. C. (2015). Effect of compost of Parthenium hysterophorus on seed germination and survival. International Journal of Bioassays, 4, 4325–4328.
Ansari, M. F., Tipre, D. R., & Dave, S. R. (2015). Efficiency evaluation of commercial liquid biofertilizers for growth of Cicer aeritinum (chickpea) in pot and field study. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 4(1), 17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2014.09.010
Aydinalp, C., & Marinova, S. (2009). The effects of heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth on alfalfa plant (Medicago sativa). Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 15(4), 347–350.
Azeem, M., Sun, D., Crowley, D., Hayat, R., Hussain, Q., Ali, A., Tahir, M. I., Jeyasundar, P. G. S. A., Rinklebe, J., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Crop types have stronger effects on soil microbial communities and functionalities than biochar or fertilizer during two cycles of legume-cereal rotations of dry land. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 136958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136958
Bannink A, & Spoelstra SF. (2000). Relationships between animal nutrition and manure quality ; a literature review on C , N , P and S compounds A literature review on C , N , P and S compounds. June 2014
Baruah, N., Mondal, S. C., Farooq, M., & Gogoi, N. (2019). Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4329-0
Basso, B., & Ritchie, J. T. (2005). Impact of compost, manure and inorganic fertilizer on nitrate leaching and yield for a 6-year maize-alfalfa rotation in Michigan. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 108(4), 329–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.01.011
Biederman, L. A., & Stanley, H. W. (2013). Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: a meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy, 5(2), 202–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12037
Brtnicky, M., Datta, R., Holatko, J., Bielska, L., Gusiatin, Z. M., Kucerik, J., Hammerschmiedt, T., Danish, S., Radziemska, M., & Mravcova, L. (2021). A critical review of the possible adverse effects of biochar in the soil environment. Science of the Total Environment, 796, 148756.
Ding, Z., Kheir, A. M. S., Ali, M. G. M., Ali, O. A. M., Abdelaal, A. I. N., Lin, X., Zhou, Z., Wang, B., Liu, B., & He, Z. (2020). The integrated effect of salinity, organic amendments, phosphorus fertilizers, and deficit irrigation on soil properties, phosphorus fractionation and wheat productivity. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59650-8
El Moussaoui, H., Ainlhout, L. F. Z., & Bouqbis, L. (2023). Effect of biochar, biocompost and manure on the growth and productivity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): Field and pots study. International Journal of Recycling Organic Waste in Agriculture, 12(3), 425–440. https://doi.org/10.30486/ijrowa.2023.1962480.1500
El Moussaoui, H., Ainlhout, L. F. Z., Bourezi, A., & Bouqbis, L. (2022). Alfalfa in arid and semi-arid regions Taroudant as an example, good and bad cultural practices on the environment: a statistical study. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1090(1), 12012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1090/1/012012
El Moussaoui, H., & Bouqbis, L. (2022). Interactive effect of biochar and bio-compost on starting growth and physiologic parameters of argan. Sustainability, 14(12), 7270. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127270
El-Bassi, L., Azzaz, A. A., Jellali, S., Akrout, H., Marks, E. A. N., Ghimbeu, C. M., & Jeguirim, M. (2021). Application of olive mill waste-based biochars in agriculture: impact on soil properties, enzymatic activities and tomato growth. Science of the Total Environment, 755, 142531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142531
Griffin, T. S., Cassida, K. A., Hesterman, O. B., & Rust, S. R. (1994). Alfalfa maturity and cultivar effects on chemical and in situ estimates of protein degradability. Crop Science, 34(6), 1654–1661. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400060043x
Hafeez, Y., Iqbal, S., Jabeen, K., Shahzad, S., Jahan, S., & Rasul, F. (2017). Effect of biochar application on seed germination and seedling growth of Glycine max (L.) merr. under drought stress. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 49(Special Issue), 7–13.
Haynes, R. J. (1983). Soil acidification induced by leguminous crops. Grass and Forage Science, 38(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2494.1983.tb01614.x
Himanen, M., & Hänninen, K. (2011). Composting of bio-waste, aerobic and anaerobic sludges - effect of feedstock on the process and quality of compost. Bioresource Technology, 102(3), 2842–2852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.059
Hossain, M. K., Strezov Vladimir, V., Chan, K. Y., Ziolkowski, A., & Nelson, P. F. (2011). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production and nutrient properties of wastewater sludge biochar. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(1), 223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.09.008
Jeffery, S., Abalos, D., Prodana, M., Bastos, A. C., Van Groenigen, J. W., Hungate, B. A., & Verheijen, F. (2017). Biochar boosts tropical but not temperate crop yields. Environmental Research Letters, 12(5). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa67bd
Kelling, K. A., & Schmitt, M. A. (2018). Applying manure to alfalfa: pros, cons and recommendations for three application strategies. https://doi.org/10.31274/icm-180809-758
Khanmohammadi, Z., Afyuni, M., & Mosaddeghi, M. R. (2015). Effect of pyrolysis temperature on chemical and physical properties of sewage sludge biochar. Waste Management and Research, 33(3), 275–283. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X14565210
Kocsis, T., Kotroczó, Z., Kardos, L., & Biró, B. (2020). Optimization of increasing biochar doses with soil–plant–microbial functioning and nutrient uptake of maize. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 20, 101191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101191
Krzyszczak, A., Dybowski, M. P., Kończak, M., & Czech, B. (2022). Low bioavailability of derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biochar obtained from different feedstock. Environmental Research, 214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113787
Lamb, J. A. F. S., Sheaffer, C. C., & Samac, D. A. (2003). Population density and harvest maturity effects on leaf and stem yield in alfalfa. Agronomy Journal, 95(3), 635–641. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.6350
Lehmann, J., & Joseph, S. (2015). Biochar for environmental management: an introduction. In Biochar for environmental management (pp. 1–13). Routledge.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42(3), 421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Liu, B., Li, H., Li, H., Zhang, A., & Rengel, Z. (2021). Long-term biochar application promotes rice productivity by regulating root dynamic development and reducing nitrogen leaching. GCB Bioenergy, 13(1), 257–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12766
Liu, W. R., Zeng, D., She, L., Su, W. X., He, D. C., Wu, G. Y., Ma, X. R., Jiang, S., Jiang, C. H., & Ying, G. G. (2020). Comparisons of pollution characteristics, emission situations, and mass loads for heavy metals in the manures of different livestock and poultry in China. Science of the Total Environment, 734, 139023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139023
Llorach-Massana, P., Lopez-Capel, E., Peña, J., Rieradevall, J., Montero, J. I., & Puy, N. (2017). Technical feasibility and carbon footprint of biochar co-production with tomato plant residue. Waste Management, 67, 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.021
Lu, H., Zhang, W., Wang, S., Zhuang, L., Yang, Y., & Qiu, R. (2013). Characterization of sewage sludge-derived biochars from different feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 102, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2013.03.004
Luo, Y., Liang, J., Zeng, G., Chen, M., Mo, D., Li, G., & Zhang, D. (2018). Seed germination test for toxicity evaluation of compost: Its roles, problems and prospects. Waste Management, 71, 109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.09.023
Mahdi, Z., El Hanandeh, A., & Yu, Q. J. (2015). Date palm (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) seed characterization for biochar preparation (pp. 2–4). The 6th International Conference on Engineering, Project, and Production Management (EPPM).
Major, J., Rondon, M., Molina, D., Riha, S. J., & Lehmann, J. (2010). Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant and Soil, 333(1), 117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0327-0
Martin, E. C., Slack, D. C., Tanksley, K. A., & Basso, B. (2006). Effects of fresh and composted dairy manure applications on alfalfa yield and the environment in Arizona. Agronomy Journal, 98(1), 80–84. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2005.0039
Mbarki, S., Cerdà, A., Zivcak, M., Brestic, M., Rabhi, M., Mezni, M., Jedidi, N., Abdelly, C., & Pascual, J. A. (2018). Alfalfa crops amended with MSW compost can compensate the effect of salty water irrigation depending on the soil texture. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 115, 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.001
Nana, R., Maïga, Y., Ouédraogo, R. F., Kaboré, W. G. B., Badiel, B., & Tamini, Z. (2019). Effect of water quality on the germination of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) seeds. International Journal of Agronomy, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4938349
Oldfield, T. L., Sikirica, N., Mondini, C., López, G., Kuikman, P. J., & Holden, N. M. (2018). Biochar, compost and biochar-compost blend as options to recover nutrients and sequester carbon. Journal of Environmental Management, 218, 465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.061
Olsen, S. R. (1954). Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate (Issue 939). US Department of Agriculture.
Osman, A. I., Fawzy, S., Farghali, M., El-Azazy, M., Elgarahy, A. M., Fahim, R. A., Maksoud, M. I. A. A., Ajlan, A. A., Yousry, M., Saleem, Y., & Rooney, D. W. (2022). Biochar for agronomy, animal farming, anaerobic digestion, composting, water treatment, soil remediation, construction, energy storage, and carbon sequestration: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 20(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01424-x
Palansooriya, K. N., Wong, J. T. F., Hashimoto, Y., Huang, L., Rinklebe, J., Chang, S. X., Bolan, N., Wang, H., & Ok, Y. S. (2019). Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: a critical review. Biochar, 1(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-019-00009-2
Peralta, J. R., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Tiemann, K. J., Gomez, E., Arteaga, S., Rascon, E., & Parsons, J. G. (2001). Uptake and effects of five heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in alfalfa ( L.). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66(6), 727–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-001-0069-z
Rasa, K., Heikkinen, J., Hannula, M., Arstila, K., Kulju, S., & Hyväluoma, J. (2018). How and why does willow biochar increase a clay soil water retention capacity? Biomass and Bioenergy, 119, 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.10.004
Redmann, R. E. (1974). Osmotic and specific ion effects on the germination of alfalfa. Canadian Journal of Botany, 52(4), 803–808.
Rocci, K. S., Fonte, S. J., von Fischer, J. C., & Cotrufo, M. F. (2019). Nitrogen dynamics in an established Alfalfa field under low biochar application rates. Soil Systems, 3(4), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3040077
Rogovska, N., Laird, D., Cruse, R. M., Trabue, S., & Heaton, E. (2012). Germination tests for assessing biochar quality. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41(4), 1014–1022.
Rombolà, A. G., Marisi, G., Torri, C., Fabbri, D., Buscaroli, A., Ghidotti, M., & Hornung, A. (2015). Relationships between chemical characteristics and phytotoxicity of biochar from poultry litter pyrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63(30), 6660–6667. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01540
Roy, R., Núñez-Delgado, A., Wang, J., Kader, M. A., Sarker, T., Hasan, A. K., & Dindaroglu, T. (2022). Cattle manure compost and biochar supplementation improve growth of Onobrychis viciifolia in coal-mined spoils under water stress conditions. Environmental Research, 205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112440
Sethy, S. K., & Ghosh, S. (2013). Effect of heavy metals on germination of seeds. Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine, 4(2), 272–275. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-9668.116964
Shaikh, F., Gul, B., Li, W. Q., Liu, X. J., & Khan, M. A. (2007). Effect of calcium and light on the germination of Urochondra setulosa under different salts. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 8(1), 20–26. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0020
Siedt, M., Schäffer, A., Smith, K. E. C., Nabel, M., Roß-Nickoll, M., & van Dongen, J. T. (2021). Comparing straw, compost, and biochar regarding their suitability as agricultural soil amendments to affect soil structure, nutrient leaching, microbial communities, and the fate of pesticides. Science of the Total Environment, 751, 141607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141607
Smider, B., & Singh, B. (2014). Agronomic performance of a high ash biochar in two contrasting soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 191, 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.01.024
Song, X. D., Xue, X. Y., Chen, D. Z., He, P. J., & Dai, X. H. (2014). Application of biochar from sewage sludge to plant cultivation: influence of pyrolysis temperature and biochar-to-soil ratio on yield and heavy metal accumulation. Chemosphere, 109, 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.070
Song, Y., Lv, J., Ma, Z., & Dong, W. (2019). The mechanism of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) response to abiotic stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 89(3), 239–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00530-1
Spokas, K. A., Novak, J. M., Masiello, C. A., Johnson, M. G., Colosky, E. C., Ippolito, J. A., & Trigo, C. (2014). Physical disintegration of biochar: an overlooked process. Environmental Science and Technology Letters, 1(8), 326–332. https://doi.org/10.1021/ez500199t
Steel, H., Vandecasteele, B., Willekens, K., Sabbe, K., Moens, T., & Bert, W. (2012). Nematode communities and macronutrients in composts and compost-amended soils as affected by feedstock composition. Applied Soil Ecology, 61, 100–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.05.004
Tang, Y., Alam, M. S., Konhauser, K. O., Alessi, D. S., Xu, S., Tian, W. J., & Liu, Y. (2019). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production of digested sludge biochar and its application for ammonium removal from municipal wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209, 927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.268
Touhtouh, D., Moujahid, Y., El Faleh, E., & REL, H. (2015). Caractérisations physico-chimiques de trois types de sols du Saïs, Maroc Physical and chemical characterization of three types of soils of Saïs, Morocco. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 6(12), 3582–3593.
Tucak, M., Ravlić, M., Horvat, D., & Čupić, T. (2021). Improvement of forage nutritive quality of alfalfa and red clover through plant breeding. Agronomy, 11(11), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112176
Turk Sekulić, M., Pap, S., Stojanović, Z., Bošković, N., Radonić, J., & Šolević, K. T. (2018). Efficient removal of priority, hazardous priority and emerging pollutants with Prunus armeniaca functionalized biochar from aqueous wastes: experimental optimization and modeling. Science of the Total Environment, 613–614, 736–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.082
Visioli, G., Conti, F. D., Menta, C., Bandiera, M., Malcevschi, A., Jones, D. L., & Vamerali, T. (2016). Assessing biochar ecotoxicology for soil amendment by root phytotoxicity bioassays. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5173-y
Yeboah, E., Ofori, P., Quansah, G. W., Dugan, E., & Sohi, S. P. (2009). Improving soil productivity through biochar amendments to soils. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 3(2), 34–41.
Zheng, X., Yang, Z., Xu, X., Dai, M., & Guo, R. (2018). Characterization and ammonia adsorption of biochar prepared from distillers’ grains anaerobic digestion residue with different pyrolysis temperatures. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 93(1), 198–206. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5340
Zhu, L., Tong, L., Zhao, N., Wang, X., Yang, X., & Lv, Y. (2020). Key factors and microscopic mechanisms controlling adsorption of cadmium by surface oxidized and aminated biochars. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 382, 121002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121002
Zong, Y., Xiao, Q., Malik, Z., Su, Y., Wang, Y., & Lu, S. (2021). Crop straw-derived biochar alleviated cadmium and copper phytotoxicity by reducing bioavailability and accumulation in a field experiment of rice-rape-corn rotation system. Chemosphere, 280, 130830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130830
Funding
The authors wish to thank the Laboratory of Biotechnology, Materials and Environment of the Faculty of Science of Agadir, the Polydisciplinary Faculty of Taroudant, and the Faculty of Applied Sciences of Ait Melloul, University Ibn Zohr, for the funding of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El Moussaoui, H., Idardare, Z. & Bouqbis, L. Assessing Alfalfa Productivity and Physiological Parameters: Biochar and Biocompost Versus Conventional Fertilizers with Manure and Chemical Fertilizers. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 606 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06618-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06618-9