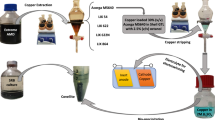
Abstract
Desalination techniques have been implemented for years to supply freshwater in some areas. Although it could address water shortage, it would simultaneously produce a high salinity byproduct, brine. Brine as a pollutant would lead to marine, soil, and groundwater pollution when directly disposed into the sea and land. According to the above narrative, it can be observed that another problem is generated when human beings solve the original problem. Under this situation, recovering critical resources from brine is thought to be a method to enhance brine’s value and reduce its disposal. This study then applied the LIX 984N/kerosene system to recover copper from brine. The optimal extraction parameters were pH 9, 0.3 M of LIX 984N, O/A (organic/aqueous) ratio 0.5, extraction time for 3 min, and extraction temperature at 278 K. The result revealed that extraction efficiency was 94.4%. Moreover, H2SO4 was employed to strip copper from the organic phase, and the stripping efficiency was 100%. After the whole process, the copper product and LIX 984N could be generated and reused. In sum, the environmental hazards caused by desalination brine could be minimized, and copper resources were obtained through this study.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahuja, S. (2015). Water Challenges and Solutions on a Global Scale. USA: Oxford University Press.
Akbari, S., & Ahmadi, A. (2019). Recovery of copper from a mixture of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and sulphidic tailings using bioleaching and solvent extraction processes. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 142, 107584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107584
Alothman, Z. A., Bahkali, A. H., Khiyami, M. A., Alfadul, S. M., Wabaidur, S. M., Alam, M., & Alfarhan, B. Z. (2020). Low cost biosorbents from fungi for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Separation Science and Technology, 55(10), 1766–1775. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1608242
Arroyo, F., Morillo, J., Usero, J., Rosado, D., & El Bakouri, H. (2019). Lithium recovery from desalination brines using specific ion-exchange resins. Desalination, 468, 114073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114073
Backer, S. N., Bouaziz, I., Kallayi, N., Thomas, R. T., Preethikumar, G., Takriff, M. S., et al. (2022). Review: Brine Solution: Current Status. Future Management and Technology Development. Sustainability, 14(11), 6752. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116752
Bank, A. D. (2016). Asian Water Development Outlook 2016. Asian Development Bank.
Bello, A. S., Zouari, N., Da’ana, D. A., Hahladakis, J. N., & Al-Ghouti, M. A. (2021). An overview of brine management: Emerging desalination technologies, life cycle assessment, and metal recovery methodologies. Journal of Environmental Management, 288, 112358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112358
Candal, R. J., Regazzoni, A. E., & Blesa, M. A. (1992). Precipitation of copper(II) hydrous oxides and copper(II) basic salts. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2(6), 657. https://doi.org/10.1039/jm9920200657
Chen, W.-S., Lee, C.-H., Chung, Y.-F., Tien, K.-W., Chen, Y.-J., & Chen, Y.-A. (2020). Recovery of Rubidium and Cesium Resources from Brine of Desalination through t-BAMBP Extraction. Metals, 10(5), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050607
Devi, N. B., & Nayak, B. (2014). Liquid-liquid extraction and separation of copper(II) and nickel(II) using LIX®984N, 114(11), 937–943. http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2225-62532014001100012.
Dindi, A., Quang, D. V., & Abu-Zahra, M. R. M. (2015). Simultaneous carbon dioxide capture and utilization using thermal desalination reject brine. Applied Energy, 154, 298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.05.010
Dindi, A., Quang, D. V., Hadri, N. E., Rayer, A., Abdulkadir, A., & Abu-Zahra, M. R. M. (2014). Potential for the Simultaneous Capture and Utilization of CO2 Using Desalination Reject Brine: Amine Solvent Selection and Evaluation. Energy Procedia, 63, 7947–7953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.829
El-Naas, M. H., Al-Marzouqi, A. H., & Chaalal, O. (2010). A combined approach for the management of desalination reject brine and capture of CO2. Desalination, 251(1–3), 70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.09.141
El-Naas, M. H., Mohammad, A. F., Suleiman, M. I., Al Musharfy, M., & Al-Marzouqi, A. H. (2017). A new process for the capture of CO2 and reduction of water salinity. Desalination, 411, 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.02.005
Figueira, M., Reig, M., Fernández de Labastida, M., Cortina, J. L., & Valderrama, C. (2022). Boron recovery from desalination seawater brines by selective ion exchange resins. Journal of Environmental Management, 314, 114984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114984
Giwa, A., Dufour, V., Al Marzooqi, F., Al Kaabi, M., & Hasan, S. W. (2017). Brine management methods: Recent innovations and current status. Desalination, 407, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.12.008
Gude, G. (2018). Sustainable Desalination Handbook. Butterworth-Heinemann.
Guo, Z.-Y., Ji, Z.-Y., Chen, Q.-B., Liu, J., Zhao, Y.-Y., Li, F., et al. (2018). Prefractionation of LiCl from concentrated seawater/salt lake brines by electrodialysis with monovalent selective ion exchange membranes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 193, 338–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.077
Jones, E., Qadir, M., van Vliet, M. T. H., Smakhtin, V., & Kang, S. (2019). The state of desalination and brine production: A global outlook. Science of the Total Environment, 657, 1343–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.076
Kang, D., Yoo, Y., & Park, J. (2020). Accelerated chemical conversion of metal cations dissolved in seawater-based reject brine solution for desalination and CO2 utilization. Desalination, 473, 114147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114147
Korngold, E., Aronov, L., & Daltrophe, N. (2009). Electrodialysis of brine solutions discharged from an RO plant. Desalination, 242(1–3), 215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.008
Lee, C., & Chen, W. (2022). Resources recovery—Separation and recovery of copper from desalination brine through Lewatit TP 207 resin. Water Environment Research, 94(10). https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.10794.
Lee, C.-H., Chen, P.-H., & Chen, W.-S. (2021a). Recovery of Alkaline Earth Metals from Desalination Brine for Carbon Capture and Sodium Removal. Water, 13(23), 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233463
Lee, C.-H., Chen, P.-H., & Chen, W.-S. (2022). Recovery of boron from desalination brine through amberlite IRA 743 resin. DWT, 264, 133–140. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.28569
Lee, C.-H., Chen, W.-S., & Wu, J.-Y. (2021b). Adsorption of cesium from waste desalination brine through Dowex G26 resin and comparison with t-BAMBP/kerosene and t-BAMBP/C2mimNTf2 systems. DWT, 236, 69–75. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27668
Le Long, H., Jeong, J., Lee, J.-C., Pandey, B. D., Yoo, J.-M., & Huyunh, T. H. (2011). Hydrometallurgical Process for Copper Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 32(2), 90–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2010.530720
Mishra, B., Kumar, P., Saraswat, C., Chakraborty, S., & Gautam, A. (2021). Water Security in a Changing Environment: Concept Challenges and Solutions. Water, 13(4), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040490
Missimer, T. M., & Maliva, R. G. (2018). Environmental issues in seawater reverse osmosis desalination: Intakes and outfalls. Desalination, 434, 198–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.07.012
Morillo, J., Usero, J., Rosado, D., El Bakouri, H., Riaza, A., & Bernaola, F.-J. (2014). Comparative study of brine management technologies for desalination plants. Desalination, 336, 32–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.12.038
Mustafa, J., Mourad, A.A.-H.I., Al-Marzouqi, A. H., & El-Naas, M. H. (2020). Simultaneous treatment of reject brine and capture of carbon dioxide: A comprehensive review. Desalination, 483, 114386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114386
Naidu, G., Jeong, S., Johir, M. A. H., Fane, A. G., Kandasamy, J., & Vigneswaran, S. (2017). Rubidium extraction from seawater brine by an integrated membrane distillation-selective sorption system. Water Research, 123, 321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.06.078
Panagopoulos, A. (2022). Brine management (saline water & wastewater effluents): Sustainable utilization and resource recovery strategy through Minimal and Zero Liquid Discharge (MLD & ZLD) desalination systems. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 176, 108944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2022.108944
Panagopoulos, A., Haralambous, K.-J., & Loizidou, M. (2019). Desalination brine disposal methods and treatment technologies - A review. Science of The Total Environment, 693, 133545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.351
Panda, R., Jha, M. K., Pathak, D. D., & Gupta, R. (2020). Recovery of Ag, Cu, Ni and Fe from the nitrate leach liquor of waste ICs. Minerals Engineering, 158, 106584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106584
Rodriguez-DeLaNuez, F., Suarez, N. F., Santiago, D. E., Veza, J. M., & Sadhwani, J. J. (2012). Reuse and minimization of desalination brines: A review of alternatives. DWT, 39, 137–148. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2012.2977
Schorr, M. (2011). Desalination trends and technologies. United Kingdom: IntechOpen Limited.
Shakibania, S., Mahmoudi, A., Mokmeli, M., & Rashchi, F. (2020). The effect of chloride ions on copper solvent extraction from sulfate-chloride medium using LIX 984N. Minerals Engineering, 156, 106498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106498
Shatat, M., & Riffat, S. B. (2014). Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, 9(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/cts025
Shrivastava, I., & Adams, E. E. (2019). Pre-dilution of desalination reject brine: Impact on outfall dilution in different water depths. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 24, 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2018.09.001
Sinha, M. K., Sahu, S. K., Pramanik, S., Prasad, L. B., & Pandey, B. D. (2016). Recovery of high value copper and zinc oxide powder from waste brass pickle liquor by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy, 165, 182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.09.012
Sridhar, V., & Verma, J. K. (2011). Recovery of Copper, Nickel and Zinc from Sulfate Solutions by Solvent Extraction Using LIX 984N. E-Journal of Chemistry, 8(s1), S434–S438. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/108628
UNESCO. (2012). Managing Water Under Uncertainty And Risk. USA: United Nations.
Voutchkov, N. (2020). Management of Concentrate from Desalination Plants. Elsevier.
Wiechert, A. I., Ladshaw, A. P., Gill, G. A., Wood, J. R., Yiacoumi, S., & Tsouris, C. (2018). Uranium Resource Recovery from Desalination Plant Feed and Reject Water Using Amidoxime Functionalized Adsorbent. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 57(50), 17237–17244. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b04673
Yoo, Y., Kang, D., Park, S., & Park, J. (2020). Carbon utilization based on post-treatment of desalinated reject brine and effect of structural properties of amines for CaCO3 polymorphs control. Desalination, 479, 114325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114325
Zhang, X., Zhao, W., Zhang, Y., & Jegatheesan, V. (2021). A review of resource recovery from seawater desalination brine. Reviews in Environmental Science & Biotechnology, 20(2), 333–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09570-4
Ziolkowska, J. R., & Reyes, R. (2017). Prospects for Desalination in the United States—Experiences from California, Florida, and Texas, 298–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803237-4.00017-3.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Laboratory of Resource Circulation in the Department of Resources Engineering, National Cheng-Kung University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, C. H. Lee; methodology, C. H. Lee and W. S. Chen; validation, C. H. Lee and J. Y. Wu; formal analysis, C. H. Lee; investigation, C. H. Lee; data curation, W. S. Chen; writing—original draft preparation, C.-H. Lee; writing—review and editing, C. H. Lee and J. Y. Wu; visualization, C.-H. Lee; supervision, W. S. Chen. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Chen, WS. & Wu, JY. Pollution Prevention- Recovery of Copper Resource from Desalination Brine through LIX 984N/Kerosene System. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 584 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06604-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06604-1