Abstract
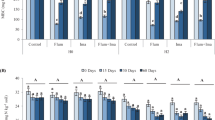
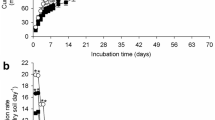
Herbicide application is a widely utilized approach for weed management in agriculture. However, it is essential to acknowledge that these chemical compounds can affect non-target soil microorganisms and their functions. To address this concern, a pot experiment was conducted to assess the effects of Clopyralid, Butisanstar, and their combination (But + Clo) at different doses (zero, 0.5x, recommended field dose (x), 2x, and 5x) on microbial indicators, including microbial population, microbial biomass carbon (MBC), basal soil respiration (BSR), substrate-induced respiration (SIR), microbial quotient (qmicro), and respiratory quotient (qCO2) at 10, 30, 60, and 90 days following their application to the soil. The results revealed a significant reduction (p < 0.01) in all microbial indicators (except qCO2, which exhibited an increase) compared to the control soil after herbicide application. Among the treatments, the combination of But + Clo exhibited the greatest decrease, followed by clopyralid and butisanstar. Bacterial populations experienced a more pronounced and persistent inhibitory effect from the herbicides compared to fungi, with a significant decrease (67%) observed from day 10 to day 30, followed by a less substantial decrease (12%) until day 90. The impact of clopyralid and butisanstar on microbial indicators demonstrated a dose-dependent relationship, with the highest and lowest values observed at 0.5 × and 5x doses, respectively. Furthermore, the adverse effects of the herbicides resulted in a substantial reduction of the evaluated indicators, particularly during the initial 30 days following application. However, temporary recovery and an increase in microbial indicators (excluding bacterial populations) were observed on day 60, likely due to the microbial community's adaptation to the applied herbicides. This study emphasizes the negative consequences of herbicide application on the soil microbial community, raising concerns regarding soil health, quality, and fertility in relation to crop production.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made on available in reasonable request.
References
Adetunji, A. T., Lewu, F. B., Mulidzi, R., & Ncube, B. (2017). The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 17(3), 794–807.
Adomako, M. O., & Akyeampong, S. (2016). Effect of some commonly used herbicides on soil microbial population. Environment and Earth Science, 6, 30–38.
Al-Ani, M. A. M., Hmoshi, R. M., Kanaan, I. A., & Thanoon, A. A. (2019). Effect of pesticides on soil microorganisms. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1294(7). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1294/7/072007
Alef, K., & Nannipieri, P. (1995). Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic Press.
Anderson, J. P. E. (1982). Soil respiration. In A. L. Page (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Amer. Soc. Agronomy, and Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Madison.
Anderson, T., & Domsch, K. H. (1986). Carbon assimilation and microbial activity in soil. Zeitschrift Für Pflanzenernährung Und Bodenkunde, 149(4), 457–468.
Anderson, T.-H., & Domsch, K. H. (1990). Application of eco-physiological quotients (qCO2 and qD) on microbial biomasses from soils of different cropping histories. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 22(2), 251–255.
Anonymous. (2021). Agricultural statistics of the crop year (2020), Volume Two: Water and Affairs. Ministry of Agriculture Jihad, Planning and Economic Deputy. In Persian.
Antisari, L. V., Carbone, S., Gatti, A., Vianello, G., & Nannipieri, P. (2013). Toxicity of metal oxide (CeO2, Fe3O4, SnO2) engineered nanoparticles on soil microbial biomass and their distribution in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 60, 87–94.
Arunrat, N., Sereenonchai, S., Chaowiwat, W., Wang, C., & Hatano, R. (2022). Carbon, nitrogen and water footprints of organic rice and conventional rice production over 4 years of cultivation: A case study in the Lower North of Thailand. Agronomy, 12(2), 380.
Arunrat, N., Sereenonchai, S., Sansupa, C., Kongsurakan, P., & Hatano, R. (2023). Effect of rice straw and stubble burning on soil physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in central Thailand. Biology, 12(4), 501.
Ayansina, A. D. V., & Oso, B. A. (2006). Effect of two commonly used herbicides on soil microflora at two different concentrations. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(2), 129–132. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/view/137739
Baboo, M., Pasayat, M., Samal, A., Kujur, M., Kumar Maharana, J., & Kumar Patel, A. (2013). Effect of four herbicides on soil organic carbon, microbial biomass-C, enzyme activity and microbial populations in agricultural soil. International Journal of Research in Environmental Science and Technology, 3(4), 100–112.
Baćmaga, M., Kucharski, J., Wyszkowska, J., Borowik, A., & Tomkiel, M. (2014). Responses of microorganisms and enzymes to soil contamination with metazachlor. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(7), 2251–2262.
Baćmaga, M., Borowik, A., Kucharski, J., Tomkiel, M., & Wyszkowska, J. (2015). Microbial and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with a mixture of diflufenican+ mesosulfuron-methyl+ iodosulfuron-methyl-sodium. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(1), 643–656.
Bolan, N. S., & Baskaran, S. (1996). Biodegradation of 2, 4-D herbicide as affected by its adsorption-desorption behavior and microbial activity of soils. Soil Research, 34(6), 1041–1053.
Boldt, T. S., & Jacobsen, C. S. (1998). Different toxic effects of the sulfonylurea herbicides metsulfuron methyl, chlorsulfuron and thifensulfuron methyl on fluorescent pseudomonads isolated from an agricultural soil. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 161(1), 29–35.
Brookes, P. (2001). The soil microbial biomass: Concept, measurement and applications in soil ecosystem research. Microbes and Environments, 16(3), 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.2001.131
Cech, R. M., Jovanovic, S., Kegley, S., Hertoge, K., Leisch, F., & Zaller, J. G. (2022). Reducing overall herbicide use may reduce risks to humans but increase toxic loads to honeybees, earthworms and birds. Environmental Sciences Europe, 34(1), 44.
Cycoń, M., Wójcik, M., Borymski, S., & Piotrowska-Seget, Z. (2013). Short-term effects of the herbicide napropamide on the activity and structure of the soil microbial community assessed by the multi-approach analysis. Applied Soil Ecology, 66, 8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.01.014
Filimon, M. N., Roman, D. L., Bordean, D. M., & Isvoran, A. (2021). Impact of the herbicide oxyfluorfen on the activities of some enzymes found in soil and on the populations of soil microorganisms. Agronomy, 11(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091702
Geisseler, D., & Horwath, W. R. (2009). Short-term dynamics of soil carbon, microbial biomass, and soil enzyme activities as compared to longer-term effects of tillage in irrigated row crops. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 46, 65–72.
Gharde, Y., Singh, P. K., Dubey, R. P., & Gupta, P. K. (2018). Assessment of yield and economic losses in agriculture due to weeds in India. Crop Protection, 107, 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2018.01.007
Gillespie, W., Czapar, G., & Hager, A. (2011). Pesticide fate in the environment: a guide for field inspectors. ISWS Contract Report CR-2011–07.
Hart, M. (1995). Effects of pesticides on the soil microbial biomass and microbial activity. University of Nottingham.
Hristeva, T., Yanev, M., Bozukov, H., & Kalinova, S. (2015). Condition of soil microbial communities when exposed to some chloroacetamide herbicides. Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 21(4), 730–735.
Jaiswal, D. K., Krishna, R., Singh, S., Belwal, T., Verma, J. P., Yadav, J. (2021). Toxicity of organophosphate pesticide on soil microorganism: risk assessments strategies. In: Singh, K. P., Jahagirdar, S., Sarma, B. K. (eds). Emerging Trends in Plant Pathology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6275-4_12
Jenkinson, D. S., & Ladd, J. N. (2021). Microbial biomass in soil: measurement and turnover. In Soil biochemistry (pp. 415–472). CRC Press.
Kibblewhite, M. G., Ritz, K., & Swift, M. J. (2008). Soil health in agricultural systems. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society b: Biological Sciences, 363(1492), 685–701.
Kniss, A. R. (2017). Long-term trends in the intensity and relative toxicity of herbicide use. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1–7.
Lupwayi, N. Z., Harker, K. N., Clayton, G. W., Turkington, T. K., Rice, W. A., & O’Donovan, J. T. (2004). Soil microbial biomass and diversity after herbicide application. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 84(2), 677–685.
Mahmood, I., Imadi, S. R., Shazadi, K., Gul, A., & Hakeem, K. R. (2016). Effects of pesticides on environment. Plant, Soil and Microbes: Volume 1: Implications in Crop Science, 253–269.
Mamy, L., Barriuso, E., & Gabrielle, B. (2005). Environmental fate of herbicides trifluralin, metazachlor, metamitron and sulcotrione compared with that of glyphosate, a substitute broad spectrum herbicide for different glyphosate-resistant crops. Pest Management Science: Formerly Pesticide Science, 61(9), 905–916.
Mukherjee, S., Tripathi, S., Mukherjee, A. K., Bhattacharyya, A., & Chakrabarti, K. (2016). Persistence of the herbicides florasulam and halauxifen-methyl in alluvial and saline alluvial soils, and their effects on microbial indicators of soil quality. European Journal of Soil Biology, 73, 93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.01.009
Myers, J. P., Antoniou, M. N., Blumberg, B., Carroll, L., Colborn, T., Everett, L. G., Hansen, M., Landrigan, P. J., Lanphear, B. P., & Mesnage, R. (2016). Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environmental Health, 15(1), 1–13.
Nur, M. M. Z., Rosli, B. M., Kamaruzaman, S., Md, M. M., & Yahya, A. (2013). Effects of selected herbicides on soil microbial populations in oil palm plantation of Malaysia: A microcosm experiment. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 7(5), 367–374. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajmr12.1277
Pampulha, M. E., & Oliveira, A. (2006). Impact of an herbicide combination of bromoxynil and prosulfuron on soil microorganisms. Current Microbiology, 53(3), 238–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0116-4
Pansu, M. (2006). Handbook of soil analysis. Springer.
Parlakidis, P., Rodriguez, M. S., Gikas, G. D., Alexoudis, C., Perez-Rojas, G., Perez-Villanueva, M., Carrera, A. P., Fernández-Cirelli, A., & Vryzas, Z. (2022). Occurrence of banned and currently used herbicides, in groundwater of northern greece: A human health risk assessment approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), 8877.
Pertile, M., Antunes, J. E. L., Araujo, F. F., Mendes, L. W., Van den Brink, P. J., & Araujo, A. S. F. (2020). Responses of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity to herbicides imazethapyr and flumioxazin. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–9.
Quilchano, C., & Marañón, T. (2002). Dehydrogenase activity in Mediterranean forest soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 35(2), 102–107.
Rana, S. S., & Rana, M. C. (2015). Advances in weed management. Department of Agronomy, College of Agriculture, CSK Himachal Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya, Palampur, 183.
Roberts, T. R., Hutson, D. H., Lee, P. W., Nicholls, P. H., Plimmer, J. R., Roberts, M. C., & Croucher, L. (1998). Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals: Part 1: Herbicides and plant growth regulators. Royal Society of Chemistry.
Sándor, Z., Kincses, I., Tállai, M., Lowy, D. A., Melendez, J. R., Guananga Diaz, N. I., Guevara Iñiguez, L. E., Cuenca Nevarez, G., Talledo Solórzano, V., & Kátai, J. (2020). Effect of herbicides on soil respiration: a case study conducted at Debrecen-Látókép Plant Cultivation Experimental Station. F1000Research, 9, 1348. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.27057.1
Santos, J. B., Jakelaitis, A., Silva, A. A., Costa, M. D., Manabe, A., & Silva, M. C. S. (2006). Action of two herbicides on the microbial activity of soil cultivated with common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in conventional-till and no-till systems. Weed Research, 46(4), 284–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.2006.00510
Sebiomo, A., Ogundero, V. W., & Bankole, S. A. (2011). Effect of four herbicides on microbial population, soil organic matter and dehydrogenase activity. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10(5), 770–778.
Serafini, C. G., Clerici, N. J., Della-Flora, I. K., Dupont, G. K., da Costa Cabrera, L., & Daroit, D. J. (2022). Effects of atrazine on soil microbial indicators and the evaluation of herbicide attenuation in microcosms. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22(4), 1165–1175.
Shimi, P., Darvish, N., & Meighani, F. (2014). Evaluation of the efficacy of a new herbicide, Butisan Star (Metazachlor + Quinmerac), in controlling weeds and improving yield of canola. Journal of Crop Improv, 6(1), 31–38. In Persian.
Sofo, A., Scopa, A., Dumontet, S., Mazzatura, A., & Pasquale, V. (2012). Toxic effects of four sulphonylureas herbicides on soil microbial biomass. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part B Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 47(7), 653–659. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.669205
Sun, S., Hou, Y.-N., Wei, W., Sharif, H. M. A., Huang, C., Ni, B.-J., Li, H., Song, Y., Lu, C., & Han, Y. (2022). Perturbation of clopyralid on bio-denitrification and nitrite accumulation: Long-term performance and biological mechanism. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 9, 100144.
Takeshita, V., Mendes, K. F., Alonso, F. G., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2019). Effect of organic matter on the behavior and control effectiveness of herbicides in soil. Planta Daninha, 37. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582019370100110.
Tomco, P. L., Duddleston, K. N., Schultz, E. J., Hagedorn, B., Stevenson, T. J., & Seefeldt, S. S. (2016). Field degradation of aminopyralid and clopyralid and microbial community response to application in Alaskan soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 35(2), 485–493.
Tomkiel, M., Baćmaga, M., Borowik, A., Kucharski, J., & Wyszkowska, J. (2019). Effect of a mixture of flufenacet and isoxaflutole on population numbers of soil-dwelling microorganisms, enzymatic activity of soil, and maize yield. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 54(10), 832–842.
Tu, M., Hurd, C., & Randall, J. M. (2001). Weed control methods handbook: tools & techniques for use in natural areas. https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/govdocs/533
Tyagi, S., Mandal, S. K., Kumar, R., & Kumar, S. (2018). Effect of different herbicides on soil microbial population dynamics in rabi maize (Zea mays L.). International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7, 3751–3758. http://www.ijcmas.com
Use, F. A. O. P. (2022). Pesticides Trade and Pesticides Indicators–Global, Regional and Country Trends, 1990–2020. FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs, 46.
Vasic, V., Hajnal-Jafari, T., Djuric, S., Kovacevic, B., Stojnic, S., Vasic, S., Galovic, V., & Orlovic, S. (2022). Effect of herbicide clopyralid and imazamox on dehydrogenase enzyme in soil of regenerated pedunculate Oak forests. Forests, 13(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060926
Vats, S. (2015). Herbicides: history, classification and genetic manipulation of plants for herbicide resistance. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews (pp. 153–192). Springer.
Visser, S., & Parkinson, D. (1992). Soil biological criteria as indicators of soil quality: Soil microorganisms. American Journal of Alternative Agriculture, 7(1–2), 33–37. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0889189300004434
Wilkinson, V., & Lucas, R. L. (1969). Effects of herbicides on the growth of soil fungi. New Phytologist, 68(3), 709–719.
Yadaei, H., Vafaei, F., Valaei, A., Saeedi, H., & Sarhadi, M. (2019). Executive guidelines for weed control and herbicide usage in canola farming. p 6. In Persian
Zhang, C., Nie, S., Liang, J., Zeng, G., Wu, H., Hua, S., Liu, J., Yuan, Y., Xiao, H., & Deng, L. (2016). Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 557, 785–790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kelarlou, T.R., Golchin, A. & Toolarood, AA.S. Evaluation of the Impacts of Clopyralid and Butisanstar Herbicides on Selected Soil Microbial Indicators. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 572 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06597-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06597-x