Abstract
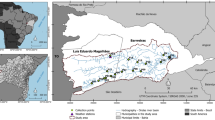
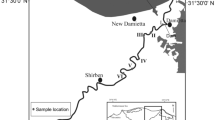
Yamuna River Delhi stretch is a leading source of water supply to Delhi. The river stretch is a receptacle of urban liquid waste of human interference from domestic and industrial fields and conduces to the most contaminant reach of the country. The present study used multivariate techniques to represent the spatiotemporal water quality variations and interpreted a large hourly complex dataset (March 2021–February 2022) obtained from two real-time monitoring stations situated upstream and downstream of this reach. Eleven water quality parameters were assessed, and Box Whisker plots were drawn monthly basis. The increased concentrations of conductivity, BOD, COD, TOC, NH4, and low DO downstream indicated the influence of outfalling drains and diffused sources contributing pollutants into the river stretch. A higher BOD, COD, and TOC concentration was observed downstream in monsoon attributed to the organic substance in surface runoff. FA and PCA were implemented in the standardized data set to reveal the correlation between the water parameter. For upstream, turbidity, TOC, COD, and TSS have strongly positively loaded for factor 1 for all the seasons except monsoon. For downstream. TOC and COD contributed strongly positive load except in winter. The study reveals that the urban river flows with agricultural and surface runoff: industrial and domestic wastewater with organic and inorganic substances. This present study is a novel approach to assessing spatial and temporal variation of an urban reach for the current geomorphological conditions with real-time data.

(Source: DPCC)







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset analyzed during the present study is available in RTWQMS, Delhi.
References
Achieng’, A. O. et al. (2017). Assessment of water quality using multivariate techniques in River Sosiani, Kenya. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5992-5.
Akbal, F., et al. (2011). Multivariate Statistical techniques for the assessment of surface water quality at the mid-Black Sea Coast of Turkey. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 216(1), 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0511-0
Arora, S., & Keshari, A. K. (2021). Pattern recognition of water quality variance in Yamuna River (India) using hierarchical agglomerative cluster and principal component analyses. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09318-1.
Atakoglu, O. O., & Yalcin, F. (2022). Evaluation of the surface water and sediment quality in the Duger basin (Burdur, Turkey) using multivariate statistical analyses and identification of heavy metals. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(7), 484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10147-z
Avtar, R., et al. (2013). Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality of Bundelkhand, India Using Statistical Approach. Water Quality, Exposure and Health, 5(3), 105–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0094-2
Bonansea, M., et al. (2018). Multivariate statistical analysis for estimating surface water quality in reservoirs. International Journal of Hydrology Science and Technology, 8(1), 52–68. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2018.088675
Bu, H., et al. (2010). Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(8), 1631–1639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0297-9
Calijuri, M. L., et al. (2012). Evaluation of the influence of natural and antrhopogenic processes on water quality in Karstic Region. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(5), 2157–2168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1012-5
Central Pollution Control Board. (2012). River Yamuna – Waste water management plan in Delhi. Central Pollution Control Board (Ministry of Environment and Forests, Govt. of India).
Clark, R. B. (1986). Marine pollution (3rd ed., pp. 433–443). Oxford Science Press Publication, Clarendon Press.
CPCB. (2006). Water quality status of Yamuna River, Assessment and development of River Basin. pp. 1–115. Available at: www.cpcb.nic.in.
Das, J., Das, S. N., & Sahoo, R. K. (1997). Semidiurnal variation of some physico-chemical parameters in the Mahanadi estuary, east coast of India. Indian Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 26, 323–326.
Dehghanzadeh, R., et al. (2015). Integrated Assessment of spatial and temporal variations of groundwater quality in the Eastern Area of Urmia Salt Lake Basin Using multivariate statistical analysis. Water Resources Management, 29(4), 1351–1364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0877-7
Fan, X., et al. (2010). Assessment of river water quality in Pearl River Delta using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2(5), 1220–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.133
Gadhia, M., Surana, R., & Ansari, E. (2013). Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characterstics of Tapi Estuary in Hazira Industrial Area. Our Nature, 10(1), 249–257. https://doi.org/10.3126/on.v10i1.7811
Githaiga, K. B., et al. (2021). Water quality assessment, multivariate analysis and human health risks of heavy metals in eight major lakes in Kenya. Journal of Environmental Management, 297(July), 113410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113410
Helena, B., et al. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34(3), 807–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00225-0
Hinge, G., et al. (2022). Integrated groundwater quality analysis using Water Quality Index, GIS and multivariate technique: A case study of Guwahati City. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(16), 412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10544-0
Izonfuo, L., & Bariweni, A. (2010). The effect of urban runoff water and human activities on some physico- chemical parameters of the Epie Creek In The Niger Delta. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v5i1.54941.
Joseph, K. O., & Srivastava, J. P. (1993). Heavy metal load in edible oyster, Crassostrea madrasensis(Preston) from the Ennore Estuary in Madras. Journal of Environmental Biology, 14(2), 121–127.
Khullar, S., & Singh, N. (2022). Water quality assessment of a river using deep learning Bi-LSTM methodology: Forecasting and validation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(9), 12875–12889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13875-w
Koklu, R., Sengorur, B., & Topal, B. (2010). Water quality assessment using multivariate statistical methods-a case study: Melen river system (Turkey). Water Resources Management, 24(5), 959–978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9481-7
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313(1–3), 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6
Mandal, P., Upadhyay, R., & Hasan, A. (2010). Seasonal and spatial variation of Yamuna River water quality in Delhi, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170(1–4), 661–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1265-2
Odokuma, L. O., & Okpokwasili, G. C. (1997). Seasonal influences of the organic pollution monitoring of the New Calabar River, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 45(1), 43–56. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005709709031
Ogwueleka, T. C. (2015). Use of multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of temporal and spatial variations in water quality of the Kaduna River, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4354-4.
Pati, S., et al. (2014). Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in the coastal region of Visakhapatnam, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(10), 6385–6402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3862-y
Priya, K. L., & Arulraj, G. P. (2011). A correlation-regression model for the physicochemical parameters of the groundwater in Coimbatore city, India. Environmental Technology, 32(7), 731–738. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2010.510852
Rajasegar, M. (2003). Physico-chemical characteristics of the Vellar estuary in relation to shrimp farming. Journal of environmental biology, 24(1), 95—101. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/12974418.
Rana, A., et al. (2012). Trend analysis for rainfall in Delhi and Mumbai, India. Climate Dynamics, 38(1–2), 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1083-4
Setia, R., et al. (2021). Hydrochemical evaluation of surface water quality of Sutlej river using multi-indices, multivariate statistics and GIS. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80(17), 565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09875-1
Sharma, D., & Kansal, A. (2011). Water quality analysis of River Yamuna using water quality index in the national capital territory, India (2000–2009). Applied Water Science, 1(3–4), 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-011-0011-4
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling and Software, 22(4), 464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.02.001
Singh, K. P., et al. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India) - A case study. Water Research, 38(18), 3980–3992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011
Singh, G. et al. (2020). Assessment of spatial and temporal variations in water quality by the application of multivariate statistical methods in the Kali River, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08307-0.
Upadhyay, R., et al. (2011). Managing water quality of River Yamuna in NCR Delhi. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 36(9–11), 372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2010.03.018
Vega, M., et al. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32(12), 3581–3592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00138-9
Venkatramanan, S., et al. (2014). Assessment of river water quality via environmentric multivariate statistical tools and water quality index: A case study of Nakdong River Basin, Korea. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 9(2), 125–132.
Vieira, J. S., et al. (2012). Surface water quality assessment of Lis River Using multivariate statistical methods. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(9), 5549–5561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1267-5
Wang, Y., et al. (2013). Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 7(1), 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2012.10.003
Water Science School. (2018). Dissolved oxygen and water. U.S. Geological Survey’s (USGS).
Yilma, M., et al. (2019). Assessment and interpretation of river water quality in Little Akaki River using multivariate statistical techniques. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(7), 3707–3720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2000-8
Zhang, Y., et al. (2009). Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152(1–4), 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0300-z
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring Stations at Wazirabad and Okhla, Delhi Pollution Control Committee for providing data. The authors are grateful to the reviewers for giving their valuable time and suggestions to improve the quality of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NV has completed the research work under the supervision of GS and NA. The manuscript was written by NV and critically reviewed by GS and NA. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, N., Singh, G. & Ahsan, N. Assessment of Spatiotemporal Variations in Water Quality of the Urban River Reach, Yamuna, Delhi. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 571 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06569-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06569-1