Abstract
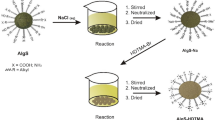
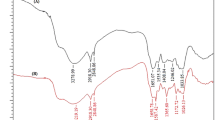
In this study, Medulla tetrapanacis (MT), a kind of herbaceous plant, was modified by phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to obtain the adsorbent MT-H3PO4-CTAB. It could quickly and efficiently remove the anionic azo dyes, Congo Red (CR) and Ponceau S (Po.S), from solution. For 500 mg/L CR and 150 mg/L Po.S dye solution, the removal efficiency could reach 84.52% and 95.29% within 10 min, and the maximum adsorption capacities of MT-H3PO4-CTAB towards CR and Po.S were 719.42 mg/g and 230.94 mg/g at 303 K, respectively. The effects of initial pH of the solution, temperature, initial dye concentration, and contact time were optimized. The adsorption process followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the equilibrium adsorption data fitted the Langmuir isotherm well. Moreover, thermodynamic studies indicated that the adsorption of two anionic azo dyes was spontaneous. The adsorption of CR onto MT-H3PO4-CTAB was endothermic while the adsorption of Po.S was exothermic. Molecular interactions, such as electrostatic attraction and hydrogen bonding between dyes molecules and adsorbent, play an important role in the adsorption process. This study demonstrates that acid-activated and surfactant-modified herbaceous plant adsorbent has a simple preparation process and exhibits excellent adsorption properties for anionic azo dyes, which could extend the potential applicability for biomass.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aravindhan, R., Rao, J. R., & Nair, B. U. (2007). Removal of basic yellow dye from aqueous solution by sorption on green alga Caulerpa scalpelliformis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142(1–2), 68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.058
Bayramoglu, G., & Arica, M. Y. (2021). Grafting of regenerated cellulose films with fibrous polymer and modified into phosphate and sulfate groups: Application for removal of a model azo-dye. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 614, 126173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126173
Bayramoglu, G., Salih, B., Akbulut, A., & Arica, M. Y. (2019). Biodegradation of Cibacron Blue 3GA by insolubilized laccase and identification of enzymatic byproduct using MALDI-ToF-MS: Toxicity assessment studies by Daphnia magna and Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 170, 453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.014
Cao, J., Sanganyado, E., Liu, W., Zhang, W., & Liu, Y. (2019). Decolorization and detoxification of Direct Blue 2B by indigenous bacterial consortium. Journal of Environmental Management, 242, 229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.067
Chen, L., & Bai, B. (2013). Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic, and in situ regeneration studies about methylene blue adsorption by the raspberry-like TiO2@yeast microspheres. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52(44), 15568–15577. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4020364
Chen, H., Sharma, S. K., Sharma, P. R., Chi, K., Fung, E., Aubrecht, K., Keroletswe, N., Chigome, S., & Hsiao, B. S. (2021). Nitro-oxidized carboxycellulose nanofibers from moringa plant: Effective bioadsorbent for mercury removal. Cellulose, 28(13), 8611–8628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04057-5
Dogan, M., Abak, H., & Alkan, M. (2009). Adsorption of methylene blue onto hazelnut shell: Kinetics, mechanism and activation parameters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(1), 172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.155
Fadillah, G., Saleh, T. A., & Wahyuningsih, S. (2019). Enhanced electrochemical degradation of 4-Nitrophenol molecules using novel Ti/TiO2-NiO electrodes. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 289, 111108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111108
Fu, J., Chen, Z., Wang, M., Liu, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Han, R., & Xu, Q. (2015). Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chemical Engineering Journal, 259, 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.101
Gomaa, H., Sayed, A., Mahross, M. H., Abdel-Hakim, M., Othman, I. M. M., Li, J., & El-Bahy, S. M. (2022). A hybrid spongy-like porous carbon-based on azopyrazole-benzenesulfonamide derivative for highly selective Fe3+-adsorption from real water samples. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 330, 111578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111578
Gomaa, H., Shenashen, M. A., Cheira, M. F., Sueki, K., Seaf El-Nasr, T. A., Selim, M. M., & El-Safty, S. A. (2023). Green extraction of uranium (238U) from natural radioactive resources. Chemical Engineering Journal, 461, 142014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142014
Gorgulu Ari, A., & Celik, S. (2013). Biosorption potential of Orange G dye by modified Pyracantha coccinea: Batch and dynamic flow system applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226, 263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.073
Heo, J. W., An, L., Chen, J., Bae, J. H., & Kim, Y. S. (2022). Preparation of amine-functionalized lignins for the selective adsorption of Methylene blue and Congo red. Chemosphere, 295, 133815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133815
Hussain, D., Khan, S. A., & Khan, T. A. (2021). Fabrication and characterization of mesoporous guar gum/NiWO4 nanocomposite for efficient adsorption of phloxine B and crystal violet from aqueous solution and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Colloid and Interface Science Communications, 44, 100488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100488
Ihsanullah, A. A., Al-Amer, A. M., Laoui, T., Al-Marri, M. J., Nasser, M. S., Khraisheh, M., & Atieh, M. A. (2016). Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: Critical review of adsorption applications. Separation and Purification Technology, 157, 141–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.11.039
Jia, Z., Li, Z., Ni, T., & Li, S. (2017). Adsorption of low-cost absorption materials based on biomass (Cortaderia selloana flower spikes) for dye removal: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 229, 285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.12.059
Jin, Y., Zeng, C., Lu, F., & Yu, Y. (2019). Efficient adsorption of methylene blue and lead ions in aqueous solutions by 5-sulfosalicylic acid modified lignin. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 123, 50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.213
Karaman, C., Karaman, O., Show, P. L., Karimi-Maleh, H., & Zare, N. (2022). Congo red dye removal from aqueous environment by cationic surfactant modified-biomass derived carbon: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic modeling, and forecasting via artificial neural network approach. Chemosphere, 290, 133346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133346
Khan, T. A., Sharma, S., Khan, E. A., & Mukhlif, A. A. (2014). Removal of congo red and basic violet 1 by chir pine (Pinus roxburghii) sawdust, a saw mill waste: Batch and column studies. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 96(4), 555–568. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2014.959017
Khan, T. A., Rahman, R., & Khan, E. A. (2016). Decolorization of bismarck brown R and crystal violet in liquid phase using modified pea peels: Non-linear isotherm and kinetics modeling. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2(3), 141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0195-6
Khan, T. A., Nouman, M., Dua, D., Khan, S. A., & Alharthi, S. S. (2022). Adsorptive scavenging of cationic dyes from aquatic phase by H3PO4 activated Indian jujube (Ziziphus mauritiana) seeds based activated carbon: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic study. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 26(2), 101417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101417
Khodabandehloo, A., Rahbar-Kelishami, A., & Shayesteh, H. (2017). Methylene blue removal using Salix babylonica (Weeping willow) leaves powder as a low-cost biosorbent in batch mode: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 244, 540–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.108
Li, D., Li, H., Wu, H., & Wang, Y. (2021). Using the group contribution method and molecular dynamics to predict the glass transition temperatures and mechanical properties of poly-(p-phenylenediamine-alt-2,6-diformyl multiphenyl). Journal of Chemical Research, 45(9–10), 823–830. https://doi.org/10.1177/17475198211011696
Litefti, K., Freire, M. S., Stitou, M., & Gonzalez-Alvarez, J. (2019). Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 16530. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53046-z
Liu, H., Cai, X., Wang, Y., & Chen, J. (2011). Adsorption mechanism-based screening of cyclodextrin polymers for adsorption and separation of pesticides from water. Water Research, 45(11), 3499–3511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.04.004
Liu, B., Yang, M., Yang, D., Chen, H., & Li, M. (2018). Medulla tetrapanacis-derived O/N co-doped porous carbon materials for efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts and high-rate supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 272, 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.04.001
Liu, Q., Li, Y., Chen, H., Lu, J., Yu, G., Moslang, M., & Zhou, Y. B. (2020). Superior adsorption capacity of functionalised straw adsorbent for dyes and heavy-metal ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 382, 121040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121040
Mahmoud, M. E., Abdelfattah, A. M., Tharwat, R. M., & Nabil, G. M. (2020). Adsorption of negatively charged food tartrazine and sunset yellow dyes onto positively charged triethylenetetramine biochar: Optimization, kinetics and thermodynamic study. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 318, 114297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114297
Moradi, O., & Sharma, G. (2021). Emerging novel polymeric adsorbents for removing dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive review and comparison with other adsorbents. Environmental Research, 201, 111534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111534
Nodehi, R., Shayesteh, H., & Kelishami, A. R. (2020). Enhanced adsorption of congo red using cationic surfactant functionalized zeolite particles. Microchemical Journal, 153, 104281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104281
Ntakirutimana, S., Tan, W., & Wang, Y. (2019). Enhanced surface activity of activated carbon by surfactants synergism. RSC Advances, 9(45), 26519–26531. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA04521J
Pang, X., Sellaoui, L., Franco, D., Netto, M. S., Georgin, J., Luiz Dotto, G., Abu Shayeb, M. K., Belmabrouk, H., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., & Li, Z. (2020). Preparation and characterization of a novel mountain soursop seeds powder adsorbent and its application for the removal of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 391, 123617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123617
Patra, C., Gupta, R., Bedadeep, D., & Narayanasamy, S. (2020). Surface treated acid-activated carbon for adsorption of anionic azo dyes from single and binary adsorptive systems: A detail insight. Environmental Pollution, 266(2), 115102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115102
Plaza Cazon, J., Bernardelli, C., Viera, M., Donati, E., & Guibal, E. (2012). Zinc and cadmium biosorption by untreated and calcium-treated Macrocystis pyrifera in a batch system. Bioresource Technology, 116, 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.014
Prajapati, A. K., & Mondal, M. K. (2021). Development of CTAB modified ternary phase α-Fe2O3-Mn2O3-Mn3O4 nanocomposite as innovative super-adsorbent for Congo red dye adsorption. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104827
Rehman, M. S. U., Munir, M., Ashfaq, M., Rashid, N., Nazar, M. F., Danish, M., & Han, J. I. (2013). Adsorption of Brilliant Green dye from aqueous solution onto red clay. Chemical Engineering Journal, 228, 54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.094
Sakr, A. K., Al-Hamarneh, I. F., Gomaa, H., Abdel Aal, M. M., Hanfi, M. Y., Sayyed, M. I., Khandaler, M. U., & Cheira, M. F. (2022). Removal of uranium from nuclear effluent using regenerated bleaching earth steeped in β-naphthol. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 200, 110204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2022.110204
Saleh, T. A., Sari, A., & Tuzen, M. (2019). Carbon nanotubes grafted with poly(trimesoyl, m-phenylenediamine) for enhanced removal of phenol. Journal of Environmental Management, 252, 109660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109660
Sathishkumar, K., AlSalhi, M. S., Sanganyado, E., Devanesan, S., Arulprakash, A., & Rajasekar, A. (2019). Sequential electrochemical oxidation and bio-treatment of the azo dye congo red and textile effluent. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 200, 111655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111655
Shao, H., Li, Y., Zheng, L., Chen, T., & Liu, J. (2017). Removal of methylene blue by chemically modified defatted brown algae Laminaria japonica. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 80, 525–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.08.023
Shayesteh, H., Rahbar-Kelishami, A., & Norouzbeigi, R. (2016). Evaluation of natural and cationic surfactant modified pumice for congo red removal in batch mode kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 221, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.05.053
Siddiqui, M. F., Khan, S. A., Hussain, D., Tabrez, U., Ahamad, I., Fatma, T., & Khan, T. A. (2022). A sugarcane bagasse carbon-based composite material to decolor and reduce bacterial loads in waste water from textile industry. Industrial Crops and Products, 176, 114301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114301
Sun, Q., & Yang, L. (2003). The adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution on modified peat–resin particle. Water Research, 37(7), 1535–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00520-1
Sun, Y., Gu, Y., & Zha, Q. (2021). A novel surface imprinted resin for the selective removal of metal-complexed dyes from aqueous solution in batch experiments: ACB GGN as a representative contaminant. Chemosphere, 280, 130611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130611
Tang, Z., Peng, S., Hu, S., & Hong, S. (2017). Enhanced removal of bisphenol-AF by activated carbon-alginate beads with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 495, 191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.103
Wang, W., Huang, G., An, C., Xin, X., Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2017). Transport behaviors of anionic azo dyes at interface between surfactant-modified flax shives and aqueous solution: Synchrotron infrared and adsorption studies. Applied Surface Science, 405, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.311
Wang, G., Zhang, J., Lin, S., Xiao, H., Yang, Q., Chen, S., Yan, B., & Gu, Y. (2019). Environmentally friendly nanocomposites based on cellulose nanocrystals and polydopamine for rapid removal of organic dyes in aqueous solution. Cellulose, 27(4), 2085–2097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02944-6
Wong, S., Tumari, H. H., Ngadi, N., Mohamed, N. B., Hassan, O., Mat, R., & Saidina Amin, N. A. (2019). Adsorption of anionic dyes on spent tea leaves modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI-STL). Journal of Cleaner Production, 206, 394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.201
Xu, X., Gao, B., Yue, Q., & Zhong, Q. (2010). Preparation and utilization of wheat straw bearing amine groups for the sorption of acid and reactive dyes from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 182(1–3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.071
Yao, Y., Xu, F., Chen, M., Xu, Z., & Zhu, Z. (2010). Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on carbon nanotubes. Bioresource Technology, 101(9), 3040–3046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.042
Yao, A., Yan, Y., Tan, L., Shi, Y., Zhou, M., Zhang, Y., Zhu, P., & Huang, S. (2021). Improvement of filtration and antifouling performance of cellulose acetate membrane reinforced by dopamine modified cellulose nanocrystals. Journal of Membrane Science, 637, 119621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119621
You, X., Wang, R., Zhu, Y., Sui, W., & Cheng, D. (2021). Comparison of adsorption properties of a cellulose-rich modified rice husk for the removal of methylene blue and aluminum (III) from their aqueous solution. Industrial Crops and Products, 170, 113687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113687
Yu, L., Kanezashi, M., Nagasawa, H., & Tsuru, T. (2017). Fabrication and CO2 permeation properties of amine-silica membranes using a variety of amine types. Journal of Membrane Science, 541, 447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.07.024
Zhang, L., Li, W., Cao, H., Hu, D., Chen, X., Guan, Y., Tang, J., & Gao, H. (2019). Ultra-efficient sorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions by light biochar derived from Medulla tetrapanacis. Bioresource Technology, 291, 121818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121818
Zhou, B., Wang, Z., Shen, D., Shen, F., Wu, C., & Xiao, R. (2017). Low cost earthworm manure-derived carbon material for the adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous solution: Impact of pyrolysis temperature. Ecological Engineering, 98, 189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.061
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (21374029, 21776076), Open Research Fund of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Chemical Processes, East China Normal University and Open Research Fund of International Joint Laboratory on Resource Chemistry, Shanghai Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lianpeng Yan carried out the concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, data acquisition, data analysis and manuscript preparation. Keming Zhou provided assistance for data acquisition, data analysis and statistical. Rui Zhang and Xuedong Zhu performed manuscript review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
I have not submitted my manuscript to a preprint server before submitting it to Water, Air, & Soil Pollution.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Zhou, K., Zhang, R. et al. Efficient Adsorption of Anionic Azo Dye in Wastewater with Medulla tetrapanacis Modified by Cationic Surfactant. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 511 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06464-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06464-9