Abstract
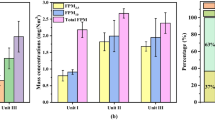
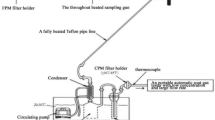
Combustion is an effective disposal method for sewage sludge (SS), but the corresponding condensable particulate matter (CPM) emission poses a big risk to the environment. To investigate the CPM characteristics from pelleted SS combustion, tests were conducted in a tube furnace experimental system, and the effects of combustion temperatures on CPM generation and the impacts of sampling temperatures on CPM migration were studied. Results showed that the inorganic components took up the majority (60.75–86.24%) of the total CPM. Significant PO43− was first detected in CPM mainly due to the remarkable phosphorus content in SS. The CPM exhibited distinct acidity, and SO42− was the primary water-soluble ion in CPM, followed by PO43− and Cl−. Ca, Na, and K accounted for the vast majority of metal elements in CPM. Alkanes and esters were the predominant organic species of CPM. With the combustion temperature increasing, the inorganic CPM increased by the enhanced volatilization of relevant elements, and the organic CPM decreased owing to the improved combustion conditions. As the sampling temperature decreased, more CPM precursors converted to FPM, resulting in a decrease in both inorganic and organic components of CPM. Particularly, a drastic cooling process contributed to the enlargement of CPM by strengthening the heterogeneous condensation and agglomeration. CPM from SS incineration could do great harm to the environment and human health for its fine particle size and complex compositions, and combustion control and proper flue gas cooling devices would be conducive to CPM control.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Batistella, L., Silva, V., Suzin, R. C., Virmond, E., Althoff, C. A., Moreira, R. F., & José, H. J. (2015). Gaseous emissions from sewage sludge combustion in a moving bed combustor. Waste Management, 46, 430–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.08.039
Beck, J., & Unterberger, S. (2006). The behaviour of phosphorus in the flue gas during the combustion of high-phosphate fuels. Fuel, 85(10), 1541–1549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.01.005
Beck, J., & Unterberger, S. (2007). The behaviour of particle bound phosphorus during the combustion of phosphate doped coal. Fuel, 86(5), 632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.08.028
Beck, J., Brandenstein, J., Unterberger, S., & Hein, K. (2004). Effects of sewage sludge and meat and bone meal Co-combustion on SCR catalysts. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental, 49, 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.007
Beck, J., Müller, R., Brandenstein, J., Matscheko, B., Matschke, J., Unterberger, S., & Hein, K. R. G. (2005). The behaviour of phosphorus in flue gases from coal and secondary fuel co-combustion. Fuel, 84(14), 1911–1919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2005.03.011
Bekiaris, G., Bruun, S., Peltre, C., Houot, S., & Jensen, L. S. (2015). FTIR-PAS: A powerful tool for characterising the chemical composition and predicting the labile C fraction of various organic waste products. Waste Management, 39, 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.02.029
Bozdogan Sert, E., Turkmen, M., & Cetin, M. (2019). Heavy metal accumulation in rosemary leaves and stems exposed to traffic-related pollution near Adana-İskenderun Highway (Hatay, Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(9), 553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7714-7
Cetin, M., Aljama, A. M. O., Alrabiti, O. B. M., Adiguzel, F., Sevik, H., & Zeren Cetin, I. (2022). Determination and mapping of regional change of Pb and Cr pollution in Ankara City Center. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(5), 163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05638-1
Cetin, M., Aljama, A. M. O., Alrabiti, O. B. M., Adiguzel, F., Sevik, H., & Zeren Cetin, I. (2022). Using topsoil analysis to determine and map changes in Ni Co pollution. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(8), 293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05762-y
Cetin, M., & Jawed, A. A. (2022). Variation of Ba concentrations in some plants grown in Pakistan depending on traffic density.Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02334-2
Cieslik, B. M., Namiesnik, J., & Konieczka, P. (2015). Review of sewage sludge management: Standards, regulations and analytical methods. Journal of Cleaner Production, 90, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.031
Cong, S., Feng, D., Yousong, Z., Jian, L., Jinpeng, Z., & Lihui, Z. (2013). SO2 emission from municipal sewage sludge cocombustion with bituminous coal under O2/CO2 atmosphere versus O2/N2 atmosphere. Energy & Fuels, 27, 7067–7071. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef401342x
Feng, Y., Li, Y., & Cui, L. (2018). Critical review of condensable particulate matter. Fuel, 224, 801–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.118
Feng, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, Z., Dong, Y., & Ma, C. (2020). Characteristics of condensable particulate matter discharging from a one-dimensional flame furnace firing lignite. Fuel, 277, 118198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118198
Feng, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Su, S., Zhang, Z., Gan, Z., & Dong, Y. (2021). Comparative study on the characteristics of condensable particulate matter emitted from three kinds of coal. Environmental Pollution, 270, 116267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116267
Johansen, J., Jakobsen, J., Frandsen, F., & Glarborg, P. (2011). Release of K, Cl, and S during pyrolysis and combustion of high-chlorine biomass. Energy & Fuels, 25, 4961–4971. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef201098n
Kacprzak, M., Neczaj, E., Fijalkowski, K., Grobelak, A., Grosser, A., Worwag, M., Rorat, A., Brattebo, H., Almas, A., & Singh, B. R. (2017). Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environmental Research, 156, 39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.03.010
Lee, C.-G., Alvarez, P. J. J., Kim, H.-G., Jeong, S., Lee, S., Lee, K. B., Lee, S.-H., & Choi, J.-W. (2018). Phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge using calcium silicate hydrates. Chemosphere, 193, 1087–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.129
Li, J., Li, X., Zhou, C., Li, M., Lu, S., Yan, J., & Qi, Z. (2017). Study on the influencing factors of the distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in condensable particulate matter. Energy & Fuels, 31(12), 13233–13238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01991
Li, J., Qi, Z., Li, M., Wu, D., Zhou, C., Lu, S., Yan, J., & Li, X. (2017). Physical and chemical characteristics of condensable particulate matter from an ultralow-emission coal-fired power plant. Energy & Fuels, 31(2), 1778–1785. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02919
Li, Y., Cui, R., Yang, T., Zhai, Z., & Li, R. (2017). Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in different size fly ash from a sewage sludge circulating fluidized bed incinerator. Energy & Fuels, 31(2), 2044–2051. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02676
Li, X., Zhou, C., Li, J., Lu, S., & Yan, J. (2019). Distribution and emission characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter before and after a low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13), 12798–12806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04570-y
Li, Y., Man, J., Fang, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, F., & Li, R. (2019). Formation and growth mechanisms of ultrafine particles in sludge-incineration flue gas. Waste Disposal & Sustainable Energy, 1(2), 143–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-019-00008-w
Li, R., Man, J., Fang, Z., Li, Y., Liu, F., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Effects of particle size and additives on the formation of fine particulate matter during sludge incineration. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1834028
Lin, Y., Zou, J., Yang, W., & Li, C. Q. (2018). A review of recent advances in research on PM(2.5) in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030438
Mian, I., Li, X., Dacres, O. D., Wang, J., Wei, B., Jian, Y., Zhong, M., Liu, J., Ma, F., & Rahman, N. (2020). Combustion kinetics and mechanism of biomass pellet. Energy, 205, 117909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117909
Pan, P., Li, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, N., & Chen, H. (2022). Effect of temperature on hot corrosion of nickel-based alloys for 700°C A-USC power plants. Corrosion Science, 203, 110350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2022.110350
Pei, B., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Hu, M., Sun, Y., Deng, J., Dong, L., Fu, Q., & Yan, N. (2016). Emissions and source profiles of PM25 for coal-fired boilers in the Shanghai megacity, China. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 7(4), 577–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.01.005
Qi, Z., Li, J., Wu, D., Xie, W., Li, X., & Liu, C. (2017). Particulate matter emission characteristics and removal efficiencies of a low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator. Energy & Fuels, 31(2), 1741–1746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02692
Syed-Hassan, S. S. A., Wang, Y., Hu, S., Su, S., & Xiang, J. (2017). Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: Fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 80, 888–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.262
Wang, G., Deng, J., Ma, Z., Hao, J., & Jiang, J. (2018). Characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter emitted from two waste incineration power plants in China. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 695–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.105
Wang, Y. G., Liu, Y., Yang, W. J., Zhao, Q. X., & Dai, Y. J. (2020). Evaluation of combustion properties and pollutant emission characteristics of blends of sewage sludge and biomass. Science of the Total Environment, 720, 137365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137365
Werle, S., & Wilk, R. K. (2010). A review of methods for the thermal utilization of sewage sludge: The Polish perspective. Renewable Energy, 35(9), 1914–1919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2010.01.019
Werther, J., & Ogada, T. (1999). Sewage sludge combustion. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 25(1), 55–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-1285(98)00020-3
Wu, H., Castro, M., Jensen, P. A., Frandsen, F. J., Glarborg, P., Dam-Johansen, K., Røkke, M., & Lundtorp, K. (2011). Release and transformation of inorganic elements in combustion of a high-phosphorus fuel. Energy and Fuels, 25, 2874–2886. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef200454y
Wyslouzil, B. E., & Wölk, J. (2016). Overview: Homogeneous nucleation from the vapor phase-The experimental science. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 145, 211702. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962283
Xu, J., Zhang, J., Yu, Y., Meng, Q., & Zhong, H. (2016). Characteristics of vapor condensation on coal-fired fine particles. Energy & Fuels, 30(3), 1822–1828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02200
Xu, J., Yu, Y., Zhang, J., Meng, Q., & Zhong, H. (2017). Heterogeneous condensation of water vapor on particles at high concentration. Powder Technology, 305, 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2016.09.078
Xu, Z., Wu, Y., Liu, S., Tang, M., & Lu, S. (2022). Distribution and emission characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter in the flue gas emitted from an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), 107667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107667
Xu, J., Shen, G., Fu, B., Han, Y., Suo, X., Chen, Z., Lai, Y., Li, J., Li, L., Han, L., Tao, S., & Li, B. (2023). Emissions ofparticulate and previously ignored gaseous phosphorus from coal and biomass combustion in household stoves. Environmental Science & Technology Letters. (on line) https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.3c00029
Yang, H.-H., Lee, K.-T., Hsieh, Y.-S., Luo, S.-W., & Li, M.-S. (2014). Filterable and condensable fine particulate emissions from stationary sources. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 14(7), 2010–2016. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.08.0178
Yang, G., Zhang, G., & Wang, H. (2015). Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Research, 78, 60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.002
Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, L., Wang, X., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Environmental investigation on co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal gangue: SO2, NOx and trace elements emissions. Waste Management, 50, 213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.011
Yang, H.-H., Arafath, S. M., Lee, K.-T., Hsieh, Y.-S., & Han, Y.-T. (2018). Chemical characteristics of filterable and condensable PM2.5 emissions from industrial boilers with five different fuels. Fuel, 232, 415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.080
Yang, H.-H., Gupta, S. K., Dhital, N. B., Lee, K.-T., Hsieh, Y.-S., & Huang, S.-C. (2019). Establishment of indicatory metals for filterable and condensable PM2.5 emitted from important stationary emission sources. Energy & Fuels, 33(11), 10878–10887. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b02889
Yang, W., Zou, L., Shao, H., Zhao, Q., & Wang, Y. (2022). Research on thermal behaviors and NOx release properties during combustion of sewage sludge, sawdust, and their blends. ACS Omega, 7(23), 20172–20185. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c02015
Yi, X., Ruihua, Z., & Juan, C. (2021). Phosphorous transformation during coal and sewage sludge co-combustion. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 793, 012034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/793/1/012034
Yuan, C., Wang, Z., Cheng, H., Liang, S., Hu, Y., Dong, X., & Wu, J. (2021). Characteristics of water-soluble ions in condensable particulate matter emitted from stationary sources in Wuhan. Fuel, 295, 120626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120626
Yuan, C., Liang, S., Cheng, H., Xu, R., Su, S., Yao, Z., Wang, P., Tuo, X., & Wang, Z. (2022). Assessing the dry impinger method for condensable particulate matter from ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant measurement. Science of the Total Environment, 834, 155002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155002
Zhang, L., & Ninomiya, Y. (2007). Transformation of phosphorus during combustion of coal and sewage sludge and its contributions to PM10. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 31(2), 2847–2854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2006.07.113
Zheng, C., Hong, Y., Liu, S., Yang, Z., Chang, Q., Zhang, Y., & Gao, X. (2018). Removal and emission characteristics of condensable particulate matter in an ultralow emission power plant. Energy & Fuels, 32(10), 10586–10594. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b02464
Zheng, C., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, Z., Qu, R., Ye, D., Liang, C., Liu, S., & Gao, X. (2019). Formation, transformation, measurement, and control of SO3 in coal-fired power plants. Fuel, 241, 327–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.12.039
Zheng, C., Zheng, H., Shen, J., Gao, W., Yang, Z., Zhao, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., & Gao, X. (2020). Evolution of condensable fine particle size distribution in simulated flue gas by external regulation for growth enhancement. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(7), 3840–3848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06569
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC3001803), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51876165), and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2021 GXLH-Z-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenjun Yang and Huaishuang Shao contributed to the writing of the original draft, data curation, investigation, and conceptualization. Li Zou and Shifeng Deng contributed to the interpretation and corrections. Qinxin Zhao supervised the findings of this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Shao, H., Zou, L. et al. Research on Condensable Particulate Matter Emission Characteristics from Sewage Sludge Combustion. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 372 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06379-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06379-5