Abstract
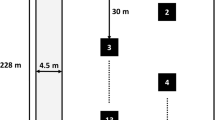
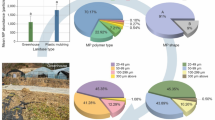
The amount and characteristics of micro- (100 nm to 5 mm) and mesoplastics (5 to 20 mm) in farmlands irrigated with three different water sources (groundwater, surface water, and treated wastewater effluent) in the south of Tehran were determined. Uncultivated fields were used as controls to provide background plastic concentrations. Soil samples were analyzed using ZnCl2 density extraction, H2O2 digestion, and Raman spectroscopy. In farmlands with surface water irrigation, the abundance of microplastics (326–2406 particles.kg–1) was significantly higher than that in farmlands with groundwater irrigation source (274–2053 particles.kg–1) and treated wastewater (114–800 particles.kg–1). The microplastic concentrations in the uncultivated control fields was 33–52 particles.kg–1. Mesoplastics were found with abundances of 5 to 134, 7 to 260 and 11 to 660 particles.kg–1 in soil samples for irrigation with treated wastewater, surface water and groundwater, respectively, and 2 to 11 particles.kg–1 were found in the uncultivated control fields. These fibers were found to be the most abundant plastic form in all three farmlands, followed by fragments and films. We found that irrigation can be a considerable source of micro- and mesoplastic in soil, while compost fertilizing practices may affect plastic pollution. The results shed light on the extent of micro- mesoplastic pollution in agricultural fields, highlighting the need for further investigation into the factors that influence soil plastic pollution.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The manuscript has data included as electronic supplementary material.
References
Alavian Petroody, S. S., Hashemi, S. H., & van Gestel, C. A. (2020). Factors affecting microplastics retention and emission by a wastewater treatment plant on the southern coast of Caspian Sea. Chemosphere, 261, 128179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128179
Amrutha, A., & Warrier, A. K. (2020). The first report on the source–to–sink characterization of microplastic pollution from a riverine environment in tropical India. Science of The Total Environment, 739, 140377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140377
ASTM–C702/C702M. (2018). Standard Practice for Reducing Samples of Aggregate to Testing Size, C702/C702M–18. ASTM International.
Bellas, J., Martínez-Armental, J., Martínez-Cámara, A., Besada, V., & Martínez-Gómez, C. (2016). Ingestion of microplastics by demersal fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 109, 55–60.
Beriot, N., Peek, J., Zornoza, R., Geissen, V., & Lwanga, E. (2021). Low density–microplastics detected in sheep faeces and soil: a case study from the intensive vegetable farming in Southeast Spain. Science of The Total Environment, 755, 142653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142653
Bharath, K. M., Natesan, U., Vaikunth, R., Kumar, P., Ruthra, R., & Srinivasalu, S. (2021). Spatial distribution of microplastic concentration around landfill sites and its potential risk on groundwater. Chemosphere, 277, 130263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130263
Blasing, M., & Amelung, W. (2018). Plastics in soil: analytical methods and possible sources. Science of The Total Environment, 612, 422–435.
Boughattas, I., Hattab, S., Zitouni, N., Mkhinini, M., Missawi, O., Bousserrhine, N., & Banni, M. (2021). Assessing the presence of microplastic particles in Tunisian agriculture soils and their potential toxicity effects using Eisenia Andrei as bioindicator. Science of The Total Environment, 796, 148959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148959
Brahney, J., Mahowald, N., Prank, M., Cornwell, G., Klimont, Z., Matsui, H., & Kimberly, A. P. (2021). Constraining the atmospheric limb of the plastic cycle. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118, e2020719118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2020719118
Browne, M. A., Crump, P., Niven, S. J., Teuten, E., Tonkin, A., Galloway, T., & Thompson, R. (2011). Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: sources and sinks. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(21), 9175–9179.
Di, M., & Wang, J. (2018). Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Science of The Total Environment., 616, 1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.150
Ding, L., Zhang, S., Wang, X., Yang, X., Zhang, C., Qi, Y., & Guo, X. (2020). The occurrence and distribution characteristics of microplastics in the agricultural soils of Shaanxi Province, in north–western China. Science of The Total Environment, 720, 137525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137525
Ding, L., Wang, X., Ouyang, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Liu, D., Liu, S., Yang, X., Jia, H., & Guo, X. (2021). The occurrence of microplastic in Mu Us Sand Land soils in northwest China: Different soil types, vegetation cover and restoration years. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403, 123982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123982
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). (2016). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA Journal, 14, 4501. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4501
Faure, F., Demars, C., Wieser, O., Kunz, M., & Felippe de Alencastro, L. (2015). Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environment and Chemistry, 12, 582–591. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14218
Geyer, R., Jambeck, J. R., & Law, K. L. (2017). Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Science Advances, 3, e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Gigault, J., ter Halle, A., Baudrimont, M., Pascal, P. Y., Gauffre, F., Phi, T. L., Hadri, H. E., Grassl, B., & Reynaud, S. (2018). Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environmental Pollution, 235, 1030–1034.
Gui, J., Sun, Y., Wang, J., Chen, X., Zhang, S., & Wu, D. (2021). Microplastics in composting of rural domestic waste: abundance, characteristics, and release from the surface of macroplastics. Environmental Pollution, 274, 116553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116553
Horton, A. A., Walton, A., Spurgeon, D. J., Lahive, E., & Svendsen, C. (2017). Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Science of The Total Environment, 586, 127–141.
Hu, L., Chernick, M., Hinton, D. E., & Shi, H. (2018). Microplastics in small water bodies and tadpoles from Yangtze River Delta, China. Environmental Science Technology, 52, 8885–8893. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02279
Huang, Y., Liu, Q., Jia, W., Yan, C., Wang, J. (2020). Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114096
Huerta-Lwanga, E., Gertsen, H., Gooren, H., Peters, P., Salánki, T., van der Ploeg, M., Besseling, E., Koelmans, A. A., & Geissen, V. (2016). Microplastics in the terrestrial ecosystem: implications for Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 2685–2691.
Kong, S., Ji, Y., Liu, L., Chen, L., Zhao, X., Wang, J., Bai, Z., & Sun, Z. (2012). Diversities of phthalate esters in suburban agricultural soils and wasteland soil appeared with urbanization in China. Environmental Pollution, 170, 161–168.
Li, X., Chen, L., Mei, Q., Dong, B., Dai, X., Ding, G., & Zeng, E. Y. (2018). Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater treatment plants in China. Water Resources, 142, 75–85.
Liu, M., Lu, S., Song, Y., Lei, L., Hu, J., Lv, W., Zhou, W., Cao, C., Shi, H., Yang, X., & He, D. (2018). Microplastic and mesoplastic pollution in farmland soils in suburbs of Shanghai, China. Environment Pollution, 242, 855–862.
Lusher, A. L., Burke, A., O'Connor, I., & Officer, R. (2014). Microplastic pollution in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: validated and opportunistic sampling. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88, 325–333.
Lv, W., Zhou, W., Lu, S., Huang, W., Yuana, Q., Tian, M., Lv, W., & He, D. (2019). Microplastic pollution in rice-fish co-culture system: A report of three farmland stations in Shanghai, China. Science of The Total Environment, 652, 1209–1218.
Mahjoub, A., Hashemi, S. H., & Alavian Petroody, S. S. (2021). Microplastics in surface runoff (Case study: Tehran city), Master thesis. Shahid Beheshti University, Environmental Sciences Research Institute (ESRI).
Masura, J., Baker, J., Foster, G., & Arthur, C. (2015). Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in Beach Samples. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments (pp. 13–19). NOAA Technical Memorandum.
Mintenig, S. M., Loder, M. G. J., Primpke, S., & Gerdts, G. (2019). Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from groundwater sources. Science of The Total Environment, 648, 631–635.
Mizraji, R., Ahrendt, C., Perez-Venegas, D., Vargas, J., Pulgar, J., Aldana, M., Ojeda, F. P., Duarte, C., & Galbán-Malagón, C. (2017). Is the feeding type related with the content of microplastics in intertidal fish gut? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 116, 498–500.
Ng, E., Lwanga, E., Eldridge, S., Johnston, P., Hu, H., Geissen, V., & Chen, D. (2018). An overview of microplastic and nanoplastic pollution in agroecosystems. Science of The Total Environment, 627, 1377–1388.
Nizzetto, L., Futter, M., & Langaas, S. (2016). Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin? Environmental Science and Technology, 20, 10777–10779.
Panno, S. V., Kelly, W. R., Scott, J., Zheng, W., McNeish, R. E., Holm, N., Hoellein, T. J., & Baranski, E. L. (2019). Microplastic contamination in karst groundwater systems. Groundwater, 57, 189–196.
Parchianloo, S., Hashemi, S. H., & Alavian Petroody, S. S. (2021). Microplastics and fragments in urban solid waste compost (case study: Tehran compost plant), Master thesis. Shahid Beheshti University Environmental Sciences Research Institute (ESRI).
Pérez-Reverón, R., González-Sálamo, J., Hernández-Sánchez, C., González-Pleiter, M., Hernández-Borges, J., & Díaz-Peña, F. J. (2022). Recycled wastewater as a potential source of microplastics in irrigated soils from an arid-insular territory (Fuerteventura, Spain). Science of The Total Environment, 817, 152830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152830
Piehl, S., Leibner, A., Löder, M. G. J., Dris, R., Bogner, C., & Laforsch, C. (2018). Identification and quantification of macro– and microplastics on an agricultural farmland. Scientific Reports, 8, 17950. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36172-y
PlasticsEurope. (2021). Plastics–the facts: an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. https://www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/1115/7236/4388/FINAL_web_version_Plastics_the_facts2019_14102019.pdf.
Ragoobur, D., Huerta-Lwanga, E., & Devi Somaroo, G. (2021). Microplastics in agricultural soils, wastewater effluents and sewage sludge in Mauritius. Science of The Total Environment, 798, 149326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149326
Rodrigues, M. O., Abrantes, N., Gonçalves, F. J. M., Nogueira, H., Marques, J. C., & Gonçalves, A. M. M. (2018). Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Science of The Total Environment, 633, 1549–1559.
Selvam, S., Jesuraja, K., Venkatramanan, S., Roy, P. D., & Jeyanthi Kumari, V. (2021). Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 123786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123786
Shirazi, S., Mafigholami, R., Moghimi, H., & Borghaei, S. M. (2021). Quantitative and qualitative study of micro and nanoplastics in the effluent of the municipal wastewater treatment plant in the south of Tehran. Journal of Natural Environment, 65, 28–34.
Shruti, V., & Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. (2019). Bioplastics: missing link in the era of microplastics. Science of The Total Environment, 697, 134139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134139
Talvitie, J., Heinonen, M., Pääkkönen, J.-P., Vahtera, E., Mikola, A., Setälä, O., & Vahala, R. (2015). Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Science Technology, 729, 1495–1504.
Van Schothorst, B., Beriot, N., Huerta Lwanga, E., & Geissen, V. (2021). Sources of light density microplastic related to two agricultural practices: the use of compost and plastic mulch. Environments, 8, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8040036
Wang, Z., Taylor, S. E., Sharma, P., & Flury, M. (2018). Poor extraction efficiencies of polystyrene nano- and microplastics from biosolids and soil. PLoS One, 13(11), e0208009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208009
Wang, W., Ge, J., Yu, X., & Li, H. (2020). Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in soil ecosystems: progress and perspective. Science of The Total Environment, 708, 134841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134841
Weber, C. J., & Opp, C. (2020). Spatial patterns of mesoplastics and coarse microplastics in floodplain soils as resulting from land use and fluvial processes. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115390
WHO. (2006). Guidelines for the Safe use of Wastewater, Excreta and Grey Water. WHO.
Wolff, S., Kerpen, J., Prediger, J., Barkmann, L., & Müller, L. (2019). Determination of the microplastics emission in the effluent of a municipal waste water treatment plant using Raman microspectroscopy. Water Resources, 2, 100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wroa.2018.100014
Wu, R.-T., Cai, Y.-F., Chen, Y.-X., Yang, Y.-W., Xing, S.-C., & DiLiao, X. (2021). Occurrence of microplastic in livestock and poultry manure in South China. Environmental Pollution, 277, 116790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116790
Xu, B., Liu, F., Cryder, Z., Huang, D., Lu, Z., He, Y., Wang, H., Lu, Z., Brookes, P. C., Tang, C., Gan, J., & Xu, J. (2020). Microplastics in the soil environment: occurrence, risks, interactions and fate – a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 50, 2175–2222.
Ya, H., Jiang, B., Xing, Y., Zhang, T., Lv, M., & Wang, X. (2021). Recent advances on ecological effects of microplastics on soil environment. Science of The Total Environment, 798, 149338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149338
Yang, J., Li, R., Zhou, Q., Li, L., Li, Y., Tu, C., Zhao, X., Xiong, K., Christie, P., & Luo, Y. (2021). Abundance and morphology of microplastics in an agricultural soil following long–term repeated application of pig manure. Environmental Pollution, 272, 116028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116028
Yang, L., Zhang, Y., Kang, S., Wang, Z., & Wu, C. (2021). Microplastics in soil: A review on methods, occurrence, sources, and potential risk. Science of The Total Environment, 780, 146546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146546
Yu, L., Zhang, J. D., Liu, Y., Chen, L. Y., Tao, S., & Liu, W. X. (2021). Distribution characteristics of microplastics in agricultural soils from the largest vegetable production base in China. Science of The Total Environment, 756, 143860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143860
Yu, Y., & Flury, M. (2021). How to take representative samples to quantify microplastic particles in soil? Science of The Total Environment, 784, 147166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147166
Zhang, G. S., & Liu, Y. F. (2018). The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China. Science of The Total Environment, 642, 12–20.
Zhang, L., Sintim, H. Y., Bary, A. I., Hayes, D. G., Wadsworth, L. C., Anunciado, M. B., & Flury, M. (2018). Interaction of Lumbricus terrestris with macroscopic polyethylene and biodegradable plastic mulch. Science of The Total Environment, 635, 1600–1608.
Zhang, M., Zhao, Y., Qin, X., Jia, W., Chai, L., Huang, M., & Huang, L. (2019). Microplastics from mulching film is a distinct habitat for bacteria in farmland soil. Science of The Total Environment, 688, 470–478.
Zhou, Y., Liu, X., & Wang, J. (2019). Characterization of microplastics and the association of heavy metals with microplastics in suburban soil of central China. Science of The Total Environment, 694, 133798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133798
Zhou, Y., Wang, J., Zou, M., Jia, Z., Zhou, S., & Li, Y. (2020). Microplastics in soils: a review of methods, occurrence, fate, transport, ecological and environmental risks. Science of The Total Environment, 748, 141368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141368
Ziajahromi, S., Neale, P. A., Rintoul, L., & Leusch, F. D. L. (2017). Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: development of a new approach to sample wastewater–based microplastics. Water Resources, 112, 93–99.
Zubris, K. A. V., & Richards, B. K. (2005). Synthetic fibers as an indicator of land application of sludge. Environmental Pollution, 138, 201–211.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Freek Ariese of Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam for providing some of the reference Raman spectra.
Credit Author Statement
Conceptualization: Zohreh Salehi, Seyed Hossein Hashemi
Roles/Writing---original draft: Zohreh Salehi, Seyed Hossein Hashemi, Markus Flury
Methodology: Zohreh Salehi, Seyed Hossein Hashemi, Markus Flury
Formal analysis: Zohreh Salehi
Visualization: Zohreh Salehi, Seyed Hossein Hashemi
Writing---review & editing: all co-authors
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Differences in plastic abundance in farmlands with different irrigation waters were significant.
• The irrigated farmlands with surface water showed the highest microplastics contamination.
• The fertilized farmlands with compost showed the highest mesoplastics contamination.
• Polypropylene fibers and polyethylene particles were the most common in the farmlands.
• Polypropylene fibers were the most abundant particles in soil.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 32168 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, Z., Hashemi, S.H. & Flury, M. Micro- and Mesoplastics in Farmlands with Different Irrigation Water Sources. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 267 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06289-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06289-6