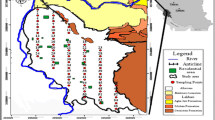
Abstract
The irrational use of pesticides has raised a negative influence on the environment and food security. Therefore, it is imperative to comprehend the current status of pesticide residues in the soil for agricultural production and their impact on the ecological environment. The effect of the main pesticides accounted for soil contamination (such as chlorpyrifos, deltamethrin, cypermethrin, and lambda-cyhalothrin) were studied in 115 representative soil samples (collected from a greenhouse and agricultural field, in Shaanxi, China). The avoidance test of earthworms to soil with studied pesticide was studied. Among them, chlorpyrifos has the highest residue concentration in the soil. Distinct geographical areas and types of land usage had different pesticide distributions. The detection rates of deltamethrin in Guanzhong were higher in greenhouses than in fields. The results manifested that the detection rates of chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin in greenhouses were higher in northern and southern Shaanxi. In addition, the concentration levels of pesticides in different soils are as follows: field soil > orchard soil > vegetable soil, and the concentration of chlorpyrifos was much higher in comparison to other pesticides. The results of the earthworm toxicity experiments showed that the soil treatments with the addition of pesticides caused toxic reactions in earthworms as compared to control treatments (without pesticide application). The earthworms exposed to toxic conditions showed morphological changes in their epidermis. Significant avoidance behavior was observed by earthworms, with avoidance rates exceeding 55%. The research results revealed the residual amounts of organophosphorus and pyrethroid pesticides in Shaanxi Province and their effects on the morphology and behavior of soil animals, providing a reference for pesticide application and control in the study area.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alex, A. V., & Mukherjee, A. (2020). Review of recent developments (2018–2020) on acetylcholinesterase inhibition based biosensors for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Microchemical Journal, 161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105779
Anandha, R. R., & Suresh, Y. (2021). Pyrethroid based pesticides – Chemical and biological aspects. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 51(2), 117–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2021.1879007
Bose, S., Kumar, P. S., & Vo, D. (2021). A review on the microbial degradation of chlorpyrifos and its metabolite TCP. Chemosphere, 283, 131447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131447
Cesar, R., Arruda, F., & Ramiro, V. (2022). Deposition of gold mining tailings in tropical soils: metal pollution and toxicity to earthworms. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22, 547–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03105-8
Cui, N., Cao, L., Sui, J., Lin, H., & Sun, X. (2020). Quick and convenient construction of lambda-cyhalothrin antigen for the generation of specific antibody. Analytical Biochemistry, 597(30), 113669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113669
Cupples, A. M., Sims, G. K., Hultgren, R. P., & Hart, S. E. (2000). Effect of soil conditions on the degradation of cloransulam-methyl. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 786–794. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2000.00472425002900030014x
Gurpreet, K. S., Simranjeet, S., Vijay, K., Daljeet, S. D., Shivika, D., & Joginder, S. (2019). Toxicity, monitoring, and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 49(13), 1135–1187. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1565554
Heupel, K. (2002). Avoidance response of different collembolan species to Betanal. European Journal of Soil Biology, 38(3), 273–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1164-5563(02)01158-5
Jallow, M. A., Awadh, D. G., Albaho, M. S., Devi, V. Y., & Thomas, B. M. (2017). Pesticide risk behaviors and factors influencing pesticide use among farmers in Kuwait. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.085
Jepson, P. C., Murray, K., Bach, O., Bonilla, M. A., & Neumeister, L. (2020). Selection of pesticides to reduce human and environmental health risks: A global guideline and minimum pesticides list. Lancet Planet Health, 4(2), e56–e63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(19)30266-9
Kaur, R., Singh, D., Kumari, A., et al. (2021). Pesticide residues degradation strategies in soil and water: A review. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03696-2
Klaudia, P., & Monika, M. (2016). The QuEChERS approach for the determination of pesticide residues in soil samples: An overview. Journal of AOAC International, 99(6), 1403–1414. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.16-0274
Lee, J., Kim, L., Shin, Y., Lee, J., Lee, J., Kim, E., Moon, J., & Kim, J. (2017). Rapid and simultaneous analysis of 360 pesticides in brown rice, spinach, orange, and potato using microbore GC-ms/ms. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(16), 3387–3395. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00576
Lianhui, Z. (2020). Responsible for the survival of Future generations -- The tortuous course of the prohibition of organochlorine pesticides BHC and DDT in China. System Sciences And Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 27(5), 101–114, 159 (in Chinese).
Li, J., Jiang, H., Wu, P., Li, S., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Toxicological effects of deltamethrin on quail cerebrum: Weakened antioxidant defense and enhanced apoptosis. Environmental Pollution, 286, 117319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117319
Li, Z., Sun, J., & Zhu, L. (2020). Organophosphorus pesticides in greenhouse and open-field soils across china: Distribution characteristic, polluted pathway and health risk. Science of the Total Environment, 765(5), 142757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142757
Liu, C. C., Men, W. J., Liu, Y. J., & Zhang, H. (2002). The pollution of pesticides in soil and its bioremediation. System Sciences And Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 04, 291–292+297 (in Chinese).
Ma, W. C., & Bonten, L. C. (2011). Bioavailability pathways underlying zinc-induced avoidance behavior and reproduction toxicity in (Lumbricus rubellus) earthworms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(6), 1721–1726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.04.004
Melanie, K., Sabine, B., & Brown, C. D. (2007). Factors influencing degradation of pesticides in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(11), 4487–4492. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0635356
Nusair, S. D., Abu Zarour, Y. S., & Altarifi, A. A. (2017). Effects of dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans on acetylcholinesterase activity and histopathology of the body wall of earthworm Eisenia andrei: A potential biomarker for ecotoxicity monitoring. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3448-8
Shahla, Y., & Doris, D. (2010). Effects of pesticides on the growth and reproduction of earthworm: a review. System Sciences And Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/678360
Samal, S., Sahoo, S., & Mishra, C. S. K. (2017). Morpho-histological and enzymatic alterations in earthworms Drawida willsi and Lampito mauritii exposed to urea, phosphogypsum and paper mill sludge. Chemistry and Ecology, 33(8), 762–776. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2017.1357700
Ukalska-Jaruga, A., Bożena, S., & Grzegorz, S. (2020). Assessment of pesticide residue content in Polish agricultural soils. Molecules, 25, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030587
Weiping, L. (2006). Environmental chemistry of pesticides. Chemical Industry Press (in Chinese).
Wenfeng, W., Qun, W., Yixin, L., Wenjun, X., & Xiangyang, Y. (2019). Uptake, translocation and subcellular distribution of pesticides in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa var Chinensis). Ecotox Environ Safe, 183, 109488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019
Yun, S. M., Jk, Y., Kim, J. I., et al. (2022). Evaluation of residual level and distribution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils in South Korea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 46003–46017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18858-z
Zhang, J. Y., Xiong, K., Chen, A., & Li, F. X. (2017). Toxicity of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide paichongding to earthworm Eisenia foetida. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 26(3), 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2017.1276153
Zhao, L., Teng, Y., & Luo, Y. M. (2017). Present pollution status and control strategy of pesticides in agricultural soil in China: A review. Soil, (03), 417–427. https://doi.org/10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.03.001 (in Chinese).
Zhihua, Q., Peiyao, L., Jiaqi, T., et al. (2022). Oxidative stress and detoxification mechanisms of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) after exposure to flupyradifurone in a soil-earthworm system. Journal of Environmental Management, 322, 115989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115989
Zhou, S. P., Duan, C. Q., & Hui, F. U. (2007). Toxicity assessment for chlorpyrifos-contaminated soil with three different earthworm test methods. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(7), 854–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60142-9
Funding
The study was partially supported by the Key Research and Development Program in Shaanxi Province (2023-YBNY-237) and the Science and Technology Program Special Project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Agriculture (2020NCNY0016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Li Hua, Huining Wang, and Danyang Zhao performed material preparation, data collection, and analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Huining Wang, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
No approval of research ethics committees was required to accomplish the goals of this study because experimental work was conducted with an unregulated invertebrate species.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Novelty or Significance
This study bridged the gap between the residues and safety of organophosphorus and polyester pesticides in agricultural soil in Shaanxi Province and provided a reference for appropriate pesticide management.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, L., Wang, H., Zhao, D. et al. Study on Residues and Safety of Organophosphorus and Polyester Pesticides in Shaanxi Agricultural Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 245 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06266-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06266-z