Abstract
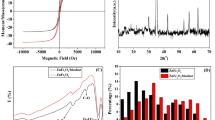
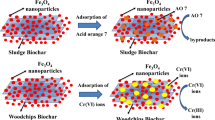
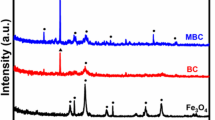
The efficient and relatively simple modification of various biochars to facilitate their environmental applications and enhance the cost/effectiveness ratio is still a challenge. In this work, biochar prepared by pyrolysis of wastewater sewage sludge at 400 °C and 750 °C was tested for methylene blue (MB) adsorption. Biochar which was prepared at 750 °C (SSB) and presented high adsorption capacity was magnetized by applying co-precipitation techniques. The magnetic biochar was obtained (SSMB) and the pristine biochar for methylene blue (MB) was removed in an aqueous solution. The sewage sludge biochar (SSB) and the magnetic sewage sludge biochar (SSMB) were characterized by SEM-EDS, BET, mercury porosimeter, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy. The results showed a decrease in specific surface area and total pore volume after magnetization from 51.82 to 3.37 m2/g and from 0.899 to 0.588 cm3/g, respectively. An increase in the average pore diameter (from 0.086 to 1.109 μm) and surface functional groups was recorded in SSMB compared to SSB. SSMB presented 55.6 mg/g of adsorption capacity meanwhile SSB presented a value of 54.23 mg/g for the removal of C0 = 40 mg/L of MB under an optimized pH and biochar dose. The kinetic study and isotherm modeling revealed that the adsorption of MB on SSB and SSMB is driven by physical interactions on heterogenous sites dominated by pore filling, hydrogen bonding, π-π, and n-π interaction mechanism. The thermodynamic study showed that the adsorption is endothermic and favorable on both biochars. The regeneration tests exhibit NaOH treatment for MB desorption as a promising technique with a minor loss of adsorption capacities of 7.6 and 5.8% for SSB and SSMB, respectively.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data required to reproduce these findings are available on request.
References
Ahmad, K., Shah, H.-R., Ahmad, M., Ahmed, M., Naseem, K., Riaz, N., et al. (2022a). Comparative study between two zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as adsorbents for removal of organoarsenic, As(III) and As(V) species from water. Brazilian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 9(36), 78–97. https://doi.org/10.30744/brjac.2179-3425.ar-112-2021
Ahmad, K., Shah, H., Khan, M. S., Iqbal, A., Potrich, E., Amaral, L. S., et al. (2022b). Lead In drinking water: Adsorption method and role of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for its remediation: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 368(June), 133010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133010
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., et al. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.071
Ahmad, R., & Kumar, R. (2010). Adsorption studies of hazardous malachite green onto treated ginger waste. Journal of Environmental Management, 91(4), 1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.12.016
Al-Jubouri, S. M., Al-Jendeel, H. A., Rashid, S. A., & Al-Batty, S. (2022). Antibiotics adsorption from contaminated water by composites of ZSM-5 zeolite nanocrystals coated carbon. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 47(January), 102745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102745
Assadi, I., Guesmi, A., Baaloudj, O., Zeghioud, H., Elfalleh, W., Benhammadi, N., et al. (2022). Review on inactivation of airborne viruses using non-thermal plasma technologies: From MS2 to coronavirus. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(4), 4880–4892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17486-3
Atugoda, T., Gunawardane, C., Ahmad, M., & Vithanage, M. (2021). Mechanistic interaction of ciprofloxacin on zeolite modified seaweed (Sargassum crassifolium) derived biochar: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Chemosphere, 281(April), 130676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130676
Ayawei, N., Angaye, S. S., Wankasi, D., & Dikio, E. D. (2015). Synthesis, characterization and application of Mg/Al layered double hydroxide for the degradation of Congo Red in aqueous solution. Open Journal of Physical Chemistry, 05(03), 56–70. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojpc.2015.53007
Ayawei, N., Ebelegi, A. N., & Wankasi, D. (2017). Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 3039817. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Berizi, Z., Hashemi, S. Y., Hadi, M., Azari, A., & Mahvi, A. H. (2016). The study of non-linear kinetics and adsorption isotherm models for Acid Red 18 from aqueous solutions by magnetite nanoparticles and magnetite nanoparticles modified by sodium alginate. Water Science and Technology, 74(5), 1235–1242. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.320
Chakraborty, I., Das, S., Dubey, B. K., & Ghangrekar, M. M. (2020). Novel low cost proton exchange membrane made from sulphonated biochar for application in microbial fuel cells. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 239, 122025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122025
Chen, L., Jiang, X., Xie, R., Zhang, Y., Jin, Y., & Jiang, W. (2020). A novel porous biochar-supported Fe-Mn composite as a persulfate activator for the removal of acid red 88. Separation and Purification Technology, 250(May), 117232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117232
Chen, S., Qin, C., Wang, T., Chen, F., Li, X., Hou, H., & Zhou, M. (2019). Study on the adsorption of dyestuffs with different properties by sludge-rice husk biochar: Adsorption capacity, isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamics and mechanism. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 285, 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.04.035
Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Lu, W., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Y., & Ren, L. (2014). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and heavy metal adsorptive performance of biochar derived from municipal sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 164, 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.048
Couillard, D. (1980). Évaluation De La Pollution Et Des Répercussions Des Rejets Des Industries Des Pâtes Et Papiers Sur La Vie Aquatique. Science of the Total Environment, The, 14(2), 167–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(80)90072-8
Czech, B., Kończak, M., Rakowska, M., & Oleszczuk, P. (2021). Engineered biochars from organic wastes for the adsorption of diclofenac, naproxen and triclosan from water systems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125686
Dai, Y., Li, J., & Shan, D. (2020). Adsorption of tetracycline in aqueous solution by biochar derived from waste Auricularia auricula dregs. Chemosphere, 238, 124432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124432
Dardouri, S., & Sghaier, J. (2017). Adsorptive removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using different agricultural wastes as adsorbents. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(4), 1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0008-2
De Bhowmick, G., Sarmah, A. K., & Sen, R. (2018). Production and characterization of a value added biochar mix using seaweed, rice husk and pine sawdust: A parametric study. Journal of Cleaner Production, 200, 641–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.002
Ding, H., Tong, G., Sun, J., Ouyang, J., Zhu, F., Zhou, Z., et al. (2023). Regeneration of methylene blue-saturated biochar by synergistic effect of H2O2 desorption and peroxymonosulfate degradation. Chemosphere, 316, 137766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137766
Dong, F. X., Yan, L., Zhou, X. H., Huang, S. T., Liang, J. Y., Zhang, W. X., et al. (2021). Simultaneous adsorption of Cr(VI) and phenol by biochar-based iron oxide composites in water: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 416(April), 125930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125930
Duman, O., Özcan, C., Gürkan Polat, T., & Tunç, S. (2019). Carbon nanotube-based magnetic and non-magnetic adsorbents for the high-efficiency removal of diquat dibromide herbicide from water: OMWCNT, OMWCNT-Fe3O4 and OMWCNT-Κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Environmental Pollution, 244, 723–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.071
Duman, O., Tunç, S., Bozoğlan, B. K., & Polat, T. G. (2016a). Removal of triphenylmethane and reactive azo dyes from aqueous solution by magnetic carbon nanotube-κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4nanocomposite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 687, 370–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.160
Duman, O., Tunç, S., Polat, T. G., & Bozoǧlan, B. K. I. (2016b). Synthesis of magnetic oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube-κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4 nanocomposite adsorbent and its application in cationic Methylene Blue dye adsorption. Carbohydrate Polymers, 147, 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.099
Elgarahy, A. M., Mostafa, H. Y., Zaki, E. G., ElSaeed, S. M., Elwakeel, K. Z., Akhdhar, A., & Guibal, E. (2023). Methylene blue removal from aqueous solutions using a biochar/gellan gum hydrogel composite: Effect of agitation mode on sorption kinetics. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 232, 123355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123355
Tong, F., Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Chen, W., Fan, G., Gao, Y., Xueyuan, G., & C. G. (2022). Heavy metal-mediated adsorption of antibiotic tetracycline and ciprofloxacin on two microplastics: Insights into the role of complexation. Environmental Research, 110, 114716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114716
Fu, C., Zhang, H., Xia, M., Lei, W., & Wang, F. (2020). The single/co-adsorption characteristics and microscopic adsorption mechanism of biochar-montmorillonite composite adsorbent for pharmaceutical emerging organic contaminant atenolol and lead ions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 187(October 2019), 109763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109763
Ghodbane, I., & Hamdaoui, O. (2008). Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous media using eucalyptus bark: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(2–3), 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.116
Gurav, R., Bhatia, S. K., Choi, T. R., Choi, Y. K., Kim, H. J., Song, H. S., et al. (2021). Adsorptive removal of crude petroleum oil from water using floating pinewood biochar decorated with coconut oil-derived fatty acids. Science of the Total Environment, 781, 146636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146636
Hagemann, N., Spokas, K., Schmidt, H. P., Kägi, R., Böhler, M. A., & Bucheli, T. D. (2018). Activated carbon, biochar and charcoal: Linkages and synergies across pyrogenic carbon’s ABCs. Water (Switzerland), 10(2), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020182
Han, X., Chen, H., Liu, Y., & Pan, J. (2020). Study on removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide based on macroalgae biochars. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 73(July 2019), 103068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2019.103068
Hao, D., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., & You, N. (2021). Nanocomposites of zero-valent iron@biochar derived from agricultural wastes for adsorptive removal of tetracyclines. Chemosphere, 284(June), 131342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131342
Reddy, D. H. K., & Lee, S. M. (2014). Magnetic biochar composite: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 454(1), 96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.03.105
Hossain, M. K., Strezov Vladimir, V., Chan, K. Y., Ziolkowski, A., & Nelson, P. F. (2011). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production and nutrient properties of wastewater sludge biochar. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(1), 223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.09.008
Ifthikar, J., Wang, T., Khan, A., Jawad, A., Sun, T., Jiao, X., et al. (2017). Highly efficient lead distribution by magnetic sewage sludge biochar: Sorption mechanisms and bench applications. Bioresource Technology, 238, 399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.133
Ihsanullah, I., Khan, M. T., Zubair, M., Bilal, M., & Sajid, M. (2022). Removal of pharmaceuticals from water using sewage sludge-derived biochar: A review. Chemosphere, 289(October 2021), 133196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133196
Jang, H. M., Yoo, S., Park, S., & Kan, E. (2019). Engineered biochar from pine wood: Characterization and potential application for removal of sulfamethoxazole in water. Environmental Engineering Research, 24(4), 608–617. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2018.358
Jellali, S., Azzaz, A. A., Al-harrasi, M., Charabi, Y., Al-sabahi, J. N., Al-raeesi, A., et al. (2022). Conversion of industrial sludge into activated biochar for effective cationic dye removal : Characterization and adsorption properties assessment.
Jiang, T., Liu, W., Mao, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, J., Gong, M., et al. (2015). Adsorption behavior of copper ions from aqueous solution onto graphene oxide-CdS composite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 259, 603–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.022
Jin, J., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Wu, S., Cao, Y., Liang, P., et al. (2016). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 320, 417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.050
Kaetzl, K., Lübken, M., Nettmann, E., Krimmler, S., & Wichern, M. (2020). Slow sand filtration of raw wastewater using biochar as an alternative filtration media. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57981-0
Karanjikar, S. R., Singh Sena, A., Manekar, P., Mudagi, S., & Singh Juneja, A. (2022). Utilization of graphene and its derivatives for air & water filtration: A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 50, 2007–2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.346
Kumar, K. V., Porkodi, K., & Rocha, F. (2008). Comparison of various error functions in predicting the optimum isotherm by linear and non-linear regression analysis for the sorption of basic red 9 by activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150(1), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.020
Li, F., Yuasa, A., Ebie, K., Azuma, Y., Hagishita, T., & Matsui, Y. (2002). Factors affecting the adsorption capacity of dissolved organic matter onto activated carbon: Modified isotherm analysis. Water Research, 36(18), 4592–4604. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00174-4
Li, H., Budarin, V. L., Clark, J. H., North, M., & Wu, X. (2022). Rapid and efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by hierarchically porous, activated starbons®: Mechanism and porosity dependence. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 436(April), 129174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129174
Li, J., Yu, G., Pan, L., Li, C., You, F., & Wang, Y. (2020). Ciprofloxacin adsorption by biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and bamboo waste. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(18), 22806–22817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08333-y
Li, P., Fu, T., Gao, X., Zhu, W., Han, C., Liu, N., et al. (2019). Adsorption and reduction transformation behaviors of Cr(VI) on mesoporous polydopamine/titanium dioxide composite nanospheres. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 64(6), 2686–2696. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00111
Li, R., Wang, J. J., Zhou, B., Awasthi, M. K., Ali, A., Zhang, Z., et al. (2016). Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Science of the Total Environment, 559, 121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.151
López-Luna, J., Ramírez-Montes, L. E., Martinez-Vargas, S., Martínez, A. I., Mijangos-Ricardez, O. F., González-Chávez, M. d. C. A., et al. (2019). Linear and nonlinear kinetic and isotherm adsorption models for arsenic removal by manganese ferrite nanoparticles. SN Applied Sciences, 1(8), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0977-3
Lourthuraj, A. A., Hatshan, M. R., & Hussein, D. S. (2022). Biocatalytic degradation of organophosphate pesticide from the wastewater and hydrolytic enzyme properties of consortium isolated from the pesticide contaminated water. Environmental Research, 205(December 2021), 112553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112553
Ma, Y., Qi, Y., Lu, T., Yang, L., Wu, L., Cui, S., et al. (2021). Highly efficient removal of imidacloprid using potassium hydroxide activated magnetic microporous loofah sponge biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144253
McKay, G., & Al Duri, B. (1987). Simplified model for the equilibrium adsorption of dyes from mixtures using activated carbon. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 22(3), 145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/0255-2701(87)80041-7
Méndez, A., Terradillos, M., & Gascó, G. (2013). Physicochemical and agronomic properties of biochar from sewage sludge pyrolysed at different temperatures. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 102, 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2013.03.006
Momina, & Ahmad, K. (2022). Remediation of anionic dye from aqueous solution through adsorption on polyaniline/FO nanocomposite-modelling by artificial neural network (ANN). Journal of Molecular Liquids, 360, 119497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119497
Mozaffari Majd, M., Kordzadeh-Kermani, V., Ghalandari, V., Askari, A., & Sillanpää, M. (2022). Adsorption isotherm models: A comprehensive and systematic review (2010−2020). Science of the Total Environment, 812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151334
Mu, Y., Du, H., He, W., & Ma, H. (2022). Functionalized mesoporous magnetic biochar for methylene blue removal: Performance assessment and mechanism exploration. Diamond and Related Materials, 121(December 2021), 108795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108795
Ng, J. C. Y., Cheung, W. H., & McKay, G. (2002). Equilibrium studies of the sorption of Cu(II) ions onto chitosan. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 255(1), 64–74. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8664
Ngah, W. S. W., & Fatinathan, S. (2010). Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Environmental Management, 91(4), 958–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.12.003
Pereira, A. G. B., Rodrigues, F. H. A., Paulino, A. T., Martins, A. F., & Fajardo, A. R. (2021). Recent advances on composite hydrogels designed for the remediation of dye-contaminated water and wastewater: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124703
Qu, J., Shi, J., Wang, Y., Tong, H., Zhu, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2022). Applications of functionalized magnetic biochar in environmental remediation: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 434(December 2021), 128841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128841
Rafatullah, M., Sulaiman, O., Hashim, R., & Ahmad, A. (2010). Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Rong, X., Xie, M., Kong, L., Natarajan, V., Ma, L., & Zhan, J. (2019). The magnetic biochar derived from banana peels as a persulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 372(April), 294–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.135
Rubangakene, N. O., Elkady, M., Elwardany, A., Fujii, M., Sekiguchi, H., & Shokry, H. (2023). Effective decontamination of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using novel nano-magnetic biochar from green pea peels. Environmental Research, 220, 115272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115272
Salama, A. (2017). New sustainable hybrid material as adsorbent for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 487, 348–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.034
Saleh, T. A., Mustaqeem, M., & Khaled, M. (2022). Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Management, 17(December 2021), 100617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100617
Salehi, E., Askari, M., Velashjerdi, M., & Arab, B. (2020). Phosphoric acid-treated spent tea residue biochar for wastewater decoloring: Batch adsorption study and process intensification using multivariate data-based optimization. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 158(October), 108170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2020.108170
Semerciöz, A. S., Göğüş, F., Çelekli, A., & Bozkurt, H. (2017). Development of carbonaceous material from grapefruit peel with microwave implemented-low temperature hydrothermal carbonization technique for the adsorption of Cu (II). Journal of Cleaner Production, 165, 599–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.159
Senturk, H. B., Ozdes, D., Gundogdu, A., Duran, C., & Soylak, M. (2009). Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto organomodified Tirebolu bentonite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.019
Shahinpour, A., Tanhaei, B., Ayati, A., Beiki, H., & Sillanpää, M. (2022). Binary dyes adsorption onto novel designed magnetic clay-biopolymer hydrogel involves characterization and adsorption performance: Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic, and adsorption mechanism. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 366, 120303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120303
Shang, J., Pi, J., Zong, M., Wang, Y., Li, W., & Liao, Q. (2016). Chromium removal using magnetic biochar derived from herb-residue. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 68, 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.09.012
Shen, T., Wang, P., Hu, L., Hu, Q., Wang, X., & Zhang, G. (2021). Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol by wheat straw biochar and its regeneration with persulfate under microwave irradiation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105353
Shenvi, S. S., Isloor, A. M., Ismail, A. F., Shilton, S. J., & Al Ahmed, A. (2015). Humic acid based biopolymeric membrane for effective removal of methylene blue and rhodamine B. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 54(18), 4965–4975. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00761
Shiam Babu, R., & Prasanna, K. (2022). A novel adsorption process for the removal of salt and dye from saline textile industrial wastewater using a three-stage reactor with surface modified adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(6), 108729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108729
Shin, J., Kwak, J., Lee, Y. G., Kim, S., Choi, M., Bae, S., et al. (2021). Competitive adsorption of pharmaceuticals in lake water and wastewater effluent by pristine and NaOH-activated biochars from spent coffee wastes: Contribution of hydrophobic and π-π interactions. Environmental Pollution, 270, 116244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116244
Sierra, I., Iriarte-Velasco, U., Ayastuy, J. L., & Aguayo, A. T. (2022). Production of magnetic sewage sludge biochar: Investigation of the activation mechanism and effect of the activating agent and temperature. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02372-w
Song, Y. X., Chen, S., You, N., Fan, H. T., & Sun, L. N. (2020). Nanocomposites of zero-valent Iron@Activated carbon derived from corn stalk for adsorptive removal of tetracycline antibiotics. Chemosphere, 255, 126917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126917
Tan, X., Liu, Y., Zeng, G., Wang, X., Hu, X., Gu, Y., & Yang, Z. (2015). Application of biochar for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 125, 70–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.058
Tee, G. T., Gok, X. Y., & Yong, W. F. (2022). Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review. Environmental Research, 212(PB), 113248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113248
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., & Chao, H. P. (2016). Effect of pyrolysis temperatures and times on the adsorption of cadmium onto orange peel derived biochar. Waste Management and Research, 34(2), 129–138. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X15615698
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., & Chao, H. P. (2017). Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Research, 120, 88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Vadivelan, V., & Vasanth Kumar, K. (2005). Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 286(1), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.007
Velusamy, K., Periyasamy, S., Kumar, P. S., Jayaraj, T., Krishnasamy, R., Sindhu, J., et al. (2021). Analysis on the removal of emerging contaminant from aqueous solution using biochar derived from soap nut seeds. Environmental Pollution, 287(June), 117632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117632
Wang, X., Cheng, H., Ye, G., Fan, J., Yao, F., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Key factors and primary modification methods of activated carbon and their application in adsorption of carbon-based gases: A review. Chemosphere, 287(P2), 131995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131995
Wang, Y., Mu, Y., Zhao, Q. B., & Yu, H. Q. (2006). Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of dye biosorption by anaerobic sludge. Separation and Purification Technology, 50(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2005.10.012
Wong, S., Yac'cob, N. A., Ngadi, N., Hassan, O., & Inuwa, I. M. (2018). From pollutant to solution of wastewater pollution: Synthesis of activated carbon from textile sludge for dye adsorption. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 26(4), 870–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.07.015
Wu, J., Yang, J., Feng, P., Huang, G., Xu, C., & Lin, B. (2020). High-efficiency removal of dyes from wastewater by fully recycling litchi peel biochar. Chemosphere, 246, 125734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125734
Yi, Y., Huang, Z., Lu, B., Xian, J., Tsang, E. P., Cheng, W., et al. (2019). Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: A review. Bioresource Technology, 298(September 2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122468
Yue, X., Ma, N. L., Sonne, C., Guan, R., Lam, S. S., Van Le, Q., et al. (2021). Mitigation of indoor air pollution: A review of recent advances in adsorption materials and catalytic oxidation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 405(October 2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124138
Zeghioud, H., Fryda, L., Djelal, H., Assadi, A., Kane, A., & Unilasalle-ecole, M. (2022). A comprehensive review of biochar in removal of organic pollutants from wastewater : Characterization , toxicity , activation/functionalization and influencing treatment factors. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 47(April), 102801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102801
Zeghioud, H., Khellaf, N., Djelal, H., Amrane, A., & Bouhelassa, M. (2016). Photocatalytic reactors dedicated to the degradation of hazardous organic pollutants: Kinetics, mechanistic aspects, and design – A review. Chemical Engineering Communications, 203(11), 1415–1431. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2016.1202243
Zeghioud, H., Nguyen-Tri, P., Khezami, L., Amrane, A., & Assadi, A. A. (2020). Review on discharge Plasma for water treatment: Mechanism, reactor geometries, active species and combined processes. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 38(October), 101664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101664
Zeng, H., Qi, W., Zhai, L., Wang, F., Zhang, J., & Li, D. (2021). Magnetic biochar synthesized with waterworks sludge and sewage sludge and its potential for methylene blue removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 105951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105951
Zhang, H., Peng, B., Liu, Q., Wu, C., & Li, Z. (2022). Preparation of porous biochar from heavy bio-oil for adsorption of methylene blue in wastewater. Fuel Processing Technology, 238(May), 107485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107485
Zhang, P., O’Connor, D., Wang, Y., Jiang, L., Xia, T., Wang, L., et al. (2020). A green biochar/iron oxide composite for methylene blue removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384(July 2019), 121286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121286
Zhang, S., Niu, H., Cai, Y., Zhao, X., & Shi, Y. (2010). Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on coprecipitated bimetal oxide magnetic nanomaterials: MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158(3), 599–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.02.013
Zhao, J., Liang, G., Zhang, X., Cai, X., Li, R., Xie, X., & Wang, Z. (2019). Coating magnetic biochar with humic acid for high efficient removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in water. Science of the Total Environment, 688, 1205–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.287
Zheng, D., Wu, M., Zheng, E., Wang, Y., Feng, C., Zou, J., et al. (2022). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Parallel adsorption of low concentrated ciprofloxacin by a CoFe-LDH modified sludge biochar. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(5), 108381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108381
Zhou, Z., Liu, Y. G., Liu, S. B., Liu, H. Y., Zeng, G. M., Tan, X. F., Yang, C. P., Ding, Y., Yan, Z. L., Cai, X. X., et al. (2017). Sorption performance and mechanisms of arsenic(V) removal by magnetic gelatin-modified biochar. Chemical Engineering Journal, 314, 223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.113
Zubair, M., Saood, M., Awwal, M., Pinto, D., Meili, L., Al, W., et al. (2022). Journal of Water Process Engineering Production of magnetic biochar-steel dust composites for enhanced phosphate adsorption. Journal of Water. Process Engineering, 47(December 2021), 102793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102793
Zubrik, A., Matik, M., Mačingová, E., Danková, Z., Jáger, D., Briančin, J., et al. (2022). The use of microwave irradiation for preparation and fast-acting regeneration of magnetic biochars. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 178(June), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2022.109016
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ivane LELIEVRE (Unilasalle Rennes) for their technical help. All thanks also to Korbinian KAETZL (University of Kassel) for providing biochars. The authors thank Lydia Fryda and Abdoulaye Kane for their supervision of the ThreeC project.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the INTERREG NorthWest Europe ThreeC with project number NWE 1010, under the umbrella of the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeghioud, H., Mouhamadou, S. Dye Removal Characteristics of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge: Isotherm, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06251-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06251-6