Abstract
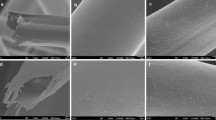
In this study, the hydrophobicity and lipophilicity of banana leaf fibers were modified by in situ synthesis and sol–gel method, and the adsorption properties of the modified fibers were investigated using petroleum as the adsorbate. The surface morphology of modified fibers was characterized by SEM. It was found that the surface formed a rough structure with granular material. At the same time, the hydrophobic and lipophilic properties of the modified fiber had been greatly improved. Firstly, the contact angles between the two modified fibers and water are greater than 110°, which greatly improves the flotation performance of the fibers, making them suitable for treating oil spills on seawater surfaces; secondly, the oil removal rates of the modified fiber in seawater were 98.7% and 94.7% respectively, and kinetic study indicated that the quasi-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isothermal adsorption model are better consistent with the adsorption of petroleum by modified fiber, which shows that the adsorption is the result of the joint action of physical adsorption and chemical adsorption; in addition, the modified fibers have good reuse characteristics because their properties did not decline significantly after they were reused.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used in the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alvarez-Díaz, M., Caballero-Miguez, G., & Solino, M. (2011). The institutional determinants of CO2 emissions: A computational modelling approach using artificial neural networks and genetic programming. Environmetrics, 1, 42–49.
Asadpour, R., Yavari, S., Kamyab, H., Ashokkumar, V., Chelliapan, S., & Yuzir, A. (2021). Study of oil sorption behaviour of esterified oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) fibre and its kinetics and isotherm studies. Environmental Technology & Innovation., 22, 101397.
Bobade, V., & Eshtiagi, N. (2015). Heavy metals removal from wastewater by adsorption process: A review. APCChE 2015 Congr. Inc. Chemeca., 6, 312–317.
Bohli, T., Ouederni, A., Fiol, N., & Villaescusa, I. (2015). Evaluation of an activated carbon from olive stones used as an adsorbent for heavy metal removal from aqueous phases. Comptes Rendus Chim., 18, 88–99.
Crain, C. M., Kroeker, K., & Halpern, B. S. (2008). Interactive and cumulative effects of multiple human stressors in marine systems. Ecology Letters, 11, 1304–1315.
Demirbas, E., Dizge, N., Sulak, M. T., & Kobya, M. (2009). Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium of copper from aqueous solutions using hazelnut shell activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal., 148, 480–487.
Fan, B., Song, Y., Wang, S., Meng, J., ang, G. Y., Guo, X., Feng, L., Jiang, L. (2015) Directly coating hydrogel on filter paper for effective oil-water separation in highly acidic, alkaline, and salty environment, Advanced Functional Materials. 25 5368-5375
Fiore, V., Scalici, T., Di Bella, G., & Valenza, A. (2015). A review on basalt fibre and its composites. Composites Part B Engineering, 74, 74–94.
Gao, Y. (2011) Study on the adsorption and recovery of oil spills at sea using crop wastes
Ismail, H., Salleh, W.N.W., Ismail, A.F., Hasbullah, H. N., usof, Y., Aziz, F., Jaafar, J. (2020) Hydrophilic polymer-based membrane for oily wastewater treatment: A review, Separation and Purification Technology. 233 116007
Mohamed Ahmed Mahmoud. (2020). Oil spill cleanup by rawflaxfiber: Modification effect, sorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Arabian Journal of Chemistry., 13, 5553–5563.
Moura, F. C. C., & Lago, R. M. (2009). Catalytic growth of carbon nanotubes and nanofibers on vermiculite to produce floatable hydrophobic “nanosponges” for oil spill remediation. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental., 90(3–4), 436–440.
Panagopoulos, A. (2022). Brine management (saline water & wastewater effluents): Sustainable utilization and resource recovery strategy through Minimal and Zero Liquid Discharge (MLD & ZLD) desalination systems. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 176, 108944.
Panagopoulos, A., & Giannika, V. (2022). Decarbonized and circular brine management/valorization for water & valuable resource recovery via minimal/zero liquid discharge (MLD/ZLD) strategies. Journal of Environmental Management, 324, 116239.
Qing, Z. X., Fu, J., Yuan, L., (2022) A study on the adsorption of quinclorac in water using TiO2-SiO2 modified banana peel biochar, Journal of Agro-Environment Science
Rabiei, R., Phang, S. M., Yeong, H. Y., Limg, P. E., Ajdari, D., Zarshenas, G., & Sohrabipour, J. (2014). Bioremediation efficiency and biochemical composition of Ulva reticulate Forsskal (Chlorophyta) cultivated in shrimp (Penaeus monodan) hatchery effluent. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 13(3), 621–639.
Ralegaonkar, R., Gavali, H., Aswath, P., & Abolmaali, S. (2018). Application of chopped basalt fibers in reinforced mortar: A review. Construction and Building Materials, 164, 589–602.
Sathasivam, K., & Mas Rosemal, H. M. H. (2010). Adsorption kinetics and capacity of fatty acid-modified banana trunk fibers for oil in water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution., 213(1), 413–423.
Soto-Onate, D., Caballero, G., & Oil spills, governance and institutional performance: The,. (1992). regime of liability and compensation for oil pollution damage. Journal of Cleaner Production., 166(2017), 299–311.
Tan L. H., Li Z. G. (2009) Utilization of tropical agricultural wastes in Hainan Province. Tropical agricultural science
Tang, X. H. (2020). Comparison of Rhodamine B removal by soybean straw ash and banana peel. Journal of Henan Institute of Education (natural Science Edition)., 29(01), 16–22.
UNCTAD (2016) Review of Maritime Transport. New York
Venkata Deepthi, K., Sita Rama Raju, M., Indra, Reddy. (2019) Dynamic mechanical analysis of banana, pineapple leaf and glass fibre reinforced hybrid polyester composites
Wang, W. X., & Fang, Y. (2018). Advances in studies on super hydrophobicity of plant leaf surface. Agriculture and Technology., 38(17), 29–30.
Wang, J., Zheng, Y., & Wang, A. (2013). Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil. Marine Pollution Bulletin., 69(1–2), 91–96.
Wang X., T. (2017) Preparation and properties of oil absorption material from Ramie fiber modified by sol-gel method
Zang, D., L. (2016) Preparation and properties of super hydrophobic and super lipophilic straw fiber
Zhao, M. Q., Huang, J. Q., Zhang, Q., et al. (2011). Improvement of oil adsorption performance by a sponge-like natural vermiculite-carbon nanotube hybrid. Applied Clay Science., 53(1), 1–7.
Funding
The experimental work involved in this paper was supported by Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 422RC596) and Key Laboratory of environmental toxicology of Haikou City, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception, design, and completion. Tingting Ye and Zengjian Su conceived the study and completed the relevant experimental content. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Min Li, Xiaoxi Li, and Tong Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tingting Ye, and later revision and improvement of the manuscript are completed by Zengjian Su. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, T., Li, M., Li, X. et al. Study on the Performance of Modified Banana Leaf Fiber in Removing Oil Spill from Seawater. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 239 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06240-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06240-9