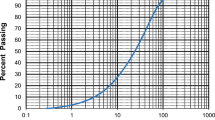
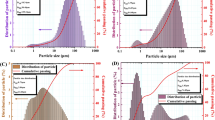
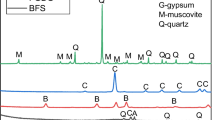
Abstract
The processing of low-grade gold ores generates a significant volume of tailings and wastewater that impacts the environment. The treatment of wastewater using reverse osmosis (RO) produces brine as a by-product with high salinity levels. Improper disposal of mine wastes can significantly pollute water bodies and soils. A novel and sustainable method for managing, disposing, and handling these wastes is vital. The use of RO brine and mine tailings to produce cement paste mixtures for backfilling applications has been investigated. Sulfide gold mine tailings and RO brine were characterized, and cement paste backfill (CPB) mixtures were prepared by mixing varying proportions of cement and RO brine. The CPB cubes were cured for a specified number of days, and their physical and mechanical properties were determined. The results indicate a decrease in slump value with increasing cement content, whilst the slump increased with RO brine content. The compressive strength at 28 days increased with binder content reaching a maximum of 1.83 MPa using 50% RO brine. The CPB cubes produced with 50% RO brine and 12 wt.% cement possessed the required combination of fluidity and strength for mine backfilling applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdul-Wahab, S. A., & Al-Weshahi, M. A. (2009). Brine management: Substituting chlorine with on-site produced sodium hypochlorite for environmentally improved desalination processes. Water Resources Management, 23(12), 2437–2454.
Afshinnia, K., & Rangaraju, P. R. (2015). Influence of fineness of ground recycled glass on mitigation of alkali–silica reaction in mortars. Construction and Building Materials, 81, 257–267.
Ahmad, J., Zaid, O., Shahzaib, M., Abdullah, M. U., Ullah, A., & Ullah, R. (2021). Mechanical properties of sustainable concrete modified by adding marble slurry as cement substitution. AIMS Materials Science, 8(3), 343–358.
Ahmed, M., Shayya, W., Hoey, D., Mahendran, A., Morris, R., & Al-Handaly, J. (2000). Use of evaporation ponds for brine disposal in desalination plants. Desalination, 130, 155–168.
Akinkurolere, O., Jiang, C., & Shobola, O. (2007). The influence of salt water on the compressive strength of concrete. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2(2), 412–415.
Al-Zoubi, H., Rieger, A., Steinberger, P., Pelz, W., Haseneder, R., & Härtel, G. (2010). Optimization study for treatment of acid mine drainage using membrane technology. Separation Science and Technology, 45(14), 2004–2016.
Ali, M. E. A. (2021). Nanofiltration process for enhanced treatment of RO brine discharge. Membranes, 11(3), 212.
Álvarez-Ayuso, E., & Murciego, A. (2021). Stabilization methods for the treatment of weathered arsenopyrite mine wastes: Arsenic immobilization under selective leaching conditions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 283, 125265.
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21st Edition, American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC.
Araujo, F. S. M., Taborda-Llano, I., Nunes, E. B., & Santos, R. M. (2022). Recycling and Reuse of Mine Tailings: A Review of Advancements and Their Implications. Geosciences, 12(9), 319.
Araya, N., Kraslawski, A., & Cisternas, L. A. (2020). Towards mine tailings valorization: Recovery of critical materials from Chilean mine tailings. Journal of Cleaner Production, 263, 121555.
ASTM Standard C305. (2020). “Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency”, ASTM International, West Conshohocken. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0305-20
ASTM Standard C143. (2012). “Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete”, ASTM International, West Conshohocken. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0143_C0143M-12
ASTM Standard D7928. (2021). “Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Distribution (Gradation) of Fine-Grained Soils Using the Sedimentation (Hydrometer) Analysis”, ASTM International, West Conshohocken. https://doi.org/10.1520/D7928-21E01
Bernier, R., Li, M. G. & Moerman, A. (1999). Effects of tailings and binder geochemistry on the physical strength of paste backfill. Proceedings of Sudburry 99:1113–1122.
Brackebusch, F. (1995). Basics of paste backfill systems. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci Geomech Abstracts, 3, 122A.
Bsi. (1999). 1015–11, Methods of test for mortar for masonry–Part 11: Determination of flexural and compressive strength of hardened mortar. Comité Européen de Normalisation, Brussels.
Chen, W., & Brouwers, H. (2010). Alkali binding in hydrated Portland cement paste. Cement and Concrete Research, 40(5), 716–722.
De Vito, C., Mignardi, S., Ferrini, V., & Martin, R. (2011). Reject brines from desalination as possible sources for environmental technologies. In P. R. Y. Ning (Ed.), Expanding Issues in Desalination (pp. 85–102). InTech.
Edori, O., & Kpee, F. (2016). Physicochemical and heavy metal assessment of water samples from boreholes near some Abattoirs in Port Harcourt, Rivers State, Nigeria. American Chemical Science Journal, 14, 1–8.
Ercikdi, B., Yilmaz, T., & Külekçi, G. (2013). Strength and ultrasonic properties of cemented paste backfill. Ultrasonics, 54, 195.
Feng, D., Aldrich, C., & Tan, H. (2000). Treatment of acid mine water by use of heavy metal precipitation and ion exchange. Minerals Engineering, 13(6), 623–642.
Fu, F., & Wang, Q. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 407–418.
Glass, G. K. Buenfeld, N. R. (1997). The presentation of the chloride threshold level for corrosion of steel in concrete. Corrosion Science, 39, 1001–1013.
Gowripalan, N., Sirivivatnanon, V., & Lim, C. (2000). Chloride diffusivity of concrete cracked in flexure. Cement and Concrete Research, 30(5), 725–730.
Greenlee, L. F., Lawler, D. F., Freeman, B. D., Marrot, B., & Moulin, P. (2009). Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Research, 43(9), 2317–2348.
Hatar, H., Rahim, S. A., Razi, W. M. & Sahrani, F. K. (2013) Heavy metals content in acid mine drainage at abandoned and active mining area. In AIP Conference Proceedings. American Institute of Physics 1571:641-646
Hefni, M., Ahmed, Ha. M., Omar, E. S., & Ali, M. A. (2021). The Potential re-use of saudi mine tailings in mine backfill: A path towards sustainable mining in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 13(11), 6204.
Islam, M. S., & Akhtar, S. (2013). A critical assessment to the performance of alkali-silica reaction (ASR) in concrete. Canadian Chemical Transactions, 1(4), 253–266.
Iyama, W., Edori, O., S, O., & S, I. (2014). Study of pollution levels in Ahoada-Ihuaba axis of Sombreiro River, Ahoada Rivers State, Nigeria. International Research Journal of Pure & Applied Chemistry, 4, 378–387.
Juenger, M., Monteiro, P., Gartner, E., & Denbeaux, G. (2005). A soft X-ray microscope investigation into the effects of calcium chloride on tricalcium silicate hydration. Cement and Concrete Research, 35(1), 19–25.
Juenger, M. C., & Siddique, R. (2015). Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete. Cement and Concrete Research, 78, 71–80.
Ke, X., Hou, H., Zhou, M., Wang, Y., & Zhou, X. (2015). Effect of particle gradation on properties of fresh and hardened cemented paste backfill. Construction and Building Materials, 96, 378–382.
Kesimal, A., Yilmaz, E., & Ercikdi, B. (2004). Evaluation of paste backfill mixtures consisting of sulphide-rich mill tailings and varying cement contents. Cement and Concrete Research, 34(10), 1817–1822.
Kishar, E. A., Ahmed, D. A., Mohammed, M. R., & Noury, R. (2013). Effect of calcium chloride on the hydration characteristics of ground clay bricks cement pastes. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2(1), 20–30.
Kiventerä, J., Lancellotti, I., Catauro, M., Poggetto, F. D., Leonelli, C., & Illikainen, M. (2018). Alkali activation as new option for gold mine tailings inertization. Journal of Cleaner Production, 187, 76–84.
Kiventerä, J., Piekkari, K., Isteri, V., Ohenoja, K., Tanskanen, P., & Illikainen, M. (2019). Solidification/stabilization of gold mine tailings using calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement. Journal of Cleaner Production, 239, 118008.
Khan, M. Al-Ghouti, M. A. (2021). DPSIR framework and sustainable approaches of brine management from seawater desalination plants in Qatar. Journal of Cleaner Production, 319, 128485.
Kwan, A. K., & Wong, H. (2008). Packing density of cementitious materials: Part 2—packing and flow of OPC+ PFA+ CSF. Materials and Structures, 41(4), 773–784.
Mahlaba, J. & Pretorius, P. (2006) Exploring paste technology as a co-disposal option for fly ash and brines. Proceedings Paste 3–7
Mahlaba, J. S., Kearsley, E. P., Kruger, R. A., & Pretorius, P. C. (2011). Evaluation of workability and strength development of fly ash pastes prepared with industrial brines rich in SO4= and Cl− to expand brine utilisation. Minerals Engineering, 24(10), 1077–1081.
Mesa Espitia, S. L., & Lapidus, G. T. (2021). Arsenic removal strategy in the processing of an arsenopyritic refractory gold ore. Hydrometallurgy, 203, 105628.
Niroshan, N., Sivakugan, N., & Veenstra, R. L. (2018). Flow characteristics of cemented paste backfill. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 36(4), 2261–2272.
Nochaiya, T., Wongkeo, W., & Chaipanich, A. (2010). Utilization of fly ash with silica fume and properties of Portland cement–fly ash–silica fume concrete. Fuel, 89(3), 768–774.
Ouattara, D., Yahia, A., Mbonimpa, M., & Tikou, B. (2017). Effects of superplasticizer on rheological properties of cemented paste backfills. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 161, 28.
Owusu-Ansah, E.-G., Sampson, A., Amponsah, S., Abaidoo, R., & Hald, T. (2015). Performance, compliance and reliability of Waste stabilization pond: Effluent discharge quality and environmental protection agency standards in Ghana. Research Journal of Applied Science, Engineering and Technology, 10(11), 1293–1302.
Panagopoulos, A., Haralambous, K.-J., & Loizidou, M. (2019). Desalination brine disposal methods and treatment technologies - A review. Science of the Total Environment, 693, 133545.
Pramanik, B. K., Shu, L., & Jegatheesan, V. (2017). A review of the management and treatment of brine solutions. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 3(4), 625–658.
Qi, C., Fourie, A., Chen, Q., Tang, X., Zhang, Q., & Gao, R. (2018). Data-driven modelling of the flocculation process on mineral processing tailings treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196, 505–516.
Roberts, D. A., Johnston, E. L., & Knott, N. A. (2010). Impacts of desalination plant discharges on the marine environment: A critical review of published studies. Water Research, 44(18), 5117–5128.
Samaei, S. M., Gato-Trinidad, S., & Altaee, A. (2020). Performance evaluation of reverse osmosis process in the post-treatment of mining wastewaters: Case study of Costerfield mining operations, Victoria Australia. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 34, 101116.
Santhanam, M., Cohen, M. D., & Olek, J. (2001). Sulfate attack research—Whither now? Cement and Concrete Research, 31(6), 845–851.
Schoenberger, E. (2016). Environmentally sustainable mining: The case of tailings storage facilities. Resources Policy, 49, 119–128.
Shanmuganathan, S., Johir, Ma. H., Listowski, A., Vigneswaran, S., & Kandasamy, J. (2016). Sustainable processes for treatment of waste water reverse osmosis concentrate to achieve zero waste discharge: A detailed study in water reclamation plant. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 35, 930–937.
Sivakugan, N., Veenstra, R., & Naguleswaran, N. (2015). Underground mine backfilling in Australia using paste fills and hydraulic fills. International Journal of Geosynthetics and Ground Engineering, 1(2), 18.
Sun, Q., Li, T., & Liang, B. (2020). Preparation of a new type of cemented paste backfill with an alkali-activated silica fume and slag composite binder. Materials, 13(2), 372.
Taylor, M. A., & Kuwairi, A. (1978). Effects of ocean salts on the compressive strength of concrete. Cement and Concrete Research, 8(4), 491–500.
Tikou, B., & Benzaazoua, M. (2007). Design and application of underground mine paste backfill technology. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 26, 147–174.
Wang, B., Gao, L., Xiong, T., Cui, X., Li, Y., & Lei, K. (2019). Study on relationship between UCS of cemented tailings backfill and weight losses of hydration products. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019, 9457309.
Wang, H.-Y., & Huang, W.-L. (2010). Durability of self-consolidating concrete using waste LCD glass. Construction and Building Materials, 24(6), 1008–1013.
Wang, X.-M., Zhao, B., Zhang, C.-S., & Zhang, Q.-L. (2009). Paste-like self-flowing transportation backfilling technology based on coal gangue. Mining Science and Technology (china), 19(2), 137–143.
Yan, B.-Q., Tannant, D., Lv, W.-S., & Cai, M.-F. (2019). Effect of fly ash on the mechanical properties of cemented backfill made with brine. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 37(2), 691–705.
Yilmaz, E., & Yilmaz, E. (2018). Sustainability and tailings managment in the mining industry: Paste technology. Mugla Journal of Science and Technology, 4(4), 16–26.
Zhou, N., Zhang, J., Ouyang, S., Deng, X., Dong, C., & Du, E. (2020). Feasibility study and performance optimization of sand-based cemented paste backfill materials. Journal of Cleaner Production, 259, 120798.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Opong, R.W., Nsiah-Baafi, E., Andrews, A. et al. Preliminary Study on the Use of Reverse Osmosis Brine and Mine Tailings as Cement Paste Mixtures for Mine Backfilling Application. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 497 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05959-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05959-1