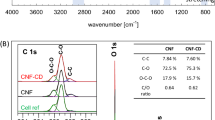
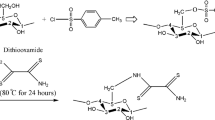
Abstract
Micropollutants such as pesticides and their derivatives can be major threats causing cancer and disrupting the endocrine system. There is an urgent need for the removal of these kinds of micropollutants. Nanocellulose-based materials, classified as “green” materials,” have been used very rarely in pesticide removal processes. Therefore, cellulose nanofiber immobilization was performed on poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-glycidyl methacrylate) [poly(HEMA-GMA)] polymeric structures under alkaline conditions to increase surface area, hydroxyl content, and transport kinetics in an adsorbent. The stability and structural verification of the polymeric adsorbent were assessed via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and swelling tests. While the water-sorption capacity for plain poly(HEMA-GMA) was 16 times higher than its weight, this value increased up to 30 times after modification. The maximum adsorption of 95.76 mg/g was obtained at the plateau value of 250 mg/L atrazine concentration. Adsorption was analyzed by mathematical models, and it has been observed that interactions dominated by chemical dynamics occur homogeneously and irreversibly.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abukhadra, M. R., Shaban, M., & Abd El Samad, M. A. (2018). Enhanced photocatalytic removal of safranin-T dye under sunlight within minute time intervals using heulandite/polyaniline@ nickel oxide composite as a novel photocatalyst. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 162, 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.081
Akveran, G. A., Köse, K., & Köse, D. A. (2018). Solvent effect on endosulfan adsorption onto polymeric arginine-methacrylate cryogels. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 25458–25467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2531-z
Alavanja, M. C., Ross, M. K., & Bonner, M. R. (2013). Increased cancer burden among pesticide applicators and others due to pesticide exposure. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 63, 120–142. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21170
Alvord, H. H., & Kadlec, R. H. (1995). The interaction of atrazine with wetland sorbents. Ecological Engineering, 5, 469–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8574(95)00036-4
Amirabad, L. M., Jonoobi, M., Mousavi, N. S., Oksman, K., Kaboorani, A., & Yousefi, H. (2018). Improved antifungal activity and stability of chitosan nanofibers using cellulose nanocrystal on banknote papers. Carbohydrate Polymers, 189, 229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.02.041
Barreiro, J. C., Capelato, M. D., Martin-Neto, L., & Bruun Hansen, H. C. (2007). Oxidative decomposition of atrazine by a Fenton-like reaction in a H2O2/ferrihydrite system. Water Research, 41, 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.09.016
Boul, H. L., Garnham, M. L., Hucker, D., Baird, D., & Aislabie, J. (1994). Influence of agricultural practices on the levels of DDT and its residues in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 1397–1402. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00057a004
Bouwman, H., Kylin, H., Sereda, B., & Bornman, R. (2012). High levels of DDT in breast milk: Intake, risk, lactation duration, and involvement of gender. Environmental Pollution, 170, 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.06.009
Breach, R. (1989). The EC directive on drinking water (EEC 80/778). Water Environment Journal, 3, 323–327.
Brinkman, U. A. T. (2008). Online monitoring of aquatic samples. Automated procedures that increase the speed of analysis and improve analyte detectability are discussed. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 79A-84A. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00002a002
Center, T. P. D. (2022). Web Page: The University of Maine, The Process Development Center, Nanocellulose Data Sheets. https://umaine.edu/pdc/nanocellulose/nanocellulose-spec-sheets-and-safety-data-sheets/. CAS Number: 9004-34-6
Chen, C., Yang, S., Guo, Y., Sun, C., Gu, C., & Xu, B. (2009). Photolytic destruction of endocrine disruptor atrazine in aqueous solution under UV irradiation: Products and pathways. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 675–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.050
Chenampulli, S., Unnikrishnan, G., Sujith, A., Thomas, S., & Francis, T. (2013). Cellulose nano-particles from Pandanus: Viscometric and crystallographic studies. Cellulose, 20, 429–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9831-0
Clement, R. E., Koester, C. J., & Eiceman, G. A. (2002). Environmental analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 65, 85–116. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00060a007
Czaplicka, M., Barchanska, H., Jaworek, K., & Kaczmarczyk, B. (2017). The interaction between atrazine and the mineral horizon of soil: A spectroscopic study. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 827–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1843-9
Dainiak, M. B., Kumar, A., Plieva, F. M., Galaev, I. Y., & Mattiasson, B. (2004). Integrated isolation of antibody fragments from microbial cell culture fluids using supermacroporous cryogels. Journal of Chromatography A, 1045, 93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2004.06.029
Das, G., Kakati, N., Lee, S. H., Karak, N., & Yoon, Y. S. (2014). Water soluble sodium sulfate nanorods as a versatile template for the designing of copper sulfide nanotubes. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 14, 4455–4461. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.8282
De Gaetano, Y., Hubert, J., Mohamadou, A., Boudesocque, S., Plantier-Royon, R., Renault, J.-H., & Dupont, L. (2016). Removal of pesticides from wastewater by ion pair centrifugal partition extraction using betaine-derived ionic liquids as extractants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 285, 596–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.012
Dong, C. D., Chen, C. W., & Hung, C. M. (2017). Synthesis of magnetic biochar from bamboo biomass to activate persulfate for the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments. Bioresource Technology, 245, 188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.204
ECETOC. (2013) Annual Report, Technical Report 123: Environmental Exposure Assessment of Ionisable Organic Compounds, Availavle at: http://bit.ly/ecetoc-tr123. European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals Brussels, Belgium.
Erol, K., Cebeci, B. K., Kose, K., & Kose, D. A. (2019). Effect of immobilization on the activity of catalase carried by poly(HEMA-GMA) cryogels. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 123, 738–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.121
Garcia, F. A. P., and Pires E. M. V. (1993) Recovery processes for biological materials. Chromatography, Wiley, London: 415–451.
Gautam, D., Kumari, S., Ram, B., Chauhan, G. S., & Chauhan, K. (2018). A new hemicellulose-based adsorbent for malachite green. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 3889–3897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.05.029
Gong, P., Wang, X. P., Li, S. H., Yu, W. S., Li, J. L., Kattel, D. B., Wang, W. C., Devkota, L. P., Yao, T. D., & Joswiak, D. R. (2014). Atmospheric transport and accumulation of organochlorine compounds on the southern slopes of the Himalayas, Nepal. Environmental Pollution, 192, 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.05.015
Gupta, V. K., & Ali, I. (2001). Removal of DDD and DDE from wastewater using bagasse fly ash, a sugar industry waste. Water Research, 35, 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00232-3
Hansen, S. P., Messer, T. L., & Mittelstet, A. R. (2019). Mitigating the risk of atrazine exposure: Identifying hot spots and hot times in surface waters across Nebraska, USA. Journal of Environmental Management, 250, 109424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109424
Hatrík, Š, & Tekel, J. (1996). Extraction methodology and chromatography for the determination of residual pesticides in water. Journal of Chromatography A, 733, 217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(95)00725-3
Hayashi, N., Kondo, T., & Ishihara, M. (2005). Enzymatically produced nano-ordered short elements containing cellulose Iβ crystalline domains. Carbohydrate Polymers, 61, 191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.04.018
Heberer, T., & Dünnbier, U. (1999). DDT metabolite bis(chlorophenyl)acetic acid: The neglected environmental contaminant. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 2346–2351. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9812711
Hedegaard, M. J., & Albrechtsen, H. J. (2014). Microbial pesticide removal in rapid sand filters for drinking water treatment–potential and kinetics. Water Research, 48, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.024
Ihsanullah, I. (2022). MXenes as next-generation materials for the photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals in water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10, 107381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107381
Ihsanullah, I., Bilal, M., & Jamal, A. (2022). Recent developments in the removal of dyes from water by starch-based adsorbents. The Chemical Record, 22, e202100312. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202100312
Ihsanullah, I., Sajid, M., Khan, S., & Bilal, M. (2022). Aerogel-based adsorbents as emerging materials for the removal of heavy metals from water: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Separation and Purification Technology, 291, 120923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120923
Ismail, M., Weng, C. N., Rahman, H. A., & Zakaria, N. A. (2013). Freundlich isotherm equilibrium equastions in determining effectiveness a low cost absorbent to heavy metal removal in wastewater (leachate) at Teluk Kitang Landfill, Pengkalan Chepa, Kelantan, Malaysia. Journal of Earth Science, 1, 01–08.
Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (1997). Determination of pesticides in water, sediments and soils by gas chromatography. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 68, 83–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319708030482
Jiang, Z., Li, J., Jiang, D., Gao, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, W., Cao, B., Tao, Y., Wang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Removal of atrazine by biochar-supported zero-valent iron catalyzed persulfate oxidation: Reactivity, radical production and transformation pathway. Environmental Research, 184, 109260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109260
Kassab, Z., Abdellaoui, Y., Salim, M. H., Bouhfid, R., & El Achaby, M. (2020). Micro-and nano-celluloses derived from hemp stalks and their effect as polymer reinforcing materials. Carbohydrate Polymers, 245, 116506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116506
Kennedy, R. M. (1990). Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods in Enzymology, 182, 339–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)82029-2
Khan, J. A., He, X., Shah, N. S., Khan, H. M., Hapeshi, E., Fatta-Kassinos, D., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2014). Kinetic and mechanism investigation on the photochemical degradation of atrazine with activated H2O2, S2O82− and HSO5−. Chemical Engineering Journal, 252, 393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.104
Khan, A., Wang, X., Gul, K., Khuda, F., Aly, Z., & Elseman, A. (2018). Microwave-assisted spent black tea leaves as cost-effective and powerful green adsorbent for the efficient removal of eriochrome black T from aqueous solutions. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5, 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2018.04.002
Kolakovic, R., Peltonen, L., Laaksonen, T., Putkisto, K., Laukkanen, A., & Hirvonen, J. (2011). Spray-dried cellulose nanofibers as novel tablet excipient. An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 12, 1366–1373. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-011-9705-z
Köse, K. (2014). Nükleik asit bazları içeren kriyojellerin sentezi, karakterizasyonu ve biyokromatografide adsorbent olarak kullanımı (p. 110). Hacettepe Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey.
Köse, K. (2016). Nucleotide incorporated magnetic microparticles for isolation of DNA. Process Biochemistry, 51, 1644–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.07.021
Köse, K., Arslan Akveran, G., Erol, K., & Köse, D. A. (2018). Nicotinamide-modified poly(HEMA-GMA)-Nic cryogels for removal of pesticides. Journal of the Turkish Chemical Society, Section A, 5, 941–952. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.394592
Köse, K., Mavlan, M., Nuruddin, M., & Youngblood, J. P. (2020). TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber based polymeric adsorbent for use in iron removal. Cellulose, 27, 4623–4635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03104-x
Köse, K., Mavlan, M., & Youngblood, J. P. (2020). Applications and impact of nanocellulose based adsorbents. Cellulose, 27, 2967–2990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03011-1
Kose, K., & Kose, D. A. (2017). Removal of DDE by exploiting the alcoho-phobic interactions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 24, 9187–9193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8576-6
Kose, K., Erol, K., Emniyet, A. A., Kose, D. A., Avci, G. A., & Uzun, L. (2015). Fe(II)-Co(II) double salt incorporated magnetic hydrophobic microparticles for invertase adsorption. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 177, 1025–1039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1794-9
Laçin, O., Demir, F., & Bastaban, B. (2019). Aktif karbon uzerine perteknetat oksoanyonunun denge izoterm modelinin belirlenmesi. Sinop Üniversitesi fen bilimleri dergisi, 4, 37–46. https://doi.org/10.33484/sinopfbd.486647
Li, J., Wei, X., Wang, Q., Chen, J., Chang, G., Kong, L., Su, J., & Liu, Y. (2012). Homogeneous isolation of nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse by high pressure homogenization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 90, 1609–1613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.038
Lopes, B., Arrebola, J. P., Serafim, A., Company, R., Rosa, J., & Olea, N. (2014). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and p, p’-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) concentrations in maternal and umbilical cord serum in a human cohort from South Portugal. Chemosphere, 114, 291–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.111
Lozinsky, V. I., Galaev, I. Y., Plieva, F. M., Savina, I. N., Jungvid, H., & Mattiasson, B. (2003). Polymeric cryogels as promising materials of biotechnological interest. Trends in Biotechnology, 21, 445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2003.08.002
MacCarthy, P., Klusman, R. W., Cowling, S. W., & Rice, J. A. (2002). Water analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 67, 525–582. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00108a039
Madivoli, E., Kareru, P., Gachanja, A., Makhanu, D. & Mugo, S. (2022). Cellulose-based hybrid nanoarchitectonics with silver nanoparticles: characterization and antimicrobial potency. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials,1-10https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02212-w
Mahendra, I., Wirjosentono, B., Ismail, H., & Mendez, J. (2019). Thermal and morphology properties of cellulose nanofiber from TEMPO-oxidized lower part of empty fruit bunches (LEFB). Open Chemistry, 17, 526–536. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2019-0063
Martini, M. C., Albicoro, F. J., Nour, E., Schluter, A., van Elsas, J. D., Springael, D., Smalla, K., Pistorio, M., Lagares, A., & Del Papa, M. F. (2015). Characterization of a collection of plasmid-containing bacteria isolated from an on-farm biopurification system used for pesticide removal. Plasmid, 80, 16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2015.05.001
Mohamed, F., Abukhadra, M. R., & Shaban, M. (2018). Removal of safranin dye from water using polypyrrole nanofiber/Zn-Fe layered double hydroxide nanocomposite (Ppy NF/Zn-Fe LDH) of enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic properties. Science of the Total Environment, 640–641, 352–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.316
Nguyen, P. A., Trinh, T. H., Fukumitsu, Y., Shimodaira, J., Miyauchi, K., Tokuda, M., Kasai, D., Masai, E., & Fukuda, M. (2013). Gene cluster and regulation system for 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethylene (DDE) degradation in Janibacter sp. TYM3221. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 116, 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.01.007
Pavlova, P. A., Schmid, P., Bogdal, C., Steinlin, C., Jenk, T. M., & Schwikowski, M. (2014). Polychlorinated biphenyls in glaciers. 1. Deposition history from an Alpine ice core. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 7842–7848. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5017922
Penn, C. J., Gonzalez, J. M., & Chagas, I. (2018). Investigation of atrazine sorption to biochar with titration calorimetry and flow-through analysis: Implications for design of pollution-control structures. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6, 307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00307
Peters, B. (2017) Chapter 6 - Collision theory, in Reaction Rate Theory and Rare Events Simulations, B. Peters, Editor. Elsevier: Amsterdam. p.147–156.
Saito, T., & Isogai, A. (2004). TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. The effect of oxidation conditions on chemical and crystal structures of the water-insoluble fractions. Biomacromolecules, 5, 1983–1989. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0497769
Salama, A. (2019). Cellulose/calcium phosphate hybrids: New materials for biomedical and environmental applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 127, 606–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.130
Saleh, T. A. (2015). Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on Hg(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by silica- multiwall carbon nanotubes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22, 16721–16731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4866-z
Scopes, R. K., & Stoter, A. (1982). Purification of all glycolytic enzymes from one muscle extract. Methods in Enzymology, 90, 479–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(82)90175-6
Scouten, W. H. (1981). Affinity chromatography : Bioselective adsorption on inert matrices. USA, John Wiley and Sons.
Sharpe, R. M. (1995). Reproductive biology. Another DDT connection. Nature, 375, 538–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/375538a0
Shen, L., & Wania, F. (2005). Compilation, evaluation, and selection of physical−chemical property data for organochlorine pesticides. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 50, 742–768. https://doi.org/10.1021/je049693f
Shikuku, V. O., Zanella, R., Kowenje, C. O., Donato, F. F., Bandeira, N. M. G., & Prestes, O. D. (2018). Single and binary adsorption of sulfonamide antibiotics onto iron-modified clay: Linear and nonlinear isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanistic studies. Applied Water Science, 8, 175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0825-4
Szewczyk, R., Rozalska, S., Mironenka, J., & Bernat, P. (2020). Atrazine biodegradation by mycoinsecticide Metarhizium robertsii: Insights into its amino acids and lipids profile. Journal of Environmental Management, 262, 110304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110304
Thambiraj, S., Sharmila, G., & Shankaran, D. R. (2018). Green adsorbents from solid wastes for water purification application. Mater. Today: Proc., 5, 16675–16683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.029
Tian, H., Chen, J., He, J., & Liu, F. (2015). Pd-loaded magnetic mesoporous nanocomposites: A magnetically recoverable catalyst with effective enrichment and high activity for DDT and DDE removal under mild conditions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 457, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.024
Turkova, J. (1993). Chapter 8 General Considerations on Sorption, Elution and Non-Specific Binding, in Journal of Chromatography Library. J. Turková, Editor. Elsevier. p. 313–370.
Uzunoğlu, G. (2013). Düşük molekül ağırlıklı heparin takılı phema kriyojel ile kandan kolesterol uzaklaştırılması (p. 83). Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey.
Vymazal, J., & Brezinova, T. (2015). The use of constructed wetlands for removal of pesticides from agricultural runoff and drainage: A review. Environment International, 75, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.10.026
Yildirim, N., & Shaler, S. (2017). A study on thermal and nanomechanical performance of cellulose nanomaterials (CNs). Materials (basel), 10, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070718
Yu, Y., Li, Y., Shen, Z., Yang, Z., Mo, L., Kong, Y., & Lou, I. (2014). Occurrence and possible sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) along the Chao River, China. Chemosphere, 114, 136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.095
Zhai, Y., Abdolahpur Monikh, F., Wu, J., Grillo, R., Arenas-Lago, D., Darbha, G. K., Vijver, M. G., & Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M. (2020). “Interaction between a nano-formulation of atrazine and rhizosphere bacterial communities: Atrazine degradation and bacterial community alterations. Environmental Science: Nano, 7, 3372–3384. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0en00638f
Zhao, L., Deng, Y. R., Du, Y. X., & Fu, X. (2012). Study on the degradation of atrazine in photo-fenton-like system under visible light irradiation promoted by N-doped Ta2O5. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 33, 1252–1259.
Zolfaghari, G. (2016). β-Cyclodextrin incorporated nanoporous carbon: Host–guest inclusion for removal of p-nitrophenol and pesticides from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 283, 1424–1434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.110
Funding
This work was supported by Hittite University Scientific Research Projects Coordination (FEF19001.20.008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Methodology was under the responsibility of Lokman Uzun and Dursun Ali Köse. Material preparation, resources, and data collection were performed by Miraç Tüysüz, Kazım Köse, and Mehtap Evci. Analysis was performed by Miraç Tüysüz and Davut Aksüt. Data curation and validation were performed by Jeffrey P. Youngblood. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Kazım Köse, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tüysüz, M., Köse, K., Aksüt, D. et al. Removal of Atrazine Using Polymeric Cryogels Modified with Cellulose Nanomaterials. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 472 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05947-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05947-5