Abstract
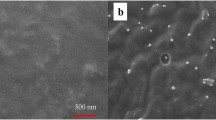
The residues of pharmaceutical compounds such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in aquatic environments are a matter of global concern because they may pose deleterious risks to human health and ecosystems. In this study, a novel composite was prepared by grafting ionic liquid hypercrosslinked polymer onto the surface of the melamine sponge skeleton. The resultant hypercrosslinked polymer@sponge was characterized using SEM, BET, FT-IR, TG-DSC, XPS, and a zeta potential analyzer. The composite can provide strong ion exchange sites and multiple interactions, which had a strong interaction with the target NSAIDs. The adsorption conditions, including pH, extraction time, salt concentration, and initial concentration of the drugs, were systematically optimized to obtain the maximum removal efficiency. Studies revealed that the prepared IL-HCPs@MS had a strong affinity for NSAIDs, particularly for diclofenac and ketoprofen. The adsorption isotherms and kinetics data of both these IL-HCPs@MS were in alignment with the Langmuir model (R2 > 0.98) and the pseudo-second-order model (R2 > 0.99), respectively. The results showed the removal of NSAIDs by the HCPs@MS was mainly based on the chemisorption process, monolayer adsorption with an endothermic mechanism, and an enthalpy-driven process. The composite will be a promising sorbent with potential applications in water environment remediation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Almeida, H. F. D., Marrucho, I. M., & Freire, M. G. (2017). Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from aqueous environments with reusable ionic-liquid-based systems, ACS Sustain. Chemical Engineering, 5, 2428–2436. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02771
Almeida, H. F. D., Neves, M. C., Trindade, T., Marrucho, I. M., & Freire, M. G. (2020). Supported ionic liquids as efficient materials to remove non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from aqueous media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 381, 122616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122616
Bhadra, B. N., Ahmed, I., Kim, S., & Jhung, S. H. (2017). Adsorptive removal of ibuprofen and diclofenac from water using metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 314, 50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.127
Chen, D., Shi, F., Xu, W., Shen, H., & Zhu, Y. (2021). A simultaneous extraction and enrichment method for rapid detection of polar chlorophenoxy acid and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from wastewater based on low-generation dendrimer poly(propylene imine). Microchemical Journal, 168, 106454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106454
Dai, L., Han, T., Ma, G., Tian, X., Meng, K., Lei, Z., & Ren, J. (2022). Effective removal of Cd(ii) by sludge biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: Characterization, adsorption properties and mechanism, New. Journal of Chemistry, 46, 13184–13195. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NJ01735K
Feng, X., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Ma, Y., Ji, W., Sun, Y., Chen, T., & Chen, Y. (2021). Preparation of a ZIF-67-modified magnetic solid phase extraction material and its application in the detection of pyridine ring insecticides, New. Journal of Chemistry, 45, 9382–9393. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ00703C
Ge, W. S., Li, S. Q., Jiang, M. Q., He, G. H., & Zhang, W. J. (2022). Cu/Fe bimetallic modified Fly Ash: An economical adsorbent for enhanced phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Poll., 233, 182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05628-3
Ghafari, M., & Atkinson, J. D. (2018). Impact of styrenic polymer one-step hyper-cross-linking on volatile organic compound adsorption and desorption performance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 351, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.051
Hu, K., Cheng, J., Zhang, W., Pang, T., Wu, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, Y., Zhao, W., & Zhang, S. (2020). Simultaneous extraction of diverse organic pollutants from environmental water using a magnetic covalent organic framework composite. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1140, 132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.10.019
Hu, K., Pang, T., Shi, Y., Han, P., Zhao, Y., Zhao, W., Zeng, H., Zhang, S., & Zhang, Z. (2021a). Magnetic borate-modified Mxene: A highly affinity material for the extraction of catecholamines. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1176, 338769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338769
Hu, K., Shi, Y., Zhu, W., Cai, J., Zhao, W., Zeng, H., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, S. (2021b). Facile synthesis of magnetic sulfonated covalent organic framework composites for simultaneous dispersive solid-phase extraction and determination of beta-agonists and fluoroquinolones in food samples. Food Chemistry, 339, 128079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128079
Jrad, A., Damacet, P., Yaghi, Z., Ahmad, M., & Hmadeh, M. (2022). Zr-based metal–organic framework nanocrystals for water remediation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 5, 10795–10808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c02128
Lei, Z., Feng, J., Yang, Y., Shen, J., Zhang, W., & Wang, C. (2020). An efficient polymer coating for highly acid-stable zeolitic imidazolate frameworks based composite sponges. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 382, 121057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121057
Li, K., Jiao, T., Xing, R., Zou, G., Zhao, Q., Zhou, J., Zhang, L., & Peng, Q. (2018). Fabrication of hierarchical MXene-based AuNPs-containing core–shell nanocomposites for high efficient catalysts. Green Energy Environment, 3, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2017.11.004
Li, Z., Ding, X., Feng, Y., Feng, W., & Han, B.-H. (2019). Structural and dimensional transformations between covalent organic frameworks via linker exchange. Macromolecules, 52, 1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b01814
Li, J., Yang, Y., Ma, W., Li, G., Lu, Q., & Lin, Z. (2021). One-pot room-temperature synthesis of covalent organic framework-coated superhydrophobic sponges for highly efficient oil-water separation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 411, 125190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125190
Liang, X., Wang, J., Wu, Q., Wang, C., & Wang, Z. (2018). Use of a hypercrosslinked triphenylamine polymer as an efficient adsorbent for the enrichment of phenylurea herbicides. Journal of Chromatography A, 1538, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.01.033
Liu, Y., Lo, S., Liou, Y., & Hu, C. (2015). Removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) by electrocoagulation–flotation with a cationic surfactant. Separation and Purification Technology, 152, 148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.08.015
Liu, W., Wang, J., Liu, J., Hou, F., Wu, Q., Wang, C., & Wang, Z. (2020). Preparation of phenylboronic acid based hypercrosslinked polymers for effective adsorption of chlorophenols. Journal of Chromatography A, 1628, 461470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461470
Liu, H., Dang, S., Gu, A., & Ye, B. (2021). A magnetic MOF derivative with rich interactions formed under mild preparation conditions for the extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from the Yellow River. Analytical Methods, 13, 3256–3263. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00378J
Makos-Chelstowska, P., Slupek, E., & Malachowska, A. (2022). Superhydrophobic sponges based on green deep eutectic solvents for spill oil removal from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425, 127972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127972
Mlunguza, N. Y., Ncube, S., Nokwethemba Mahlambi, P., Chimuka, L., & Madikizela, L. M. (2019). Adsorbents and removal strategies of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from contaminated water bodies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 103142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103142
Mo, P., Fu, D., Chen, P., Zhang, Q., Zheng, X., Hao, J., Zhuang, X., Liu, H., Liu, G., & Lv, W. (2021). Ionic covalent organic frameworks for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) removal from aqueous solution: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Separation and Purification Technology, 278, 119238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119238
Nadal, J. C., Dargo, S., Borrull, F., Cormack, P. A. G., Fontanals, N., & Marce, R. M. (2022). Hypercrosslinked polymer microspheres decorated with anion- and cation-exchange groups for the simultaneous solid-phase extraction of acidic and basic analytes from environmental waters. Journal of Chromatography A, 1661, 462715.
Nas, B., Dolu, T., & Koyuncu, S. (2021). Behavior and removal of ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole antibiotics in three different types of full-scale wastewater treatment plants: A comparative study. Water Air Soil Poll, 232, 127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05067-6
Nuckowski, L., Dzieszkowski, K., Rafinski, Z., & Studzinska, S. (2021). Application of magnetic nanoparticles coated with crosslinked zwitterionic poly(ionic liquid)s for the extraction of oligonucleotides. Materials, 14(12), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123146
Salman, M. S., Alhares, H. S., Ali, Q. A., M-Ridha, M. J., Mohammed, S. J., & Abed, K. M. (2022). Cladophora algae modified with CuO nanoparticles for tetracycline removal from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Poll, 233, 321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05813-4
Shen, R., Huang, L., Liu, R., & Shuai, Q. (2021). Determination of sulfonamides in meat by monolithic covalent organic frameworks based solid phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric. Journal of Chromatography A, 1655, 462518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462518
Song, S., Ai, J., Hu, A., Liao, G., & Wang, D. (2021a). Synthesis of carboxyl-modified hyper-cross-linked polymers with conspicuous removal capability for various water-soluble contaminants. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 106047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106047
Song, H., Zhang, H., He, Y., Gao, R., Wang, Y., Wang, W., Pfefferle, L. D., Tang, X., & Tang, Y. (2021b). Novel bayberry-and-honeycomb-like magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective enrichment of rutin from Sophora japonica. Food Chemistry, 356, 129722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129722
Suriyanon, N., Punyapalakul, P., & Ngamcharussrivichai, C. (2013). Mechanistic study of diclofenac and carbamazepine adsorption on functionalized silica-based porous materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 214, 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.052
Tan, L., & Tan, B. (2017). Hypercrosslinked porous polymer materials: Design, synthesis, and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 46, 3481–3481. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS90027A
Wang, H., Wang, E., Liu, Z., Gao, D., Yuan, R., Sun, L., & Zhu, Y. (2015). A novel carbon nanotubes reinforced superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge for selective oil–water separation through a chemical fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A, 3, 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03945A
Wang, Q., Yang, M., Qi, X., Wang, J., Sun, K., Li, Z., & Deng, G. (2021). A novel graphene oxide decorated with halloysite nanotubes (HNTs/GO) composite used for the removal of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in a wide pH range, New. Journal of Chemistry, 45, 18315–18326. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ03807A
Wu, J., Ma, R., Hao, L., Wang, C., Wu, Q., & Wang, Z. (2017). Triphenylamine-based hypercrosslinked organic polymer as adsorbent for the extraction of phenylurea herbicides. Journal of Chromatography A, 1520, 48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.09.012
Xie, Y., Liang, J., Fu, Y., Huang, M., Xu, X., Wang, H., Tu, S., & Li, J. (2018). Hypercrosslinked mesoporous poly(ionic liquid)s with high ionic density for efficient CO2 capture and conversion into cyclic carbonates. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6, 6660–6666.
Xu, M., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Wang, Q., Liu, W., An, Y., Hao, L., Wang, C., Wang, Z., & Wu, Q. (2022). Construction of hydrophilic hypercrosslinked polymer based on natural kaempferol for highly effective extraction of 5-nitroimidazoles in environmental water, honey and fish samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 429, 128288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128288
Yu, H., Jin, P., Zhu, F., Takafuji, M., Ihara, H., Nie, L., & Liu, H. (2021). Efficient extraction of quaternary ammonium alkaloids based on π-conjugated polymer coated porous silica adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 426, 131061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131061
Zhang, H. T., West, D., Shi, H. L., Ma, Y. F., Adams, C., & Eichholz, T. (2019). Simultaneous determination of selected trace contaminants in drinking water using solid-phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Water Air Soil Poll., 230, 28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4066-9
Zhang, T., Zhang, W., Xi, H., Li, Q., Shen, M., Ying, G., & Zhang, J. (2021). Polydopamine functionalized cellulose-MXene composite aerogel with superior adsorption of methylene blue. Cellulose, 28, 4281–4293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03737-6
Zhang, X., Bao, T., Wei, F., & Wang, S. (2022a). Zeotype porous coordination networks as potential adsorbents for removing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from water. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 640, 128401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128401
Zhang, Y., Zhang, G., Liu, W., Li, M., Jiang, S., Hao, L., Wang, Z., Wu, Q., & Wang, C. (2022b). Fabrication of carbonyl-functional hypercrosslinked polymers as solid-phase extraction sorbent for enrichment of chlorophenols from water, honey and beverage samples. Microchimica Acta, 189, 21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05123-2
Zuo, W. D., Wang, X., Zhang, D. Y., Sun, Y., Xu, J. B., & Guo, P. (2019). Performance and mechanism of GO-MCM-Fe composite catalyst activating persulfate to remove levofloxacin hydrochloride in water. Water Air Soil Poll., 230, 255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4303-x
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22174032, 82174187), the Training Plan for Young Backbone Teachers in Universities of Henan Province (2020GGJS105), the Key Scientific Research Project of Universities in Henan Province (22ZX007), and the Henan Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (222300420060). The authors would like to thank Xiangyu Wu from Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the XPS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, P., Hu, K., Li, L. et al. Preparation of Hypercrosslinked Polymer-Based Sponge and its Application for the Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Water Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 456 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05927-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05927-9