Abstract
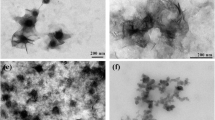
Oxyanions including common phosphates, sulfates, carbonates, hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)), and pentavalent vanadium (V(V)) occur as contaminants in aquifers. Here, carboxymethylcellulose (CMC)-modified amorphous nano zero-valent iron (CMC-AnZVI) was synthesized by liquid-phase reduction and evaluated as a potential aquifer treatment material for Cr(VI) and V(V) removal. The application rate of CMC did not change the crystallinity but affected the reactivity of the material. Furthermore, CMC-AnZVI showed high efficiency and capacity to eliminate Cr(VI) and V(V) due to its distinctive crystal structure and nano size. At pH 7.0 ± 0.2, the Cr(VI) and V(V) elimination rate constants were up to 1.77 × 10−2 min−1 and 1.67 × 10−1 min−1, respectively. In addition, CMC-AnZVI exhibited strong sequestration ability over the wide pH range of 3–11. Langmuir fitted the reaction of CMC-AnZVI and the removal capacities of Cr(VI) and V(V) were 132.8 and 269.5 mg g−1, respectively. The main Cr(VI) elimination mechanism of CMC-AnZVI was reduction and that of V(V) was rapid inner-sphere surface complexation. Consequently, the removal of V(V) was sensitive to Cr(VI) due to the strong oxidation capacity of Cr(VI) and the secondary minerals (FeCr2O4 and Cr(OH)3) created in the reaction covered the active sites. CMC-AnZVI is proposed as an efficient material for the removal of Cr(VI) and V(V) and the interrelationships between oxyanions during elimination require further study.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Adebambo, O. A., Ray, P. D., Shea, D., & Fry, R. C. (2015). Toxicological responses of environmental mixtures: Environmental metal mixtures display synergistic induction of metal-responsive and oxidative stress genes in placental cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 289, 534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.005
Ai, Z. H., Cheng, Y., Zhang, L. Z., & Qiu, J. R. (2008). Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution with Fe@Fe2O3 core-shell nanowires. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 6955–6960. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800962m
Bae, S., & Hanna, K. (2015). Reactivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron in unbuffered systems: Effect of pH and Fe(II) dissolution. Environmental Science & Technology, 49, 10536–10543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01298
Bello, A., Leiviska, T., Zhang, R., Tanskanen, J., Maziarz, P., Matusik, J., & Bhatnagar, A. (2019). Synthesis of zerovalent iron from water treatment residue as a conjugate with kaolin and its application for vanadium removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 374, 372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.056
Buerge, I. J., & Hug, S. J. (1997). Kinetics and pH dependence of chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II). Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 1426–1432. https://doi.org/10.1021/es960672i
Cao, C. Y., Qu, J., Yan, W. S., Zhu, J. F., Wu, Z. Y., & Song, W. G. (2012). Low-cost synthesis of flowerlike alpha-Fe2O3 nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal: Adsorption property and mechanism. Langmuir, 28, 4573–4579. https://doi.org/10.1021/la300097y
Catalano, J. G., Park, C., Fenter, P., & Zhang, Z. (2008). Simultaneous inner- and outer-sphere arsenate adsorption on corundum and hematite. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 72, 1986–2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.02.013
Chen, Z., Tang, X., Qiao, W., Puentes Jácome, L. A., Edwards, E. A., He, Y. & Xu, J. (2020). Nanoscale zero-valent iron reduction coupled with anaerobic dechlorination to degrade hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in historically contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123298
Chen, Z., Wei, D., Li, Q., Wang, X., Yu, S., Liu, L., Liu, B., Xie, S., Wang, J., Chen, D., Hayat, T., & Wang, X. (2018). Macroscopic and microscopic investigation of Cr(VI) immobilization by nanoscaled zero-valent iron supported zeolite MCM-41 via batch, visual, XPS and EXAFS techniques. Journal of Cleaner Production, 181, 745–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.231
Colton, R. J., Guzman, A. M., & Rabalais, J. W. (1978). Electronchromism in some thin-film transition-metal oxides characterized by X-ray electron-spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Physics, 49, 409–416. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.324349
Costa, M., & Klein, C. B. (2006). Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 36, 155–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440500534032
Coyte, R. M., & Vengosh, A. (2020). Factors controlling the risks of co-occurrence of the redox-sensitive elements of arsenic, chromium, vanadium, and uranium in groundwater from the Eastern United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 54, 4367–4375. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06471
Desimoni, E., Malitesta, C., Zambonin, P. G., & Riviere, J. C. (1988). An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of some chromium oxygen systems. Surface and Interface Analysis, 13, 173–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.740130210
Diao, J., Xie, B., Wang, Y., & Ji, C. Q. (2009). Mineralogical characterisation of vanadium slag under different treatment conditions. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 36, 476–480. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328109x410622
Dong, H. R., Deng, J. M., Xie, Y. K., Zhang, C., Jiang, Z., Cheng, Y. J., Hou, K. J., & Zeng, G. M. (2017). Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 332, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002
Dong, H. R., He, Q., Zeng, G. M., Tang, L., Zhang, C., Xie, Y. K., Zeng, Y. L., Zhao, F., & Wu, Y. A. (2016). Chromate removal by surface-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effect of different surface coatings and water chemistry. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 471, 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.011
Eary, L. E., & Rai, D. (1988). Chromate removal from aqueous wastes by reduction with ferrous ion. Environmental Science & Technology, 22, 972–977. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00173a018
Erdem Yayayürük, A., & Yayayürük, O. (2017). Adsorptive performance of nanosized zero-valent iron for V(V) removal from aqueous solutions. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 92, 1891–1898. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5209
Evans, R. M., Martin, O. V., Faust, M., & Kortenkamp, A. (2016). Should the scope of human mixture risk assessment span legislative/regulatory silos for chemicals? Science of the Total Environment, 543, 757–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.162
Fan, C., Chen, N., Qin, J., Yang, Y., Feng, C., Li, M. & Gao, Y. (2020a). Biochar stabilized nano zero-valent iron and its removal performance and mechanism of pentavalent vanadium(V(V)). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020a.124882
Fan, H., Ren, H., Ma, X., Zhou, S., Huang, J., Jiao, W., Qi, G. & Liu, Y. (2020b). High-gravity continuous preparation of chitosan-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron towards Cr(VI) removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020b.124639
Fan, Y. Y., Wang, X. W., & Wang, M. Y. (2013). Separation and recovery of chromium and vanadium from vanadium-containing chromate solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy, 136, 31–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.03.008
Fang, D., Liao, X., Zhang, X. F., Teng, A. J., & Xue, X. X. (2018). A novel resource utilization of the calcium-based semi-dry flue gas desulfurization ash: As a reductant to remove chromium and vanadium from vanadium industrial wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 342, 436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.060
Gao, J., Wang, W., Rondinone, A. J., He, F., & Liang, L. Y. (2015). Degradation of trichloroethene with a novel ball milled Fe-C nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.038
Ge, H. L., Liu, S. S., Su, B. X., & Qin, L. T. (2014). Predicting synergistic toxicity of heavy metals and ionic liquids on photobacterium Q67. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 268, 77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.006
Ghods, P., Isgor, O. B., Brown, J. R., Bensebaa, F., & Kingston, D. (2011). XPS depth profiling study on the passive oxide film of carbon steel in saturated calcium hydroxide solution and the effect of chloride on the film properties. Applied Surface Science, 257, 4669–4677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.12.120
Gupta, V. K., Fakhri, A., Bharti, A. K., Agarwal, S., & Naji, M. (2017). Optimization by response surface methodology for vanadium (V) removal from aqueous solutions using PdO-MWCNTs nanocomposites. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 234, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.03.061
He, F., Zhao, D., Liu, J., & Roberts, C. B. (2007). Stabilization of Fe-Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, 29–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0610896
He, F., & Zhao, D. Y. (2007). Manipulating the size and dispersibility of zerovalent iron nanoparticles by use of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilizers. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 6216–6221. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0705543
He, F., Zhao, D. Y., & Paul, C. (2010). Field assessment of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles for in situ destruction of chlorinated solvents in source zones. Water Research, 44, 2360–2370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.041
Hryha, E., Rutqvist, E., & Nyborg, L. (2012). Stoichiometric vanadium oxides studied by XPS. Surface and Interface Analysis, 44, 1022–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.3844
Hu, Y., Peng, X., Ai, Z., Jia, F., & Zhang, L. (2019). Liquid nitrogen activation of zero-valent iron and its enhanced Cr(VI) removal performance. Environmental Science & Technology, 53, 8333–8341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01999
Huang, X., Hou, X., Song, F., Zhao, J., & Zhang, L. (2016). Facet-dependent Cr(VI) adsorption of hematite nanocrystals. Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 1964–1972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05111
Jia, T., Zhang, B., Huang, L., Wang, S., & Xu, C. (2019). Enhanced sequestration of Cr(VI) by copper doped sulfidated zerovalent iron (SZVI-Cu): Characterization, performance, and mechanisms. Chemical Engineering Journal, 366, 200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.058
Johnson, J., Anderson, G. & Parkhurst, D.: 2000, Database “Thermo.Com. V8. R6. 230”. Revision 1–11.
Kim, D., Xie, C. L., Becknell, N., Yu, Y., Karamad, M., Chan, K., Crumlin, E. J., Norskov, J. K., & Yang, P. D. (2017). Electrochemical activation of CO2 through atomic ordering transformations of AuCu nanoparticles. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 139, 8329–8336. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b03516
Kim, H. J., Leitch, M., Naknakorn, B., Tilton, R. D., & Lowry, G. V. (2017). Effect of emplaced nZVI mass and groundwater velocity on PCE dechlorination and hydrogen evolution in water-saturated sand. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 322, 136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.037
Kong, X., Chen, J., Tang, Y., Lv, Y., Chen, T., & Wang, H. (2020). Enhanced removal of vanadium(V) from groundwater by layered double hydroxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 392, 122392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122392
Kubicki, J. D., Kwon, K. D., Paul, K. W., & Sparks, D. L. (2007). Surface complex structures modelled with quantum chemical calculations: Carbonate, phosphate, sulphate, arsenate and arsenite. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 932–944. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.00931.x
Kumar, M. A., Bae, S., Hang, S., Chang, Y., & Lee, W. (2017). Reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron particles with Ni. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 340, 399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.030
Li, D., Jiang, J., Li, T., & Wang, J. (2016). Soil heavy metal contamination related to roasted stone coal slag: A study based on geostatistical and multivariate analyses. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 23, 14405–14413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6551-2
Li, H., Chen, S., Ren, L. Y., Zhou, L. Y., Tan, X. J., Zhu, Y., Belver, C., Bedia, J., & Yang, J. (2019). Biochar mediates activation of aged nanoscale ZVI by Shewanella putrefaciens CN32 to enhance the degradation of Pentachlorophenol. Chemical Engineering Journal, 368, 148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.099
Li, X. Q., Cao, J. S., & Zhang, W. X. (2008). Stoichiometry of Cr(VI) immobilization using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI): A study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron Spectroscopy (HR-XPS). Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47, 2131–2139. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie061655x
Lin, H., Tian, Y., Dong, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, L., & Chen, S. (2016). Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals by terrestrial plants around vanadium smelters. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 38, 1410–1416.
Liu, H., Zhang, B. G., Xing, Y., & Hao, L. T. (2016). Behavior of dissolved organic carbon sources on the microbial reduction and precipitation of vanadium(v) in groundwater. RSC Advances, 6, 97253–97258. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra19720e
Liu, Y. Q., Choi, H., Dionysiou, D., & Lowry, G. V. (2005). Trichloroethene hydrodechlorination in water by highly disordered monometallic nanoiron. Chemistry of Materials, 17, 5315–5322. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0511217
Manning, B. A., Kiser, J. R., Kwon, H., & Kanel, S. R. (2007). Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(III)- and Cr(VI)-treated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 586–592. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061721m
Manohar, D. M., Noeline, B. F., & Anirudhan, T. S. (2005). Removal of vanadium(IV) from aqueous solutions by adsorption process with aluminum-pillared bentonite. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 44, 6676–6684. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0490841
Melitas, N., Chuffe-Moscoso, O., & Farrell, J. (2001). Kinetics of soluble chromium removal from contaminated water by zerovalent iron media: Corrosion inhibition and passive oxide effects. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3948–3953. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001923x
Mohamed, A. A., & El-Shahat, M. F. (2000). A spectrophotometric determination of chromium and vanadium. Analytical Sciences, 16, 151–155. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.16.151
Naeem, A., Westerhoff, P., & Mustafa, S. (2007). Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Research, 41, 1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.002
Nahuel Montesinos, V., Quici, N., Beatriz Halac, E., Leyva, A. G., Custo, G., Bengio, S., Zampieri, G., & Litter, M. I. (2014). Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water with nanoparticulated zerovalent iron: Understanding the Fe(III)–Cr(III) passive outer layer structure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 244, 569–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.093
Paparazzo, E. (1987). XPS and Auger-spectroscopy studies on mixtures of the oxides SIO2, AL2O3, FE2O3, and CR2O3. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 43, 97–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(87)80022-1
Peacock, C. L., & Sherman, D. M. (2004). Vanadium(V) adsorption onto goethite (α-FeOOH) at pH 1.5 to 12: A surface complexation model based on ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 68, 1723–1733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.018
Peak, D., Ford, R. G., & Sparks, D. L. (1999). An in situ ATR-FTIR investigation of sulfate bonding mechanisms on goethite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 218, 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1999.6405
Powell, R. M., Puls, R. W., Hightower, S. K., & Sabatini, D. A. (1995). Coupled iron corrosion and chromate reduction - Mechanisms for subsurface remediation. Environmental Science & Technology, 29, 1913–1922. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00008a008
Qiu, R., Zhang, B., Li, J., Lv, Q., Wang, S., & Gu, Q. (2017). Enhanced vanadium (V) reduction and bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cells with biocathode. Journal of Power Sources, 359, 379–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.05.099
Roncevic, S., Nemet, I., Ferri, T. Z., & Matkovic-Calogovic, D. (2019). Characterization of nZVI nanoparticles functionalized by EDTA and dipicolinic acid: A comparative study of metal ion removal from aqueous solutions. RSC Advances, 9, 31043–31051. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra04831f
Santana, C. S., Montalvan Olivares, D. M., Silva, V. H. C., Luzardo, F. H. M., Velasco, F. G., & de Jesus, R. M. (2020). Assessment of water resources pollution associated with mining activity in a semi-arid region. Journal of Environmental Management, 273, 111148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111148
Shen, W., Wang, X., Jia, F., Tong, Z., Sun, H., Wang, X., Song, F., Ai, Z., Zhang, L. & Chai, B. (2020). Amorphization enables highly efficient anaerobic thiamphenicol reduction by zero-valent iron. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118550
Shuttleworth, D. (1980). Preparation of metal-polymer dispersions by plasma techniques - An ESCA investigation. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 84, 1629–1634. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100449a038
Silversmit, G., Depla, D., Poelman, H., Marin, G. B., & De Gryse, R. (2004). Determination of the V2p XPS binding energies for different vanadium oxidation states (V5+ to V0+). Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 135, 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2004.03.004
Stollenwerk, K. G., & Grove, D. B. (1985). Adsorption and desorption of hexavalent chromium in an alluvial aquifer near Telluride, Colorado. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 150–155. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1985.00472425001400010030x
Sun, Y. K., Li, J. X., Huang, T. L., & Guan, X. H. (2016). The influences of iron characteristics, operating conditions and solution chemistry on contaminants removal by zero-valent iron: A review. Water Research, 100, 277–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.031
Takagikawai, M., Soma, M., Onishi, T., & Tamaru, K. (1980). The adsorption and the reaction of NH3 and NOX on supported V2O5 catalysts - Effect of supporting materials. Canadian Journal of Chemistry-Revue Canadienne De Chimie, 58, 2132–2137. https://doi.org/10.1139/v80-340
Ureña-Begara, F., Crunteanu, A., & Raskin, J.-P. (2017). Raman and XPS characterization of vanadium oxide thin films with temperature. Applied Surface Science, 403, 717–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.160
Villa, S., Migliorati, S., Monti, G. S., & Vighi, M. (2012). Toxicity on the luminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri (Beijerinck). II: Response to complex mixtures of heterogeneous chemicals at low levels of individual components. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 86, 93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.08.030
Vollprecht, D., Krois, L.-M., Sedlazeck, K. P., Müller, P., Mischitz, R., Olbrich, T., & Pomberger, R. (2019). Removal of critical metals from waste water by zero-valent iron. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, 1409–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.180
Wang, Q., Lee, S., & Choi, H. (2010). Aging study on the structure of Fe0-nanoparticles: Stabilization, characterization, and reactivity. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114, 2027–2033. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp909137f
Wang, S., Zhang, B. G., Diao, M. H., Shi, J. X., Jiang, Y. F., Cheng, Y. T., & Liu, H. (2018). Enhancement of synchronous bio-reductions of vanadium (V) and chromium (VI) by mixed anaerobic culture. Environmental Pollution, 242, 249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.080
Wanty, R. B., & Goldhaber, M. B. (1992). Thermodynamics and kinetics of reactions involving vanadium in natural systems - Accumulation of vanadium in sedimentary-rocks. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 56, 1471–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(92)90217-7
Westerhoff, P., Highfield, D., Badruzzaman, M., & Yoon, Y. (2005). Rapid small-scale column tests for arsenate removal in iron oxide packed bed columns. Journal of Environmental Engineering-Asce, 131, 262–271. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2005)131:2(262)
Wright, M. T., & Belitz, K. (2010). Factors controlling the regional distribution of vanadium in groundwater. Ground Water, 48, 515–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00666.x
Xu, W., Li, Z., Shi, S., Qi, J., Cai, S., Yu, Y., O’Carroll, D. M. & He, F. (2020). Carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized and sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Characterization and trichloroethene dechlorination. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118303
Yu, Q., Guo, J., Muhammad, Y., Li, Q., Lu, Z., Yun, J., & Liang, Y. (2020). Mechanisms of enhanced hexavalent chromium removal from groundwater by sodium carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Journal of Environmental Management, 276, 111245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111245
Yu, S. J., Wang, X. X., Liu, Y. F., Chen, Z. S., Wu, Y. H., Liu, Y., Pang, H. W., Song, G., Chen, J. R., & Wang, X. K. (2019). Efficient removal of uranium(VI) by layered double hydroxides supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: A combined experimental and spectroscopic studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 365, 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.024
Zhang, R., Leiviskä, T., Tanskanen, J., Gao, B., & Yue, Q. (2019). Utilization of ferric groundwater treatment residuals for inorganic-organic hybrid biosorbent preparation and its use for vanadium removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 361, 680–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.122
Funding
This project was funded by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1802900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, K., Yang, L., Qian, L. et al. Elimination of Chromium(VI) and Vanadium(V) from Waters by Carboxymethylcellulose-Stabilized Amorphous Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 499 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05899-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05899-w