Abstract
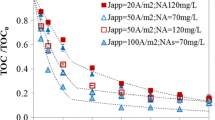
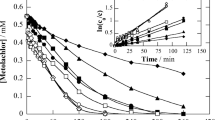
Diazinon, an organophosphorus pesticide, widely used in agricultural activities, can be effectively degraded in aqueous solutions via advanced oxidation processes. Electrochemical oxidation is a promising technique for the degradation of recalcitrant organic micropollutants in water. Thus, this study evaluated the pesticide diazinon degradation by anodic oxidation. To carry out the experiments, a synthetic solution of diazinon was used, with an initial concentration of 40 mg L−1. Two types of electrodes were evaluated, a dimensionally stable anode type, with RuO2–IrO2 composition, and a boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrode. In addition, two supporting electrolytes (NaCl and Na2SO4), the electrolyte concentration, current density and also energy consumption were evaluated. All configurations were able to promote the degradation of total organic carbon. The anodic oxidation for the degradation of diazinon was more efficient with the BDD electrode, reaching 97.5% of diazinon removal after 180 min with 25 mM of Na2SO4, a current density of 42 mA cm−2 and pH 3.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, N.U.Y., upon reasonable request.
References
Abidi, J., Samet, Y., Panizza, M., Martinez-Huitle, C. A., Carpanese, M. P., & Clematis, D. (2020). A boron-doped diamond anode for the electrochemical removal of parabens in low-conductive solution: from a conventional flow cell to a solid polymer electrolyte system. ChemElectroChem, 7(1), 314–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201901909
Aktaş, Y., Gözmen, B., & Oturan, M. A. (2022). Degradation of phthalic acid by anodic oxidation in acidic aqueous solutions with high chromium content using boron-doped diamond anode. Separation and Purification Technology, 293, 121098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121098
Brillas, E. (2022). Fenton, photo-Fenton, electro-Fenton, and their combined treatments for the removal of insecticides from waters and soils A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 284, 120290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120290
Bu, L., Zhu, S., & Zhou, S. (2018). Degradation of atrazine by electrochemically activated persulfate using BDD anode: Role of radicals and influencing factors. Chemosphere, 195, 236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.088
Cai, J., Zhou, M., Pan, Y., Du, X., & Lu, X. (2019). Extremely efficient electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants with co-generation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals on Blue-TiO2 nanotubes anode. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental, 257, 117902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117902
Cai, J., Zhou, M., Xu, X., & Du, X. (2020). Stable boron and cobalt co-doped TiO2 nanotubes anode for efficient degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 396, 122723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122723
Candia-Onfray, C., Espinoza, N., da Sabino, S. E. B., Toledo-Neira, C., Espinoza, L. C., Santander, R., et al. (2018). Treatment of winery wastewater by anodic oxidation using BDD electrode. Chemosphere, 206, 709–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.175
Chen, L., Fu, W., Tan, Y., & Zhang, X. (2021). Emerging organic contaminants and odorous compounds in secondary effluent wastewater: Identification and advanced treatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408, 124817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124817
Coha, M., Farinelli, G., Tiraferri, A., Minella, M., & Vione, D. (2021). Advanced oxidation processes in the removal of organic substances from produced water: Potential, configurations, and research needs. Chemical Engineering Journal, 414, 128668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128668
Dominguez, C. M., Oturan, N., Romero, A., Santos, A., & Oturan, M. A. (2018). Lindane degradation by electrooxidation process: effect of electrode materials on oxidation and mineralization kinetics. Water Research, 135, 220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.037
Frontistis, Z., Antonopoulou, M., Venieri, D., Konstantinou, I., & Mantzavinos, D. (2017). Boron-doped diamond oxidation of amoxicillin pharmaceutical formulation: Statistical evaluation of operating parameters, reaction pathways and antibacterial activity. Journal of Environmental Management, 195, 100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.035
Garcia-Segura, S., Lima, Á. S., Cavalcanti, E. B., & Brillas, E. (2016). Anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton degradations of pyridinium- and imidazolium-based ionic liquids in waters using a BDD/air-diffusion cell. Electrochimica Acta, 198, 268–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.057
Görmez, Ö., Akay, S., Gözmen, B., Kayan, B., & Kalderis, D. (2022). Degradation of emerging contaminant coumarin based on anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and subcritical water oxidation processes. Environmental Research, 208, 112736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112736
He, Y., Lin, H., Guo, Z., Zhang, W., Li, H., & Huang, W. (2019). Recent developments and advances in boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants. Separation and Purification Technology, 212, 802–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2018.11.056
Hu, Z., Cai, J., Song, G., Tian, Y., & Zhou, M. (2021). Anodic oxidation of organic pollutants: Anode fabrication, process hybrid and environmental applications. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 26, 100659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100659
Jose, J., & Philip, L. (2019). Degradation of chlorobenzene in aqueous solution by pulsed power plasma: Mechanism and effect of operational parameters. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(6), 103476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103476
Khadhri, N., BenMosbah, M., & Rabaaoui, N. (2021). Advancements of Electrochemical Removal of o-Methylphenol from Aqueous Using BDD Anode Compared to Pt One: Kinetics and Mechanism Determination. Iran Journal Chemical Chemical Engineering, 40(5), 1446–1456. https://doi.org/10.30492/IJCCE.2020.39880
Khaghani, R., & Zare, M. R. (2020). Toxicity of malathion and diazinon byproducts generated through the UV/Nano-Zn process. Health Scope, 9(1), e83067. https://doi.org/10.5812/jhealthscope.83067
Klidi, N., Clematis, D., Carpanese, M. P., Gadri, A., Ammar, S., & Panizza, M. (2019). Electrochemical oxidation of crystal violet using a BDD anode with a solid polymer electrolyte. Separation and Purification Technology, 208, 178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.042
Li, W., Liu, Y., Duan, J., van Leeuwen, J., & Saint, C. P. (2015). UV and UV/H2O2 treatment of diazinon and its influence on disinfection byproduct formation following chlorination. Chemical Engineering Journal, 274, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.130
Malakootian, M., Shahamat, Y. D., & Mahdizadeh, H. (2020). Purification of diazinon pesticide by sequencing batch moving-bed biofilm reactor after ozonation/Mg-Al layered double hydroxides pre-treated effluent. Separation and Purification Technology, 242, 116754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116754
Menacherry, S. P. M., Aravind, U. K., & Aravindakumar, C. T. (2022). Critical review on the role of mass spectrometry in the AOP based degradation of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) in water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(4), 108155. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2022.108155
Molla, Md. A. I., Furukawa, M., Tateishi, I., Katsumata, H., & Kaneco, S. (2020). Mineralization of Diazinon with nanosized-photocatalyst TiO2 in water under sunlight irradiation: Optimization of degradation conditions and reaction pathway. Environmental Technology, 41(27), 3524–3533. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1615129
Moreira, F. C., Boaventura, R. A. R., Brillas, E., & Vilar, V. J. P. (2017). Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental, 202, 217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Ning, Y., Li, K., Zhao, Z., Chen, D., Li, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Simultaneous electrochemical degradation of organophosphorus pesticides and recovery of phosphorus: Synergistic effect of anodic oxidation and cathodic precipitation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 125, 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.06.039
Okur, M. C., Akyol, A., Nayir, T. Y., Kara, S., Ozturk, D., & Civas, A. (2022). Performance of Ti/RuO2-IrO2 electrodes and comparison with BDD electrodes in the treatment of textile wastewater by electro-oxidation process. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 183, 398–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHERD.2022.05.016
Olvera-Vargas, H., Rouch, J.-C., Coetsier, C., Cretin, M., & Causserand, C. (2018). Dynamic cross-flow electro-Fenton process coupled to anodic oxidation for wastewater treatment: Application to the degradation of acetaminophen. Separation and Purification Technology, 203, 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.063
Oturan, M. A. (2021). Outstanding performances of the BDD film anode in electro-Fenton process: Applications and comparative performance. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 25(3), 100925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2021.100925
Oturan, N., Ganiyu, S. O., Raffy, S., & Oturan, M. A. (2017). Sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide as a new anode material for electro-Fenton process: application to electrocatalytic destruction of antibiotic amoxicillin. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental, 217, 214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.062
Ouni, A., Rabaaoui, N., Mechi, L., Enaceur, N., AlSukaibi, A. K. D., Azzam, E. M., et al. (2021). Removal of pesticide chlorobenzene by anodic degradation: Variable effects and mechanism. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 25(10), 101326. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSCS.2021.101326
Roselló-Márquez, G., Fernández-Domene, R. M., Sánchez-Tovar, R., Cifre-Herrando, M., & García-Antón, J. (2021). Degradation of Diazinon based on photoelectrocatalytic technique using enhanced WO3 nanostructures: Mechanism and pathway. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105371
Saad, M. E. K., Rabaaoui, N., Elaloui, E., & Moussaoui, Y. (2016). Mineralization of p-methylphenol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Separation and Purification Technology, 171, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2016.07.018
Salarian, A.-A., Hami, Z., Mirzaei, N., Mohseni, S. M., Asadi, A., Bahrami, H., et al. (2016). N-doped TiO2 nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of diazinon under simulated solar irradiation: optimization and modeling using a response surface methodology. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 220, 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.060
Schaefer, C. E., Andaya, C., Burant, A., Condee, C. W., Urtiaga, A., Strathmann, T. J., & Higgins, C. P. (2017). Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate: Insights into mechanisms and application to groundwater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 317, 424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.107
Seibert, D., Zorzo, C. F., Borba, F. H., de Souza, R. M., Quesada, H. B., Bergamasco, R., et al. (2020). Occurrence, statutory guideline values and removal of contaminants of emerging concern by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 748, 141527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141527
Vasseghian, Y., Berkani, M., Almomani, F., & Dragoi, E.-N. (2021). Data mining for pesticide decontamination using heterogeneous photocatalytic processes. Chemosphere, 270, 129449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129449
Vasseghian, Y., Almomani, F., Le, V. T., Moradi, M., & Dragoi, E.-N. (2022). Decontamination of toxic Malathion pesticide in aqueous solutions by Fenton-based processes: Degradation pathway, toxicity assessment and health risk assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423, 127016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127016
Wang, Q., & Lemley, A. T. (2002). Oxidation of diazinon by anodic Fenton treatment. Water Research, 36(13), 3237–3244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00041-6
Wu, Z., Zhu, W., Liu, Y., Peng, P., Li, X., Zhou, X., & Xu, J. (2020). An integrated three-dimensional electrochemical system for efficient treatment of coking wastewater rich in ammonia nitrogen. Chemosphere, 246, 125703. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.125703
Xie, J., Zhang, C., & Waite, T. D. (2022). Hydroxyl radicals in anodic oxidation systems: generation, identification and quantification. Water Research, 217, 118425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118425
Yao, J., Lv, S., Wang, Z., Hu, L., & Chen, J. (2022). Variation of current density with time as a novel method for efficient electrochemical treatment of real dyeing wastewater with energy savings. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(33), 49976–49984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18927-3
Zazou, H., Oturan, N., Sönmez-Çelebi, M., Hamdani, M., & Oturan, M. A. (2016). Mineralization of chlorobenzene in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton processes using Pt or BDD anode and carbon felt cathode. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 774, 22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JELECHEM.2016.04.051
Zekkaoui, C., Berrama, T., Dumoulin, D., Billon, G., & Kadmi, Y. (2021). Optimal degradation of organophosphorus pesticide at low levels in water using fenton and photo-fenton processes and identification of by-products by GC-MS/MS. Chemosphere, 279, 130544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130544
Zhu, X., Hu, W., Feng, C., Chen, N., Chen, H., Kuang, P., et al. (2021). Electrochemical oxidation of aniline using Ti/RuO2-SnO2 and Ti/RuO2-IrO2 as anode. Chemosphere, 269, 128734. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2020.128734
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Universidade Tiradentes (UNIT), the Instituto de Tecnologia e Pesquisa (ITP), the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), the Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP), the Laboratório de Tratamento de Resíduos e Efluentes (LTRE/ITP) and the Instituto Cesumar de Ciência e Tecnologia (ICETI/UNICESUMAR) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
The manuscript is original. It has not been published previously by any of the authors and is not under the consideration in any other journal at the time of submission.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, T.M., Marques, M.N., de Alsina, O.L.S. et al. Application of Anodic Oxidation in Diazinon Degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 415 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05895-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05895-0