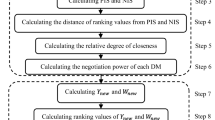
Abstract
Determining the most suitable groundwater contamination remediation among multiple discrete alternatives is usually difficult for decision makers and of great significance to ensure the green development of ecological environment. This study proposed a novel multi-attribute preference model (MAPM) method by combining the trapezoidal fuzzy information, analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy method for prioritizing the groundwater contamination remediation among a number of alternatives. This method has the advantages of (1) screening the most desirable remediation without introducing time-consuming nonlinear multi-objective optimization algorithms; (2) addressing uncertain attributes expressed as trapezoidal fuzzy information; (3) assessing priority orders of alternative remediation actions under uncertainty; and (4) being less affected by data inexactness and guaranteeing better environmental performance than MAPM. The method is applied to remediation design of practical naphthalene-contaminated aquifer located in Anhui. A total of 50 alternative remediation strategies with an attributes system which consists of ten attribute in three aspects has been proposed. Results indicate that the developed model is feasible and the priorities of groundwater cleanup systems are greatly different for four remediation schemes. The proposed method can be applied into other study area by modifying the relevant attributes appropriately in order to obtain customized remediation strategies.





Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
All relevant data are available on the supplementary data.
References
An, D., Xi, B. D., Wang, Y., Xu, D., Tang, J., Dong, L. C., Ren, J. Z., & Pang, C. F. (2016). A sustainability assessment methodology for prioritizing the technologies of groundwater contamination remediation. Journal of Cleaner ProductIon, 112, 4647–4656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.020
Borden, R. C., & Bedient, P. B. (1986). Transport of dissolved hydrocarbons influenced by oxygen-limited biodegradation: 1 Theoretical Development. Water Resources Research, 22(13), 1973–1982. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR022i013p01973
Chen, S. J., & Chen, S. M. (2007). Fuzzy risk analysis based on the ranking of generalized trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Applied Intelligence, 26, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-006-0003-5
Chen, J., Dong, H., Tian, R., Li, R., & Xie, Q. (2020). Remediation of Trichloroethylene-contaminated groundwater by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on biochar: Investigation of critical factors. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 231, 432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04797-3
Compernolle, T., Van Passel, S., & Lebbe, L. (2013). The value of groundwater modeling to support a pump and treat design. Groundwater Monitoring Remediation, 33, 111–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwmr.12018
Das, K., Mandal, T., & Edalatpanah, S. A. (2017). A mathematical model for solving fully fuzzy linear programming problem with trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Applied Intelligence, 46, 509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-016-0779-x
EEP (Energy and Environment Program). (2005). Numerical simulation for contaminant flow and transport in subsurface-a study of soil and groundwater contamination at the Goleville Site. Process Report, University of Regina, Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada.
Fessi, B. A., Benabdallah, S., Boudriga, N., & Hamdi, M. (2014). A multi-attribute decision model for intrusion response system. Information Sciences, 270, 237–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.139
Gbanie, S. P., Tengbe, P. B., Momoh, J. S., Medo, J., & Kabba, V. T. S. (2013). Modelling landfill location using geographic information systems (GIS) and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA): Case study Bo, Southern Sierra Leone. Applied Geography, 36, 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.06.013
He, L., Shao, F., & Ren, L. X. (2021). Sustainability appraisal of desired contaminated groundwater remediation strategies: An information-entropy-based stochastic multi-criteria preference model Environment. Development and Sustainability, 23, 1759–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00650-z
Huang, I. B., Keisler, J., & Linkov, I. (2011). Multi-criteria decision analysis in environmental sciences: Ten years of applications and trends. Science of the Total Environment, 409(19), 3578–3594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.022
Kazakis, N., & Voudouris, K. S. (2015). Groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment of porous aquifers to nitrate: Modifying the DRASTIC method using quantitative parameters. Journal of Hydrology, 525, 13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.035
Kazemzadeh-Parsi, M. J., Daneshmand, F., Ahmadfard, M. A., Adamowski, J., & Martel, R. (2015). Optimal groundwater remediation design of pump and treat systems via a simulation-optimization approach and firefly algorithm. Engineering Optimization, 47, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2013.858138
Klammler, H., Hatfield, K., Mohamed, M. M., Perminova, I. V., & Perlmutter, M. (2014). Capture and release zones of permeable reactive barriers under the influence of advective-dispersive transport in the aquifer. Advances in Water Resources, 69, 79–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.03.010
Ko, N. Y., Lee, K. K., & Hyun, Y. (2005). Optimal groundwater remediation design of a pump and treat system considering clean-up time. Geosciences Journal, 9, 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910551
Li, J., He, L., Lu, H. W., & Fan, X. (2015). Control of stochastic carcinogenic and noncarcinogenic risks in groundwater remediation through an integrated optimization design model. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 29(8), 2159–2172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1106-5
Li, J., He, L., Chen, Y. Z., Song, X. S., & Lu, H. W. (2017). A bilevel groundwater management model with minimization of stochastic health risks at the leader level and remediation cost at the follower level. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 31, 2547–2571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1351-2
Liu, P., Wang, G., Shang, M., & Liu, M. (2021). Groundwater nitrate bioremediation simulation of in situ horizontal well by microbial denitrifcation using PHREEQC. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 232, 356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05313-x
Lu, H. W., Li, J., Chen, Y. Z., & Lu, J. Z. (2019). A multi-level method for groundwater remediation management accommodating non-competitive objectives. Journal of Hydrology, 570, 531–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.018
Marimuthu, D., & Mahapatra, G. S. (2020). Multi-criteria decision-making using a complete ranking of generalized trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Soft Computing, 25, 9859–9871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05322-8
Mor, S., Negi, P., & Khaiwal, R. (2018). Assessment of groundwater pollution by landfills in India using leachate pollution index and estimation of error. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 10, 467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.09.002
O’Carroll, D., Sleep, B., Krol, M., Boparai, H., & Kocur, C. (2013). Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Advances in Water Resources, 51, 104–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.02.005
Polat, S., Aksoy, A., & Unlu, K. (2015). A fuzzy rule based remedial priority ranking system for contaminated sites. Groundwater, 53(2), 317–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12199
Pourghasemi, H. R., Pradhan, B., & Gokceoglu, C. (2012). Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed Iran. Natural Hazards, 63(2), 965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Ren, L. X., Lu, H. W., Zhao, H. H., & Xia, J. (2018). An interval-valued triangular fuzzy modified multi-attribute preference model for prioritization of groundwater resources management. Journal of Hydrology, 562, 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.069
Rezaei, H., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2020). Reliability-based multi-objective optimization of groundwater remediation. Water Resources Management., 34, 3079–3097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02573-w
Rosen, L., Back, P. E., Soderqvist, T., Norrman, J., Brinkhoff, P., Norberg, T., Volchko, Y., Norind, M., Bergknut, M., & Döberl, G. (2015). SCORE: A novel multi-criteria decision analysis approach to assessing the sustainability of contaminated land remediation. Science of the Total Environment, 511, 621–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.058
Singh, T. S., & Chakrabarty, D. (2011). Multiobjective optimization of pump-and-treat-based optimal multilayer aquifer remediation design with flexible remediation time. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 16, 413–420. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000327
Singh, J., Sharma, S. K., & Srivastava, R. (2019). AHP-Entropy based priority assessment of factors to reduce aviation fuel consumption. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 10, 212–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00758-0
Subramanian, N., & Ramanathan, R. (2012). A review of applications of analytic hierarchy process in operations management. International Journal of Production Economics, 138(2), 215–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.03.036
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). (1992). Guidelines for exposure assessment. Federal Register, 57, 22888–22938.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund: Volume 1-Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A), EPA/540/1–89/002, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC.
Yang, A. L., Huang, G. H., Fan, Y. R., & Zhang, X. D. (2012). A fuzzy simulation-based optimization approach for groundwater remediation design at contaminated aquifers. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/986867
Yang, A. L., Huang, G. H., Qin, X. S., & Fan, Y. R. (2012). Evaluation of remedial options for a benzene-contaminated site through a simulation-based fuzzy-MCDA approach. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 213–214, 421–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.027
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the editor and the anonymous reviewer for their helpful comments and suggestions. This research was supported by the Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFC1807904), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52079088), CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team (Grant No. JCTD-2019-04), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (2019QZKK1003), and Scientific and Technologial Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (2020L0731).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., He, L., Yao, L. et al. A Hybrid Decision Support Model Using a Trapezoidal Fuzzy-Based Multi-Attribute Preference Model with AHP-Entropy for Groundwater Remediation Selection. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 432 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05893-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05893-2