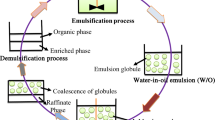
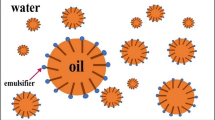
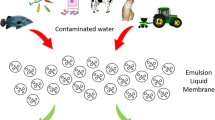
Abstract
Industrialization and the rise in population have led to the larger utilization of resources which has become the supreme risk for the environment. Different types of pollutants enter the aquatic environment from various sources which create a threat for the aquatic organisms and humans. Many separation techniques like precipitation, adsorption, reactive distillation, ion exchange, electro dialysis, solvent extraction, and ultrafiltration are available, but these techniques have various limitations like the use of excessive and expensive chemicals, high energy requirement, sludge formation, requirement of utilities in large amount and so. The green emulsion liquid membrane (GELM) is an emerging and promising method that incorporates the traits of ELM for the removal of various pollutants, metal ions, acids, and so on. In the present scenario, much focus has been diverted towards the use of green solvents derived from vegetable and plant origin. These solvents are environmentally friendly and economically viable making the ELM process more reliable. The traditionally used petroleum-based solvents for ELM formation are expensive, toxic, volatile in nature, and are detrimental to the environment. The present study tries to address the recent advancement in the field of GELM. The different factors like concentration of surfactant, carrier, types of diluents, effect of volume ratio of external feed phase to emulsion, agitation speed, effect of internal aqueous phase concentration, and emulsification time play a substantial role in the removal of several pollutants from the aqueous streams through GELM have been discussed in detail. The statistical analysis of the operating variables as executed by different investigators is also mentioned.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data used in the paper are presented in the form of tables and/or figures.
References
Abbas, A. H., Abd Alsaheb, R. A., & Abdullah, J. K. (2022). Comparative study of natural chemical for enhanced oil recovery: Focus on extraction and adsorption at quartz sand surface. Petroleum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2022.01.007
Abbassian, K., & Kargari, A. (2016). Modification of membrane formulation for stabilization of emulsion liquid membrane for extraction of phenol from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4(4), 3926–3933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.08.030
Ahmad, A. L., Kusumastuti, A., Derek, C. J. C., & Ooi, B. S. (2011). Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: An overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171(3), 870–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.102
Ahmad, A. L., Kusumastuti, A., Derek, C. J. C., & Ooi, B. S. (2012). Emulsion liquid membrane for cadmium removal: Studies on emulsion diameter and stability. Desalination, 287, 30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.002
Ahmad, A. L., Kusumastuti, A., Shah Buddin, M. M. H., Derek, C. J. C., & Ooi, B. S. (2014). Emulsion liquid membrane based on a new flow pattern in a counter rotating Taylor-Couette column for cadmium extraction. Separation and Purification Technology, 127, 46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.02.029
Ahmad, A. L., Shah Buddin, M. M. H., Ooi, B. S., & K. adhi. (2015). Cadmium removal using vegetable oil based emulsion liqid membrane (ELM): Membrane breakage investigation. Jurnal Teknologi (sciences & Engineering), 75(1), 39–46.
Ahmad, A. L., Shah Buddin, M. M. H., Ooi, B. S., & Kusumastuti, A. (2016). Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM): Influence of emulsion formulation on cadmium removal and emulsion swelling. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(58), 28274–28283. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1179674
Ahmad, A. L., Shah Buddin, M. M. H., Ooi, B. S., & Kusumastuti, A. (2017). Utilization of environmentally benign emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) for cadmium extraction from aqueous solution. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 15, 26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.05.010
Ahmad, A. L., Zaulkiflee, N. D., Kusumastuti, A., & Buddin, M. M. H. S. (2019). Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solution by Emulsion Liquid Membrane: Emulsion Stability Study. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 58(2), 713–719. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b03562
Anarakdim, K., Matos, M., Senhadji-Kebiche, O., & Benamor, M. (2017). Optimization of hexavalent chromium removal by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) using sunflower oil as eco-friendly solvent. Desalination and Water Treatment, 72, 281–289. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20428
Anarakdim, K., Matos, M., Cambiella, A., Senhadji-Kebiche, O., & Gutiérrez, G. (2020). Effect of temperature on the heat treatment to recover green solvent from emulsion liquid membranes used in the extraction of Cr(VI). Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 158, 108178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2020.108178
Anitha, M., Ambare, D. N., Singh, D. K., Singh, H., & Mohapatra, P. K. (2015). Extraction of neodymium from nitric acid feed solutions using an emulsion liquid membrane containing TOPO and DNPPA as the carrier extractants. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 98, 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2015.04.011
Arabi Ardehali, B., Zaheri, P., & Yousefi, T. (2020). The effect of operational conditions on the stability and efficiency of an emulsion liquid membrane system for removal of uranium. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 130, 103532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2020.103532
Balasubramanian, A., & Venkatesan, S. (2012). Removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane containing Ionic Liquid [BMIM]+[PF6]− in Tributyl phosphate. Desalination, 289, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.12.027
Begum, K. M. M. S., Venkatesan, S., & Anantharaman, N. (2012). Emulsion liquid membrane pertraction of metal ions from aqueous solutions and electroplating effluent using rotating disk contactor. Chemical Engineering Communications, 199(12), 1575–1595. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2012.672497
Benyahia, N., Belkhouche, N., & Jönsson, J. Å. (2014). A comparative study of experimental optimization and response surface methodology of Bi(III) extraction by emulsion organophosphorus liquid membrane. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2(3), 1756–1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.07.003
Bezerra, M. A., Santelli, R. E., Oliveira, E. P., Villar, L. S., & Escaleira, L. A. (2008). Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta, 76(5), 965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Björkegren, S., Karimi, R. F., Martinelli, A., Jayakumar, N. S., & Hashim, M. A. (2015). A new emulsion liquid membrane based on a palm oil for the extraction of heavy metals. Membranes, 5(2), 168–179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020168
Chakraborty, M., Bhattacharya, C., Datta, S. (2010). Emulsion liquid membranes: Definitions and classification, theories, module design, applications, new directions and perspectives (1st ed., pp. 141–199) Liquid Membranes. Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53218-3.00004-0
Chang, S. H. (2016). Types of bulk liquid membrane and its membrane resistance in heavy metal removal and recovery from wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(42), 19785–19793. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1102772
Chang, S. H. (2017). Parametric studies on an innovative waste vegetable oil-based continuous liquid membrane (WVCLM) for Cu(II) ion separation from aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 50, 102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.01.037
Chaouchi, S., & Hamdaoui, O. (2014). Acetaminophen extraction by emulsion liquid membrane using Aliquat 336 as extractant. Separation and Purification Technology, 129, 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.03.021
Chaouchi, S., & Hamdaoui, O. (2015). Extraction of endocrine disrupting compound propylparaben from water by emulsion liquid membrane using trioctylphosphine oxide as carrier. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 22, 296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.07.023
Chaouchi, S., & Hamdaoui, O. (2016). Removal of 4-nitrophenol from water by emulsion liquid membrane. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(12), 5253–5257. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1021104
Chiha, M., Hamdaoui, O., Ahmedchekkat, F., & Pétrier, C. (2010). Study on ultrasonically assisted emulsification and recovery of copper(II) from wastewater using an emulsion liquid membrane process. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 17(2), 318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.09.001
Chiriacò, M. V., Bellotta, M., Jusić, J., & Perugini, L. (2022). Palm oil’s contribution to the United Nations sustainable development goals: Outcomes of a review of socio-economic aspects. Environmental Research Letters, 17(6), 063007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac6e77
Choudhury, A., Sengupta, S., Bhattacharjee, C., & Datta, S. (2010). Extraction of hexavalent chromium from aqueous stream by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM). Separation Science and Technology, 45(2), 178–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903409617
Dâas, A., & Hamdaoui, O. (2010). Extraction of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 348(1–2), 360–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.11.026
Dâas, A., & Hamdaoui, O. (2014). Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ibuprofen and ketoprofen from water by emulsion liquid membrane. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(3), 2154–2164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2140-9
Daraei, P., Zereshki, S., & Shokri, A. (2019). Application of nontoxic green emulsion liquid membrane prepared by sunflower oil for water decolorization: Process optimization by response surface methodology. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 77, 215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.04.039
Daraei, P., Shokri, A., & Rostami, E. (2022). Extraction of vancomycin antibiotic from water using green emulsion liquid membrane based on sunflower oil. Journal of Membrane Science and Research, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.22079/jmsr.2021.526001.1454
Davoodi-Nasab, P., Rahbar-Kelishami, A., & Raji-Asadabadi, M. (2017). Fast and efficient chromium(VI) pertraction with aliquat 336 in emulsion liquid membrane using sunflower oil as a high potential solvent. Desalination and Water Treatment, 80, 234–246. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20990
Davoodi-Nasab, P., Rahbar-Kelishami, A., Safdari, J., & Abolghasemi, H. (2018). Evaluation of the emulsion liquid membrane performance on the removal of gadolinium from acidic solutions. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 262, 97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.062
Dharmawan, A. H., Mardiyaningsih, D. I., Komarudin, H., Ghazoul, J., Pacheco, P., & Rahmadian, F. (2020). Dynamics of rural economy: A socio-economic understanding of oil palm expansion and landscape changes in east Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land, 9(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/land9070213
de Souza, F. B., de Souza, A. A. U., Oliveira, J. V., & Ulson, S. M. D. A. G. (2021). Green extraction based on emulsion liquid membranes: Removal of Cr (III) from synthetic effluents. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 16, 100579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100579
Elsagh, A., Moradi, O., Fakhri, A., Najafi, F., Alizadeh, R., & Haddadi, V. (2017). Evaluation of the potential cationic dye removal using adsorption by graphene and carbon nanotubes as adsorbents surfaces. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, S2862–S2869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.11.013
Fang, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, M., Sun, J., Mao, S., Lu, J., & Rohani, S. (2016). A neural network approach to simulating the dynamic extraction process of l-phenylalanine from sodium chloride aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 105, 188–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2015.11.012
Fetimi, A., Dâas, A., Benguerba, Y., Merouani, S., Hamachi, M., Kebiche-Senhadji, O., & Hamdaoui, O. (2021). Optimization and prediction of safranin-O cationic dye removal from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) using artificial neural network-particle swarm optimization (ANN-PSO) hybrid model and response surface methodology (RSM). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 105837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105837
García, M. G., Acosta, A. O., & Marchese, J. (2013). Emulsion liquid membrane pertraction of Cr(III) from aqueous solutions using PC-88A as carrier. Desalination, 318, 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.03.025
Goyal, R. K., Jayakumar, N. S., & Hashim, M. A. (2011). Chromium removal by emulsion liquid membrane using [BMIM]+[NTf2]- as stabilizer and TOMAC as extractant. Desalination, 278(1–3), 50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.05.001
Gupta, S., Chakraborty, M., & Murthy, Z. V. P. (2011). Response surface modelling and optimization of mercury extraction through emulsion liquid membrane. Separation Science and Technology, 46(15), 2332–2340. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2011.595033
Hachemaoui, A., Belhamel, K., & Bart, H. J. (2010). Emulsion liquid membrane extraction of Ni(II) and Co(II) from acidic chloride solutions using bis-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid as extractant. Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 63(13), 2337–2348. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2010.500375
Harun, M. H. Z. M., Ahmad, A. L., & Rajandram, L. (2022). Emulsion liquid membrane screening for ibuprofen removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Physical Science, 33(1), 109–122. https://doi.org/10.21315/jps2022.33.1.8
He, J., Li, Y., Xue, X., Ru, H., Huang, X., & Yang, H. (2015). Extraction of Ce(IV) from sulphuric acid solution by emulsion liquid membrane using D2EHPA as carrier. RSC Advances, 5(91), 74961–74972. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra11851d
Jiao, H., Peng, W., Zhao, J., & Xu, C. (2013). Extraction performance of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane using response surface methodology. Desalination, 313, 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.12.002
Jusoh, N., Othman, N., & Nasruddin, N. A. (2016). Emulsion liquid membrane technology in organic acid purification. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Science, 20(2), 436–443. https://doi.org/10.17576/mjas-2016-2002-28
Jusoh, N., & Othman, N. (2017). Stability of palm oil-based emulsion liquid membrane for succinic acid extraction from aqueous solution. Journal of Applied Membrane Science & Technology, 19(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.11113/amst.v19i1.19
Jusoh, N., Noah, N. F. M., & Othman, N. (2019). Extraction and recovery optimization of succinic acid using green emulsion liquid membrane containing palm oil as the diluent. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 38(3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13065
Jusoh, N., Sulaiman, R. N. R., Othman, N., Noah, N. F. M., Rosly, M. B., & Rahman, H. A. (2020). Development of vegetable oil-based emulsion liquid membrane for downstream processing of bio-succinic acid. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 119, 161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2019.11.003
Kargari, A. (2013). Simultaneous extraction and stripping of 4-chlorophenol from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(10–12), 2275–2279. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.734681
Kislik, V. S. (2012). Solvent Extraction: Classical and novel approaches (1st ed.). Elsevier.
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2018). Extraction of Ethylparaben by emulsion liquid membrane: Statistical analysis of operating parameters. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 539, 371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.12.002
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2019a). Separation of diclofenac using pseudo-emulsion hollow fiber membrane: Optimization by Box-Behnken response surface design. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 32, 100880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100880
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2019b). Stability and performance study of emulsion nanofluid membrane: A combined approach of adsorption and extraction of Ethylparaben. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 579, 123675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123675
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2020a). Characterization and stability study of pseudo-emulsion hollow fiber membrane: Separation of Ethylparaben. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 587, 124308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124308
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2020). Applicability of hollow fiber strip dispersion for the removal of metal ions from aqueous streams. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India) Series E, 101(1), 91–97.
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2021a). Comparative studies on the separation of endocrine disrupting compounds from aquatic environment by emulsion liquid membrane and hollow fiber supported liquid membrane. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 19(7), 689–698. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2020-0153
Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2021b). Statistical analysis of operating variables for pseudo-emulsion hollow fiber strip dispersion technique: Ethylparaben separation from aqueous feed stream. Chemical Papers, 75(2), 629–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01317-9
Kumar, A., Thakur, A., & Panesar, P. S. (2018a). Lactic acid extraction using environmentally benign Green emulsion ionic liquid membrane. Journal of Cleaner Production, 181, 574–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.263
Kumar, A., Thakur, A., & Panesar, P. S. (2018b). Statistical optimization of lactic acid extraction using green emulsion ionic liquid membrane (GEILM). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(2), 1855–1864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.01.037
Kumar, A., Thakur, A., & Panesar, P. S. (2018c). Stability analysis of environmentally benign green emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 39(10), 1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2017.1421079
Kumar, A., & Thakur, A. (2019). Statistical optimization of lactic acid extraction using green solvent and mixed extractants (TOA and TOMAC). Chemical Engineering Research Bulletin, 21(1), 20–35. https://doi.org/10.3329/cerb.v21i1.47369
Kumar, A., Thakur, A., & Panesar, P. S. (2019a). A review on emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) for the treatment of various industrial effluent streams. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 18(1), 153–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-019-09492-2
Kumar, A., Thakur, A., & Panesar, P. S. (2019b). Extraction of hexavalent chromium by environmentally benign green emulsion liquid membrane using tridodecyamine as an extractant. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 70, 394–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.11.002
Kumbasar, R. A. (2010). Extraction and concentration of cobalt from acidic leach solutions containing Co-Ni by emulsion liquid membrane using TOA as extractant. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 16(3), 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2010.01.045
Laguel, S., & Samar, M. H. (2019). Removal of Europium(III) from water by emulsion liquid membrane using Cyanex 302 as a carrier. Desalination and Water Treatment, 165, 269–280. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24551
Laki, S., Arabi Shamsabadi, A., Madaeni, S. S., & Niroomanesh, M. (2015). Separation of manganese from aqueous solution using an emulsion liquid membrane. RSC Advances, 5(102), 84195–84206. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra08547k
Laki, S., & Kargari, A. (2016). Extraction of silver ions from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Membrane Science and Research, 2(1), 33–40. https://doi.org/10.22079/jmsr.2016.15876
Lee, S. C. (2011). Extraction of succinic acid from simulated media by emulsion liquid membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 381(1–2), 237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.07.039
Lende, A. B., & Kulkarni, P. S. (2015). Selective recovery of tungsten from printed circuit board recycling unit wastewater by using emulsion liquid membrane process. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 8, 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.09.003
Li, N. N. (1968). Separating hydrocarbons with liquid membranes. US Patent 3410794.
Lin, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., & Deng, Y. (2016). Magnetic nano-Fe3O4 stabilized Pickering emulsion liquid membrane for selective extraction and separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 288, 305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.109
Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., Liu, T., Xue, N., & Wang, K. (2017). Selective separation and recovery of vanadium from a multiple impurity acid leaching solution of stone coal by emulsion liquid membrane using di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 122, 289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.04.026
Mei, X., Li, J., Jing, C., Fang, C., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Separation and recovery of phenols from an aqueous solution by a green membrane system. Journal of Cleaner Production, 251, 119675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119675
Mohammed, A. A., Atiya, M. A., & Hussein, M. A. (2020a). Simultaneous studies of emulsion stability and extraction capacity for the removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by liquid surfactant membrane. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 159, 225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2020.04.023
Mohammed, A. A., Atiya, M. A., & Hussein, M. A. (2020b). Studies on membrane stability and extraction of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using pickering emulsion liquid membrane stabilized by magnetic nano-Fe2O3. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 585, 124044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124044
Mokhtari, B., & Pourabdollah, K. (2015). Emulsion liquid membrane for selective extraction of Bi(III). Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 23(4), 641–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.06.035
Mousavi, S. M., Kiani, S., Farmad, M. R., Hemati, A., & Abbasi, B. (2012). Extraction of arsenic(V) from water using emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 33(1), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2010.548230
Mukherjee, I., & Sovacool, B. K. (2014). Palm oil-based biofuels and sustainability in southeast Asia: A review of Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 37, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.001
Muthusaravanan, S., Vasudha Priyadharshini, S., Sivarajasekar, N., Subashini, R., Sivamani, S., Dharaskar, S., & Dhakal, N. (2019). Optimization and extraction of pharmaceutical micro-pollutant - Norfloxacin using green emulsion liquid membranes. Desalination and Water Treatment, 156, 238–244. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23833
Ng, Y. S., Jayakumar, N. S., & Hashim, M. A. (2010). Performance evaluation of organic emulsion liquid membrane on phenol removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184(1–3), 255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.030
Noah, N. F. M., Othman, N., & Jusoh, N. (2016). Highly selective transport of palladium from electroplating wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 64, 134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.047
Noah, N. F. M., Jusoh, N., Othman, N., Sulaiman, R. N. R., & Parker, N. A. M. K. (2018). Development of stable green emulsion liquid membrane process via liquid–liquid extraction to treat real chromium from rinse electroplating wastewater. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 66, 231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.05.034
Nosrati, S., Jayakumar, N. S., & Hashim, M. A. (2011). Extraction performance of chromium (VI) with emulsion liquid membrane by Cyanex 923 as carrier using response surface methodology. Desalination, 266(1–3), 286–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.08.023
Ogahara, Z., Jespersen, K., Theilade, I., & Nielsen, M. R. (2022). Review of smallholder palm oil sustainability reveals limited positive impacts and identifies key implementation and knowledge gaps. Land Use Policy, 120, 106258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106258
Olasupo, A., & Suah, F. B. M. (2021). Recent advances in the removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting compounds in the aquatic system: A case of polymer inclusion membranes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 406, 124317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124317
Ooi, Z. Y., Harruddin, N., & Othman, N. (2015). Recovery of kraft lignin from pulping wastewater via emulsion liquid membrane process. Biotechnology Progress, 31(5), 1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2129
Ooi, Z. Y., Othman, N., & Choo, C. L. (2016). The role of internal droplet size on emulsion stability and the extraction performance of kraft lignin removal from pulping wastewater in emulsion liquid membrane process. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 37(4), 544–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1050728
Othman, N., Zailani, S. N., & Mili, N. (2011a). Recovery of synthetic dye from simulated wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process containing tri-dodecyl amine as a mobile carrier. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 198, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.014
Othman, N., Djamal, R., Mili, N., & Zailani, S. N. (2011b). Removal of red 3BS dye from wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process. Journal of Applied Sciences, 11(8), 1406–1410. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2011.1406.1410
Othman, N., Yi, O. Z., Zailani, S. N., Zulkifli, E. Z., & Subramaniam, S. (2013). Extraction of rhodamine 6G dye from liquid waste solution: Study on emulsion liquid membrane stability performance and recovery. Separation Science and Technology, 48(8), 1177–1183. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2012.731123
Othman, N., Noah, N. F. M., Harruddin, N., Abdullah, N. A., & Bachok, S. K. (2014). Selective extraction of palladium from simulated liquid waste solution by emulsion liquid membrane process using D2EHPA as a mobile carrier. Jurnal Teknologi (Sciences and Engineering), 69(9), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v69.3386
Othman, N., Noah, N. F. M., Poh, K. W., & Yi, O. Z. (2016). High performance of chromium recovery from aqueous waste solution using mixture of palm-oil in emulsion liquid membrane. In Procedia Engineering, 148, 765–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.611
Othman, N., Noah, N. F. M., Shu, L. Y., Ooi, Z. Y., Jusoh, N., Idroas, M., & Goto, M. (2017). Easy removing of phenol from wastewater using vegetable oil-based organic solvent in emulsion liquid membrane process. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 25(1), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2016.06.002
Othman, N., Jusoh, N., Mohar, M. S., Rosly, M. B., & Noah, N. F. M. (2018). Extraction of succinic acid from real fermentation broth by using emulsion liquid membrane process. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 22(6), 1090–1101. https://doi.org/10.17576/mjas-2018-2206-20
Othman, N., Raja Sulaiman, R. N., Rahman, H. A., Noah, N. F. M., Jusoh, N., & Idroas, M. (2019). Simultaneous extraction and enrichment of reactive dye using green emulsion liquid membrane system. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 40(11), 1476–1484. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1424258
Parhi, P. K. (2013). Supported liquid membrane principle and its practices: A short review. Journal of Chemistry, 2013https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/618236
Peng, H., & Guo, J. (2020). Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 18(6), 2055–2068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01058-x
Peng, W., Jiao, H., Shi, H., & Xu, C. (2012). The application of emulsion liquid membrane process and heat-induced demulsification for removal of pyridine from aqueous solutions. Desalination, 286, 372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.051
Perumal, M., Soundarajan, B., & Thazhathuveettil Vengara, N. (2019). Extraction of Cr (VI) by pickering emulsion liquid membrane using amphiphilic silica nanowires (ASNWs) as a surfactant. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 40(7), 1046–1055. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1496829
Qaim, M., Sibhatu, K. T., Siregar, H., & Grass, I. (2020). Environmental, economic, and social consequences of the oil palm boom. Annual Review of Resource Economics, 12(1), 321–344. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-resource-110119-024922
Rajasimman, M., & Karthic, P. (2010). Application of response surface methodology for the extraction of chromium (VI) by emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 41(1), 105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2009.04.010
Rajasimman, M., Rajamohan, N., & Sujatha, S. (2021). Recovery of zinc from electroplating wastewater using green emulsion liquid membrane. Water Supply, 21(5), 2008–2018. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.294
Raji, M., Abolghasemi, H., Safdari, J., & Kargari, A. (2018). Selective extraction of dysprosium from acidic solutions containing dysprosium and neodymium through emulsion liquid membrane by Cyanex 572 as carrier. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 254, 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.058
Raji, M., Abolghasemi, H., Safdari, J., & Davoodi-Nasab, P. (2020). Neodymium pertraction through sunflower oil-based emulsion liquimembrane: Stability and mass transfer investigation. Desalination and Water Treatment, 187, 333–344. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25450
Razo-Lazcano, T. A., del Pilar González-Muñoz, M., Stambouli, M., Pareau, D., Hernández-Perales, L., & Avila-Rodriguez, M. (2018). Chlorpheniramine recovery from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membranes using soy lecithin as carrier. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 536, 68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.07.050
Rosly, M. B., Jusoh, N., Othman, N., Rahman, H. A., Noah, N. F. M., & Sulaiman, R. N. R. (2019). Effect and optimization parameters of phenol removal in emulsion liquid membrane process via fractional-factorial design. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 145, 268–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.03.007
Rosly, M. B., Jusoh, N., Othman, N., Rahman, H. A., Sulaiman, R. N. R., & Noah, N. F. M. (2020). Stability of emulsion liquid membrane using bifunctional diluent and blended nonionic surfactant for phenol removal. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 148, 107790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107790
Rouhani, S. H. R., Davarkhah, R., Zaheri, P., & Mousavian, S. M. A. (2020). Separation of molybdenum from spent HDS catalysts using emulsion liquid membrane system. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 153, 107958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2020.107958
Ruggeri, A., & Samoggia, A. (2018). Twitter communication of agri-food chain actors on palm oil environmental, socio-economic, and health sustainability. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 17(1), 75–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1699
Sakai, K., Hassan, M. A., Vairappan, C. S., & Shirai, Y. (2022). Promotion of a green economy with the palm oil industry for biodiversity conservation: A touchstone toward a sustainable bioindustry. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 133(5), 414–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2022.01.001
San Román, M. F., Bringas, E., Ibañez, R., & Ortiz, I. (2010). Liquid membrane technology: Fundamentals and review of its applications. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85(1), 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2252
Sarang, P., Kohli, H. P., Mungray, A. K., & Chakraborty, M. (2022). Artificial neural network approach towards the separation of ethylparaben and diclofenac using pseudo-emulsion hollow fiber strip dispersion technique. Chemical Data Collections, 40, 100890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2022.100890
Seifollahi, Z., & Rahbar-Kelishami, A. (2019). Amoxicillin extraction from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membranes using response surface methodology. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 42(1), 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201800089
Silva, G. M. E., Campos, D. F., Brasil, J. A. T., Tremblay, M., Mendiondo, E. M., & Ghiglieno, F. (2022). Advances in technological research for online and in situ water quality monitoring—A review. Sustainability, 14(9), 5059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095059
Shirasangi, R., Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2020). Separation of Methylparaben by emulsion liquid membrane: Optimization, characterization, stability and multiple cycles studies. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 597, 124761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124761
Shirasangi, R., Kohli, H. P., Gupta, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2021). Separation of methylparaben from aqueous source stream by pseudo-emulsion hollow fiber membrane strip dispersion technique: Optimization of process parameters using Grey-Taguchi method. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 161, 108302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108302
Shokri, A., Daraei, P., & Zereshki, S. (2020). Water decolorization using waste cooking oil: An optimized green emulsion liquid membrane by RSM. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 33, 101021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101021
Srivastava, A., Bhagat, A., Sharma, U., Dohare, R. K., Singh, K., & Upadhyaya, S. (2017). Comparative study of arsenic(V) removal from aqueous solution using Aliquat-336 and 2-ethyl hexanol through emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 16, 64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.12.007
Sujatha, S., & Rajasimman, M. (2021). Development of a green emulsion liquid membrane using waste cooking oil as diluent for the extraction of arsenic from aqueous solution – Screening, optimization, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 41, 102055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102055
Sujatha, S., Rajamohan, N., Anbazhagan, S., Vanithasri, M., & Rajasimman, M. (2021a). Extraction of nickel using a green emulsion liquid membrane – Process intensification, parameter optimization and artificial neural network modeling. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 165, 108444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108444
Sujatha, S., Rajamohan, N., Vasseghian, Y., & Rajasimman, M. (2021b). Conversion of waste cooking oil into value-added emulsion liquid membrane for enhanced extraction of lead: Performance evaluation and optimization. Chemosphere, 284, 131385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131385
Sujatha, S., Rajamohan, N., Anbazhagan, S., Vanithasri, M., & Rajasimman, M. (2022). Parameter screening, optimization and artificial neural network modeling of cadmium extraction from aqueous solution using green emulsion liquid membrane. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 25, 102138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102138
Thakur, A., Panesar, P. S., & Saini, M. S. (2014). Response surface modeling of lactic acid extraction by emulsion liquid membrane: Box-Behnken experimental design. International Journal of Chemical and Molecular Engineering, 8, 880–889. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1094449
Tang, B., Yu, G., Fang, J., & Shi, T. (2010). Recovery of high-purity silver directly from dilute effluents by an emulsion liquid membrane-crystallization process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.042
Teng, T. T., Muthuraman, G., Mubeena, K., & Sathya, M. (2013). Emulsion liquid membrane: Removal and recovery of organic and inorganic ions. Journal of Membrane Science & Technology, 03(02), 3–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9589.1000e117
Ting, H. C., Khan, H. W., Reddy, A. V. B., Goto, M., & Moniruzzaman, M. (2022). Extraction of salicylic acid from wastewater using ionic liquid-based green emulsion liquid membrane: COSMO-RS prediction and experimental verification. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 347, 118280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118280
Varotsos, C. A., & Krapivin, V. F. (2018). Pollution of arctic waters has reached a critical point: an innovative approach to this problem. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 229(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4004-x
Varotsos, C. A., Krapivin, V. F., & Mkrtchyan, F. A. (2019). New optical tools for water quality diagnostics. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4228-4
Wang, T., Xie, T., & Xu, C. (2020). Numerical investigations of micro-SLM extraction/stripping in a spiral channel. Chemical Engineering Science, 212, 115344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.115344
Xue, J. Q., Liu, N. N., Li, G. P., & Dang, L. T. (2016). Optimization of cyanide extraction from wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane system by response surface methodology. Water Science and Technology, 74(4), 779–786. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.220
Yan, B., Huang, X., Chen, K., Liu, H., Wei, S., Wu, Y., & Wang, L. (2021). A study of synergetic carrier emulsion liquid membrane for the extraction of amoxicillin from aqueous phase using response surface methodology. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 100, 63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.05.041
Yang, L., Xiao, J., Shen, Y., Liu, X., Li, W., Wang, W., & Yang, Y. (2017). The efficient removal of thallium from sintering flue gas desulfurization wastewater in ferrous metallurgy using emulsion liquid membrane. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(31), 24214–24222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0040-0
Yaseen, M., Farooq, M. M. U., Ahmad, W., & Subhan, F. (2021). Fabrication of rGO-CuO and/or Ag2O nanoparticles incorporated polyvinyl acetate based mixed matrix membranes for the removal of Cr6+ from anti-corrosive paint industrial wastewater. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), 105151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105151
Zaheri, P., & Davarkhah, R. (2017). Rapid removal of uranium from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane containing thenoyltrifluoroacetone. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(4), 4064–4068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.076
Zante, G., Boltoeva, M., Masmoudi, A., Barillon, R., & Trébouet, D. (2020). Selective separation of cobalt and nickel using a stable supported ionic liquid membrane. Separation and Purification Technology, 252, 117477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117477
Zaulkiflee, N. D., Ahmad, A. L., & Yaacob, M. (2021). Acetaminophen extraction study using vegetable oil-based emulsion liquid membrane: The juxtaposition of carrier and internal phase. Journal of Membrane Science and Research, 7(4), 282–287. https://doi.org/10.22079/JMSR.2021.120282.1338
Zereshki, S., Daraei, P., & Shokri, A. (2018). Application of edible paraffin oil for cationic dye removal from water using emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 356, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.05.037
Zereshki, S., Shokri, A., & Karimi, A. (2021). Application of a green emulsion liquid membrane for removing copper from contaminated aqueous solution: Extraction, stability, and breakage study using response surface methodology. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 325, 115251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115251
Zhao, L., Fei, D., Dang, Y., Zhou, X., & Xiao, J. (2010). Studies on the extraction of chromium(III) by emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178(1–3), 130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.052
Zhou, W., Liang, H., & Xu, H. (2021). Recovery of gold from waste mobile phone circuit boards and synthesis of nanomaterials using emulsion liquid membrane. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 411https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.125011
Zing-Yi, O., Othman, N., Mohamad, M., & Rashid, R. (2014). Removal performance of lignin compound from simulated pulping wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process. International Journal of Global Warming, 6(2–3), 270–283. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2014.061021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Akash R. Raval: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing, original draft preparation, and data curation; Himanshu P. Kohli: Visualization, data curation, writing, editing and reviewing; Omprakash K. Mahadwad: Supervision and reviewing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• GELM: A sustainable and reliable advancement in the field of ELM.
• Oils based on vegetable and plant origin are used as green solvents.
• GELM formulation and its transport mechanism are discussed.
• Parametric and statistical studies of GELM.
• Real-time diagnosis of water quality.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raval, A.R., Kohli, H.P. & Mahadwad, O.K. A Comprehensive Review on Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane and Its Applicability Towards the Removal of Contaminants from the Aquatic Streams. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 379 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05849-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05849-6