Abstract
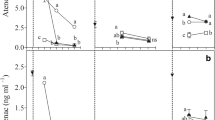
The present study aimed to evaluate the potential of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands (HSSF-CWs) with different arrangements of baffles inside and cultivated with fountain grass (Pennisetum setaceum) in the removal of microcontaminants from wastewater from a university campus. The HSSF-CWs were made of fiberglass with three different configurations: CW-A without baffles; CW-B with baffles fixed to the sides; and the CW-C with baffles fixed above and below the reactor. It was analyzed the contaminants ibuprofen (IBU), acetaminophen (PAR), 4-octylphenol (4OC), caffeine (CAF), 4-nonylphenol (4NP), naproxen (NPX), bisphenol-A (BPA), diclofenac (DCF), estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), ethinylestradiol (EE2), and estriol (E3) by pre-concentration using Strata SAX cartridge and determined by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Microcontaminants were monitored monthly between November/2018 and April/2019. Among the twelve microcontaminants evaluated, the endocrine disrupters 4NP and EE2 were not identified in any of the samples. In the affluent, the average concentrations ranged from 87.3 to 2559.2 ng L−1 for pharmaceuticals, 584.6 to 1658.3 ng L−1 for caffeine, and 49.1 to 584 ng L−1 for endocrine disruptors. The CWs with different baffle arrangements were efficient in removing the organic pollutants evaluated. Caffeine stimulant was the contaminant that presented the highest removal, followed by pharmaceuticals, and endocrine disruptors. Considering the risks related to the presence of these contaminants in wastewater, the results from this work represent an important contribution for studies related with the microcontaminants removal in HSSF-CW.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Aalam, T., & Khalil, N. (2019). Performance of horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands with different flow patterns using dual media for low-strength municipal wastewater: A case of pilot scale experiment in a tropical climate region. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A Environmental Science, 54, 1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2019.1635857
Abdel-Wareth, M. T. A., & Sayed, S. S. M. (2019). Reprotoxicity of 4-nonylphenol to Biomphalaria alexandrina snails at certain temperatures. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 18533–18540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05142-w
Arunbabu, V., Sruthy, S., Antony, I., & Ramasamy, E. V. (2015). Sustainable greywater management with Axonopus compressus (broadleaf carpet grass) planted in sub surface flow constructed wetlands. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 7, 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.06.004
Ávila, A., Nivala, J., Olsson, L., Kassa, K., Headley, T., Mueller, R. A., Bayona, J. M., & García, J. (2014). Emerging organic contaminants in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Influence of media size, loading frequency and use of active aeration. Science of the Total Environment, 494–495, 211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.128
Ávila, C., Bayona, J. M., Martín, I., Salas, J. J., & García, J. (2015). Emerging organic contaminant removal in a full-scale hybrid constructed wetland system for wastewater treatment and reuse. Ecological Engineering, 80, 108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.056
Aymerich, I., Acuña, V., Barceló, D., García, M. J., Petrovic, M., Poch, M., Rodriguez-Mozaz, S., Rodríguez-Roda, I., Sabater, S., von Schiller, D., & Corominas, Ll. (2016). Attenuation of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in a wastewater treatment plant and its receiving river ecosystem. Water Research, 100, 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.022
Belhaj, D., Baccarb, R., Jaabiri, I., Bouzid, J., Kallel, M., Ayadi, H., & Zhou, J. L. (2015). Fate of selected estrogenic hormones in an urban sewage treatment plant in Tunisia (North Africa). Science of the Total Environment, 505, 154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.018
Bhadra, B. N., Seo, P. W., & Jhung, S. H. (2016). Adsorption of diclofenac sodium from water using oxidized activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 301, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.143
Carranza-Diaz, O., Schultze-Nobre, L., Moeder, M., Nivala, J., Kuschk, P., & Koeser, H. (2014). Removal of selected organic micropollutants in planted and unplanted pilot-scale horizontal flow constructed wetlands under conditions of high organic load. Ecological Engineering, 71, 234–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.048
Castro-Correia, C., & Fontoura, M. (2015). A influência da exposição ambiental a disruptores endócrinos no crescimento e desenvolvimento de crianças e adolescentes. Rev. Port End Diab Metab, 10(2), 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpedm.2014.10.002
Chau, H. T. C., Kadokami, K., Duong, H. T., Kong, L., Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, T. Q., & Ito, Y. (2018). Occurrence of 1153 organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment of Vietnam. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(8), 7147–7156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5060-z
Cheng, Y.-X., Chen, J., Wu, D., Liu, Y.-S., Yang, Y.-Q., He, L.-X., Ye, P., Zhao, J.-L., Liu, S.-S., Yang, B., & Ying, G.-G. (2021). Highly enhanced biodegradation of pharmaceutical and personal care products in a novel tidal flow constructed wetland with baffle and plants. Water Research, 193, 116870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116870
Christofilopoulos, S., Kaliakatsos, A., Triantafyllou, K., Gounaki, I., Venieri, D., & Kalogerakis, N. (2019). Evaluation of a constructed wetland for wastewater treatment: Addressing emerging organic contaminants and antibiotic resistant bacteria. New Biotechnology, 52, 94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2019.05.006
Chu, K. H., Al-Hamadani, Y. A. J., Park, C. M., Lee, G., Jang, M., Jang, A., & Yoon, Y. (2017). Ultrasonic treatment of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products in water: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 327, 629–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.137
Costa, E. M. F., Spritzer, P. M., Hohl, A., & Bachega, T. A. S. S. (2014). Effects of endocrine disruptors in the development of the female reproductive tract. Arquivos Brasileiros De Endocrinologia e Metabologia, 58(2), 153–161. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-2730000003031
Cui, L., Ouyang, Y., Yang, W., Huang, Z., Xu, Q., & Yu, G. (2015). Removal of nutrients from septic tank effluent with baffle subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Journal of Environmental Management, 153, 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.035
Cunha, D. L., Paula, L. M., Silva, S. M. C., Bila, D. M., Fonseca, E. M., da Oliveira, J. L., & M. (2017). Ocorrência e remoção de estrogênios por processos de tratamento biológico de esgotos. Ambiente e Água, 12(2), 249–262. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1992
Dai, Y., A, D., Yang, Y., Tam, N., N, F., Tai, Y. P., & Tang, X. (2016). Factors affecting behavior of phenolic endocrine disruptors, estrone and estradiol, in constructed wetlands for domestic sewage treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 50, 11844–11852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02026
Dai, Y., Tao, R., Tai, Y., Tam, N. F., A, D., & Yang, Y. (2017). Application of a full-scale newly developed stacked constructed wetland and an assembled bio-filter for reducing phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals from secondary effluent. Ecological Engineering, 99, 496–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.007
Fonder, N., & Headley, T. (2013). The taxonomy of treatment wetlands: A proposed classification and nomenclature system. Ecological Engineering, 51, 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.011
Galletti, A., Verlicchi, P., & Ranieri, E. (2010). Removal and accumulation of Cu, Ni and Zn in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Contribution of vegetation and filling medium. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 5097–5105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.045
Garcia, S. N., Clubbs, R. L., Stanley, J. K., Scheffe, B., Yelderman, J. C., & Brooks, B. W. (2013). Comparative analysis of effluent water quality from a municipal treatment plant and two on-site wastewater treatment systems. Chemosphere, 92(1), 38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.007
Haarstad, K., Bavor, H. J., & Mæhlum, T. (2012). Organic and metallic pollutants in water treatment and natural wetlands: A review. Water Science and Technology, 65, 76–99. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.831
Haberl, R., Grego, S., Langergraber, G., Kadlec, R. H., Cicalini, A.-R., Dias, S. M., Novais, J. M., Aubert, S., Gerth, A., Thomas, H., & Hebner, A. (2003). Constructed wetlands for the treatment of organic pollutants. Journal of Soils & Sediments, 3, 109–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991077
Herrera-Melián, J. A., Guedes-Alonso, R., Borreguero-Fabelo, A., Santana-Rodríguez, J. J. S., & Sosa-Ferrera, Z. (2018). Study on the removal of hormones from domestic wastewaters with lab-scale constructed wetlands with different substrates and flow directions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(21), 20374–20384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9307-8
Hijosa-Valsero, M., Reyes-Contreras, C., Domínguez, C., Bécares, E., & Bayona, J. M. (2016). Behaviour of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in constructed wetland compartments: Influent, effluent, pore water, substrate and plant roots. Chemosphere, 145, 508–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.090
Kabir, E. R., Rahman, M. S., & Rahman, I. (2015). A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 40(1), 241–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.009
Kadlec, R. H., & Wallace, S. (2009). Treatment wetlands (2nd ed.). CRC Press.
Lehl, H. K., Ong, S.-A., Ho, L.-N., Wong, Y.-S., Saad, F. N. M., Oon, Y.-L., Oon, Y.-S., Yong, C.-Y., & Wei-Eng Thung, W.-E. (2016). Multiple aerobic and anaerobic baffled constructed wetlands for simultaneous nitrogen and organic compounds removal. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57, 29160–32916. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1189698
Li, Y., Zhu, G., Ng, W. J., & Tan, S. K. (2014). A review on removing pharmaceutical contaminants from wastewater by constructed wetlands: Design, performance and mechanism. Science of the Total Environment, 468(469), 908–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.018
Lima, D. R. S., Tonucci, M. C., Libânio, M., & Aquino, S. F. (2017). Fármacos e desreguladores endócrinos em águas brasileiras: Ocorrência e técnicas de remoção. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 22(6), 1043–1054. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-41522017165207
Luo, Y., Guo, W., Ngo, H. H., Nghiem, L. D., Hai, F. I., Zhang, J., & Wang, X. C. (2014). A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 473–474, 619–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065
Macci, C., Peruzzi, E., Doni, S., Iannelli, R., & Masciandaro, G. (2015). Ornamental plants for micropollutant removal in wetland systems. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22(4), 2406–2415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2949-x
de Machado, C. R. A., Saggioro, E. M., Silva, Y. G. L., dos Pereira, L. P. S., & Campos, J. C. (2015). Avaliação da adsorção de Fenol e Bisfenol A em carvões ativados comerciais de diferentes matrizes carbonáceas. Ambiente e Agua, 10(4), 915–927. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1698
Madikizela, L. M., & Chimuka, L. (2017). Simultaneous determination of naproxen, ibuprofen and diclofenac in wastewater using solid-phase extraction with high performance liquid chromatography. Water S.A, 43(2), 264–274. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v43i2.10
Matamoros, V., Gutiérrez, R., Ferrer, I., García, J., & Bayona, J. M. (2015). Capability of microalgae-based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants: A pilot-scale study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 288, 34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.002
Matos, A. T., Matos, M. P. (2017). Disposição de águas residuárias no solo e em sistemas alagados construídos. Viçosa Ed. UFV, 371
Meeker, J. D., Ehrlich, S., Toth, T. L., Wright, D. L., Calafat, A. M., Trisini, A. T., & Hauser, R. (2010). Semen quality and sperm DNA damage in relation to urinary bisphenol A among men from an infertility clinic. Reproductive Toxicology, 30(4), 532–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.07.005
Moreira, N. F. F., Orge, C. A., Ribeiro, A. R., Faria, J. L., Nunes, O. C., Pereira, M. F. R., & Silva, A. M. T. (2015). Fast mineralization and detoxification of amoxicillin and diclofenac by photocatalytic ozonation and application to an urban wastewater. Water Research, 87, 87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.059
Murray, T. J., Maffini, M. V., Ucci, A. A., Sonnenschein, C., & Soto, A. M. (2007). Induction of mammary gland ductal hyperplasias and carcinoma in situ following fetal bisphenol A exposure. Reproductive Toxicology, 23(3), 383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2006.10.002
Nam, S., Jung, C., Li, H., Yu, M., Flora, J. R. V., Boateng, L. K., & Yoon, Y. (2015). Adsorption characteristics of diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole to graphene oxide in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 136, 20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.061
Omar, T. F. T., Ahmad, A., Aris, A. Z., & Yosoff, F. M. (2016). Endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in environmental matrices: Review of analytical strategies for pharmaceuticals, estrogenic hormones, and alkylphenol compounds. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 85, 241–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.08.004
Papaevangelou, V. A., Gikas, G. D., Tsihrintzis, V. A., Antonopoulou, M., & Konstantinou, I. K. (2016). Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in HSF and VF pilot-scale constructed wetlands. Chemical Engineering Journal, 294, 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.103
Pessoa, G. P., De, S. N. C., Vidal, C. B., Alves, J. A. C., Firmino, P. I. M., Nascimento, R. F., & Santos, A. B. (2014). Occurrence and removal of estrogens in Brazilian wastewater treatment plants. Science of the Total Environment, 490, 288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.008
Queiroz, F. B. (2011). Desenvolvimento e validação de metodologia para determinação de fármacos e perturbadores endócrinos em amostras de esgoto utilizando extração em fase sólida e cromatografia líquida acoplada à espectrometria de massas. 114 p. Dissertação (Mestrado em Engenharia Ambiental) – Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto, Ouro Preto
Queiroz, F. B., Silva, J. C., Aquino, S. F., Coutrim, M. X., & Afonso, R. J. C. F. (2014). Determination of endocrine disrupters and pharmaceuticals in sewage samples by tandem solid phase clean up/extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-negative and positive electrospray high-resolution mass spectrometry. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 25, 298–312. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20130297
Rivera-Jaimes, J. A., Postigo, C., Melgoza-Alemán, R. M., Aceña, J., Barceló, D., & Alda, M. L. (2018). Study of pharmaceuticals in surface and wastewater from Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 613(614), 1263–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.134
Rühmland, S., Wick, A., Ternes, T. A., & Barjenbruch, M. (2015). Fate of pharmaceuticals in a subsurface flow constructed wetland and two ponds. Ecological Engineering, 80, 125–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.01.036
Ryu, J., Oh, J., Snyder, S. A., & Yoon, Y. (2014). Determination of micropollutants in combined sewer overflows and their removal in a wastewater treatment plant (Seoul, South Korea). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(5), 3239–3251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3613-5
Sanson, A. L., & Estudo da extração e desenvolvimento de metodologia para determinação simultânea de microcontaminantes orgânicos em água superficial por GC-MS e métodos quimiométricos. (2012). 151 p. Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais.
Saputra, F., Yen, C. H., Hsieh, C. Y., Ou, T. Y., Risjani, Y., Cheah, W. K., & Hu, S. Y. (2016). Toxicity effects of the environmental hormone 4-tert-octylphenol in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Journal of Marine Science Research Development, 6, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9910.1000180
Serna-Galvis, E. A., Silva-Agredo, J., Giraldo-Aguirre, A. L., Flórez-Acosta, O. A., & Torres-Palma, R. A. (2016). High frequency ultrasound as a selective advanced oxidation process to remove penicillinic antibiotics and eliminate its antimicrobial activity from water. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 31, 276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.01.007
Silva, J. C. C., Reis Teodoro, J. A., De Cássia Franco Afonso, R. J., Aquino, S. F., & Augusti, R. (2014). Photodegradation of bisphenol A in aqueous medium: Monitoring and identification of by-products by liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 28(9), 987–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.6863
Takeuchi, T., Tsutsumi, O., Ikezuki, Y., Takai, Y., & Taketani, Y. (2004). Positive relationship between androgen and the endocrine disruptor, bisphenol A, in normal women and women with ovarian dysfunction. Endocrine Journal, 51(2), 165–169. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.51.165
Tejeda, A., Torres-Bojorges, Á. X., & Zurita, F. (2017). Carbamazepine removal in three pilot-scale hybrid wetlands planted with ornamental species. Ecological Engineering, 98, 410–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.04.012
Toro-vélez, A. F., Madera-parra, C. A., Peña-varón, M. R., Lee, W. Y., Bezares-Cruz, J. C., Walker, W. S., & Lens, P. N. L. (2016). BPA and NP removal from municipal wastewater by tropical horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 542, 93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.154
Venditti, S., Brunhoferova, H., & Hansen, J. (2022). Behaviour of 27 selected emerging contaminants in vertical flow constructed wetlands as post-treatment for municipal wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 819, 153234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153234
Verlicchi, P., Al Aukidy, M., & Zambello, E. (2012). Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: Removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment-A review. Science of the Total Environment, 429, 123–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.028
Verlicchi, P., & Zambello, E. (2014). How efficient are constructed wetlands in removing pharmaceuticals from untreated and treated urban wastewaters? A Review of Science Total Environment, 470–471, 1281–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.085
Vymazal, J., Březinová, T., & Koželuh, M. (2015). Occurrence and removal of estrogens, progesterone and testosterone in three constructed wetlands treating municipal sewage in the Czech Republic. Science of the Total Environment, 536, 625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.077
Yao, L., Wang, Y., Tong, L., Deng, Y., Li, Y., Gan, Y., & Zhao, K. (2017). Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety Amsterdam, 135, 236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.006
Acknowledgements
The research study was performed with the support from Higher Education Improvement Coordination and Minas Gerais State Research Support Foundation (FAPEMIG).
Funding
The research was developed with the contribution of financial resources from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and the Minas Gerais State Research Support Foundation (FAPEMIG). This research was financially supported by the Research Supporting Foundation of Minas Gerais State (TEC-APQ-02220–15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ana Flávia Santos Rabelo de Melo: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft.
Jacineumo Falcão de Oliveira: formal analysis, software.
Fátima Resende Luiz Fia: conceptualization, supervision, project administration.
Ronaldo Fia: writing—review and editing, project administration.
Mateus Pimentel de Matos: software, investigation.
Ananda Lima Sanson: methodology, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable in this work.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Melo, A.F.S.R., Oliveira, J.F., Fia, F.R.L. et al. Microcontaminants Removal in Constructed Wetlands with Different Baffle Arrangements and Cultivated with Pennisetum setaceum. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05822-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05822-3