Abstract
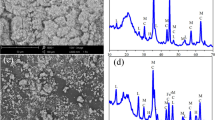
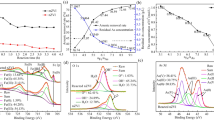
In the present study, attapulgite (ATP)-maintained nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) at different Fe/ATP mass ratios (1:3 and 1:5) was synthesized by liquid phase reduction for its use to remove chromium Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. The morphology, crystalline structure, chemical composition, and valent states of these nZVI/ATP composites were evaluated before and after the reaction. Obtained characterization data indicated an effective dispersion of nZVI on ATP surface, preventing the agglomeration of nZVI particles. Results showed that the introduction of ATP has higher Cr(VI) removal efficacy as compared to the bare nZVI or ATP. At Cr(VI) initial level of 40 mg L−1, the remediation efficacy of Cr(VI) in nZVI/ATP(1:3) reached 91.63%, which was substantially higher than that of bare nZVI (48.68%) and ATP (2.52%). Co-precipitation and reduction of Cr-containing metal deposited onto nZVI/ATP were found as the major reaction mechanisms. At lower initial level of Cr(VI) (20 mg L−1), the reduction was the dominant process where Fe(II) was the major form of iron in the reaction product. However, adsorption was the major mechanism at higher initial level of Cr(VI) (100 mg L−1) whereas the reaction product mainly comprised the ferric form of iron (Fe(III). The main reaction product was the FeCr2O4 under low or high Cr(VI) concentrations which can reduce the risk of secondary pollution because of its high stability.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chai, L., Huang, S., Yang, Z., Peng, B., Huang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2009). Cr (VI) remediation by indigenous bacteria in soils contaminated by chromium-containing slag. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1-3), 516–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.030
Chen, Y., Lin, Z., Hao, R., Xu, H., & Huang, C. (2019). Rapid adsorption and reductive degradation of naphthol green B from aqueous solution by polypyrrole/attapulgite composites supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.096
Chen, X., Li, X., Xu, D., et al. (2020). Application of nanoscale zero-valent iron in hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil: A review, DE Gruyter. Nanotechnology Reviews, 9, 736–750.
Ding, C., Xiao, S., Lin, Y., Yu, P., Zhong, M., Yang, L., Wang, H., Su, L., Liao, C., Zhou, Y., Deng, Y., & Gong, D. (2018). Attapulgite-supported nano-Fe0/peroxymonosulfate for quinclorac removal: Performance, mechanism and degradation pathway. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.189
Dong, L., Lin, L., Li, Q., Huang, Z., Tang, X., Wu, M., Li, C., Cao, X., & Scholz, M. (2018). Enhanced nitrate-nitrogen removal by modified attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron treating simulated groundwater. Journal of Environmental Management, 213, 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.073
Eltaweil, A. S., El-Tawil, A. M., El-Monaem, E. M. A., & El-Subruiti, G. M. (2021). Zero valent iron nanoparticle-loaded nano bentonite intercalated carboxymethyl chitosan for efficient removal of both anionic and cationic dyes. ACS Omega, 6, 6348–6360.
Fu, R., Yang, Y., Xu, Z., Zhang, X., Guo, X., & Bi, D. (2015). The removal of chromium (VI) and lead (II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere, 138, 726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.051
Haider, F. U., Liqun, C., Coulter, J. A., Cheema, S. A., Wu, J., Zhang, R., Wenjun, M., & Farooq, M. (2021). Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety, 211, 111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Hamdy, A. (2020). Experimental study of the relationship between dissolved iron, turbidity, and removal of Cu(II) ion from aqueous solutions using zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05079-0
Homan, N. P., Green, P.,. G., & Young, T. M. (2018). Evaluating ferrous chloride for removal of chromium from ion-exchange waste brines. Journal of American Water Works Association, 110. https://doi.org/10.5942/jawwa.2018.110.0022
Hong, L., Li, C., Fan, X., et al. (2019). 2019. Mechanism of Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution by attapulgite-loaded sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 3(42), 187–193.
Ji, Y., Zhou, Y., Ma, C., Feng, Y., Hao, Y., Rui, Y., Wu, W., Gui, X., Le, V.-N., Han, Y., Wang, Y., Xing, B., Liu, L., & Cao, W. (2016). Jointed toxicity of TiO2 NPs and Cd to rice seedlings: NPs alleviated Cd toxicity and Cd promoted NPs uptake. Plant Physiology Biochemistry S0981942816301802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.010
Konate, A., He, X., Zhang, Z., Ma, Y., Zhang, P., Alugongo, G., & Rui, Y. (2017). Magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles reduce heavy metals uptake and mitigate their toxicity in wheat seedling. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050790
Li, S., Yang, F., Li, J., & Cheng, K. (2020). Porous biochar-nanoscale zero-valent iron composites: Synthesis, characterization and application for lead ion removal. Science of the Total Environment 141037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141037
Liang, L., Li, X., Guo, Y., Lin, Z., Su, X., & Liu, B. (2020). The removal of heavy metal cations by sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI): The reaction mechanisms and the role of sulfur. Journal of Hazardous Materials 124057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124057
Liu, K., Li, F., Cui, J., Yang, S., & Fang, L. (2020). Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) by graphene-like biochar-supported zero-valent iron from irrigation waters under aerobic conditions: Synergistic effects and mechanisms. Journal of Hazardous Materials 122623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122623
Nayak, A. K., Panda, S. S., Basu, A., & Dhal, N. K. (2018). Enhancement of toxic Cr(VI), Fe, and other heavy metals phytoremediation by the synergistic combination of native Bacillus cereus strain and Vetiveria zizanioides L. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 20, 682–691.
Pasinszki, T., & Krebsz, M. (2020). Synthesis and application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in water treatment, environmental remediation, catalysis, and their biological effects. Nanomaterials, 10(5), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050917
Qian, L., Liu, S., Zhang, W., Chen, Y., Ouyang, D., Han, L., Yan, J., & Chen, M. (2019). Enhanced reduction and adsorption of hexavalent chromium by palladium and silicon rich biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 533, 428–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.075
Qiu, Y., Zhang, Q., Gao, B., Li, M., Fan, Z., Sang, W., Hao, H., & Wei, X. (2020). Removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by biochar supported nanosized zero-valent iron: Synergy of adsorption, reduction and transformation. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115018
Shehata, S. M., Badawy, R. K., & Aboulsoud, Y. I. E. (2019). Phytoremediation of some heavy metals in contaminated soil. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 43(1), 189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0214-7
Soliemanzadeh, A., & Fekri, M. (2017). The application of green tea extract to prepare bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and its performance on removal of Cr(VI): effect of relative parameters and soil experiments. Microporous Mesoporous Materials, 239, 60–69.
Stambulska, U. Y., Bayliak, M. M., & Lushchak, V. I. (2018). Chromium(VI) toxicity in legume plants: Modulation effects of rhizobial symbiosis. BioMed Research International 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8031213
Su, H., Fang, Z., Tsang, P. E., Zheng, L., Cheng, W., Fang, J., & Zhao, D. (2016). Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by biochar-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 318, 533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.039
Sun, Y., Yu, I. K. M., Tsang, D. C. W., Cao, X., Lin, D., Wang, L., Nigel, J. D. G., Daniel, S., Alessig, M. K., Ok, Y. S., Feng, Y., & Li, X.-D. (2019). Multifunctional iron-biochar composites for the removal of potentially toxic elements, inherent cations, and hetero-chloride from hydraulic fracturing wastewater. Environment International, 124, 521–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.047
Tang, W., Peng, Z., Li, L., Yue, T., Wang, J., Li, Z., Li, R., Chen, J., Colvin, V.L., Yu, W.W. (2012). Porous stainless steel supported magnetite crystalline membranes for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions., 392-393(none), 150–156. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.12.013
Ullah, S., Adeel, M., Zain, M., Rizwan, M., Irshad, M. K., Jilani, G., Hameed, A., Khan, A., Arshad, M., Raza, A., Baluch, M. A., & Rui, Y. (2020). Physiological and biochemical response of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to TiO2 nanoparticles in phosphorous amended soil: A full life cycle study. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110365
Usman, M., Byrne, J.M., Chaudhary, A., Orsetti, S., Hanna, K., Ruby, C., Kappler, A., Haderlein, S. B. (2018). Magnetite and green rust: Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications of mixed-valent iron minerals. Chemical Reviews, acs.chemrev.7b00224–. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00224.
Wang, M., Ren, L., Wang, D., Zuansi, C., Xia, X., & Ding, A. (2018). Assessing the capacity of biochar to stabilize copper and lead in contaminated sediments using chemical and extraction methods. Journal of Environmental Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.11.007
Wang, H., Cai, J., Liao, Z., Jawad, A., Ifthikar, J., Chen, Z., & Chen, Z. (2020a). Black liquor as biomass feedstock to prepare zero-valent iron embedded biochar with red mud for Cr(VI) removal: Mechanisms insights and engineering practicality. Bioresource Technology 123553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123553
Wang, Y., Zhao, D., Feng, S., Chen, Y., & Xie, R. (2020b). Ammonium thiocyanate functionalized graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI). Journal of Colloid Interface Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.016
Wu, H., Wei, W., Xu, C., Meng, Y., Bai, W., Yang, W., & Lin, A. (2020a). Polyethylene glycol-stabilized nano zero-valent iron supported by biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 188, 109902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109902
Wu, Y., Guan, C.-Y., Griswold, N., Hou, L., Fang, X., Hu, A., Zhi-qiang, H., & Yu, C.-P. (2020b). Zero-valent iron-based technologies for removal of heavy metal(loid)s and organic pollutants from the aquatic environment: Recent advances and perspectives. Journal of Cleaner Production 123478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123478
Xie, W., Bi, X., Huang, Z., et al. (2020). Adsorption mechanism of different heavy metals on the magnetic nano-zerovalent iron supported by nano-active alumina. Huanjing Kexue Xuebao, 8, 2732–2740.
Xu, X., Huang, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., & Cao, X. (2018). Biochar as both electron donor and electron shuttle for the reduction transformation of Cr(VI) during its sorption. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.068
Yamashita, T., & Hayes, P. (2008). Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Applied Surface Science, 254(8), 2441–2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.063
Yang, Y. L., Zhou, Z. M., Deng, W. N., et al. (2017). Removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solutions using improved nanoscale zero-valent iron on pumice. Environmental Chemistry, 36(3), 598–607.
Yang, D., Wang, L., Li, Z., Tang, X., He, M., Yang, S., Liu, X., & Xu, J. (2019). Simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II) and As(III) by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Science of the Total Environment 134823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134823
Yin, Y., Shen, C., Bi, X., & Li, T. (2020). Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by fabricating novel heteroaggregates of montmorillonite micro particles with nanoscale zero-valent iron. Nature (Scientific reports). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69244-z
Zeeshan, N., Nasir, A. A., Haider, F. U., Naveed, K., Naseer, S., & Murtaza, G. (2021). Risk assessment of trace metals deposition and effects on the growth of Abelmoschus esculentus L. by industrially polluted soils of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 58, 881–889.
Zhang, Q., & Liqun, C. (2021). Removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by aluminium hydroxide-modified attapulgite. Polish Journal Environmental Studies, 30, 1–11.
Zhang, W., Qian, L., Ouyang, D., Chen, Y., Han, L., & Chen, M. (2019). Effective removal of Cr(VI) by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: Enhanced adsorption and crystallization. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.070
Zhang, A., Li, X., Xing, J., Xu, G., 2020a. Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: a review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104196
Zhang, W., Qian, L., Chen, Y., Ouyang, D., Han, L., Shang, X., Li, J., Gu, M., & Chen, M. (2020b). Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by attapulgite produced at different acid modification: Synthesis mechanism and the role of silicon on Cr(VI) removal. Chemosphere, 129183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129183
Zhou, P., Adeel, M., Shakoor, N., Guo, M., Hao, Y., Azeem, I., Li, M., Liu, M., & Rui, Y. (2021). Application of nanoparticles alleviates heavy metals stress and promotes plant growth: An overview. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010026
Funding
This work was supported by the Discipline Construction Fund of Gansu Agricultural University (No. GAU-XKJS-2018-211)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Usman, M., Farooq, M. et al. Removing Hexavalent Chromium by Nano Zero-Valent Iron Loaded on Attapulgite. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 48 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05513-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05513-z