Abstract
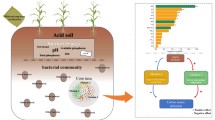
Investigations of the impact of heavy metals on microbial community structure are crucial for bioremediation of the contaminated sites. To this end, high-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing was performed to assess the variations of bacterial communities in 6 heavy metal-contaminated soils sampled from Liujiaping (LJP) and Shanping (SP) lead–zinc tailings situated in northwestern China. Compared with those of the farmland soil (NT), the heavy metal levels and chemical properties of the tailing soils were significantly different. Consistently, the bacterial community structures have been changed, displaying as the bacterial richness and diversity in the tailing soils were either increased or decreased, i.e., trending as SP > NT > LJP. The relative abundances of certain bacterial phyla mainly including Actinobacteriota, Acidobacteriota, Cyanobacteria, Gemmatimonadota, and Bacteroidota were significantly increased in certain SP and/or LJP soils. Further, the relative abundances of Actinobacteriota and Bacteroidota were positively correlated with Cd, TP, TK, SOM, TN, and pH. The abundance of Cyanobacteria was significantly upregulated by Cu, Zn, and TP. Acidobacteriota was notably positively correlated with Cr, Pb, and NO3−_N. On the contrary, the relative abundance of Chloroflexi was negatively correlated with all the environmental parameters, especially with Cd, NO3−_N, TP, SOM, and TN. Together, our results implied that the heavy metals and chemical properties were both driving forces of the variations of the bacterial community structures in the tailing soils. Overall, we have successfully identified certain bacterial species such as s__unclassified_g__Sulfurifustis, s__unclassified_f__Rhodanobacteraceae, s__unclassified_g__Conexibacter, s__unclassified_g__norank_f__norank_o__Gaiellales, and s__unclassified_g__Blastococcus which were probably heavy metal-tolerant in these specific tailing soils, and this will provide a theoretical support for further bioremediations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abia, A. L. K., Alisoltani, A., Keshri, J., & Ubomba-Jaswa, E. (2018). Metagenomic analysis of the bacterial communities and their functional profiles in water and sediments of the Apies River, South Africa, as a function of land use. Science of the Total Environment, 616–617, 326–334.
Agurto-Detzel, H., Bianchi, M., Assumpção, M., Schimmel, M., Collaço, B., Ciardelli, C., Barbosa, J. R., & Calhau, J. (2016). The tailings dam failure of 5 November 2015 in SE Brazil and its preceding seismic sequence. Geophysical Research Letters, 43, 4929–4936.
Akcil, A., Erust, C., Ozdemiroglu, S., Fonti, V., & Beolchini, F. (2015). A review of approaches and techniques used in aquatic contaminated sediments: Metal removal and stabilization by chemical and biotechnological processes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 86, 24–36.
An, F., Diao, Z., & Lv, J. (2018). Microbial diversity and community structure in agricultural soils suffering from 4 years of Pb contamination. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 64, 305–316.
Alvarez, A., Saez, J. M., Costa, J. S. D., Colin, V. L., Fuentes, M. S., Cuozzo, S. A., Benimeli, S. M., Polti, M. A., & Amoroso, J. M. (2017). Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere, 166, 41–62.
Ash, C., Tejnecký, V., Borůvka, L., & Drábek, O. (2016). Different low-molecular-mass organic acids specifically control leaching of arsenic and lead from contaminated soil. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 187, 18–30.
Ashok, B.,& Geetha, N. (2018). Chapter 18 - Recent trends in biosorption of heavy metals by Actinobacteria, Editor(s): Bhim Pratap Singh, Vijai Kumar Gupta, Ajit Kumar Passari, New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering, Elsevier, 257–275
Audu, K. E., Adeniji, S. E., & Obidah, J. S. (2020). Bioremediation of toxic metals in mining site of Zamfara metropolis using resident bacteria (Pantoea agglomerans): A optimization approach. Heliyon, 6(e04704), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04704
Becerra-Castro, C., Lopes, A. R., Vaz-Moreira, I., Silva, E. F., Manaia, C. M., & Nunes, O. C. (2015). Wastewater reuse in irrigation: A microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environmental International, 75, 117–135.
Bier, R. L., Voss, K. A., & Bernhardt, E. S. (2015). Bacterial community responses to a gradient of alkaline mountaintop mine drainage in Central Appalachian streams. The International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal, 9, 1378–1390.
Caban, J. R., Kuppusamy, S., Kim, J. H., Yoon, Y., Kim, S. Y., & Lee, Y. B. (2018). Green manure amendment enhances microbial activity and diversity in antibiotic-contaminated soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 129, 72–76.
Chikere, C. B., Mordi, I. J., Chikere, B. O., Selvarajan, R., Ashafa, T. O., & Obieze, C. C. (2019). Comparative metagenomics and functional profiling of crude oil-polluted soils in Bodo West Community, Ogoni, with other sites of varying pollution history. Annals of Microbiology, 69, 495–513.
Choudhury, S. G., Srivastava, S., Singh, R., Chaudhari, S. K., Sharma, D. K., Singh, S. K., & Sarkar, D. (2014). Tillage and residue management effects on soil aggregation, organic carbon dynamics and yield attribute in rice-wheat cropping system under reclaimed sodic soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 136, 76–83.
Cui, J. Q., He, Q. S., Liu, M. H., Chen, H., Sun, M. B., & Wen, J. P. (2020). Comparative study on different remediation strategies applied in petroleum contaminated soils. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 1–17.
Dixit, R., Malaviya, D., Pandiyan, K., Singh, U. B., Sahu, A., Shukla, R., Singh, B. P., Rai, J. P., Sharma, P. K., & Lade, H. (2015). Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: An overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability, 7, 2189–2212.
Eichorst, S. A., Breznak, J. A., & Schmidt, T. M. (2007). Isolation and characterization of soil bacteria that define Terriglobus gen. nov., in the phylum Acidobacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 2708–2717.
Fernández, N., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Field, J. A., Amils, R., & Sanz, J. L. (2008). Microbial community dynamics in a chemolithotrophic denitrification reactor inoculated with methanogenic granular sludge. Chemosphere, 70, 462–474.
Fierer, N., Morse, J. L., Berthrong, S. T., Bernhardt, E. S., & Jackson, R. B. (2007). Environmental controls on the landscape-scale biogeography of stream bacterial communities. Ecology, 88, 2162–2173.
Gabarrón, M., Faz, A., & Acosta, J. A. (2018). Use of multivariable and redundancy analysis to assess the behavior of metals and arsenic in urban soil and road dust affected by metallic mining as a base for risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 206, 192–201.
Gao, T., Wan, Z., Liu, X., Fu, J., Chang, G., & H., Sun, H., Li, H., Shen, Y., Liu, Y., & X.W. Fang, X. . (2021). Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere of Salsola collina and bulk soil in the Jinchuan mining area. Geomicrobiology Journal, 38(7), 620–630.
Guo, Y., Liu, X., Tsolmon, B., Chen, J., & Bao, Y. (2019). The influence of transplanted trees on soil microbial diversity in coal mine subsidence areas in the loess plateau of china. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21(e00877), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00877
Hooda, P. S., & Alloway, B. J. (1998). Cadmium and lead sorption behavior of selected English and Indian soils. Geoderma, 84, 121–134.
Jacobson, R., & Faust, T. (2014). Hydrologic connectivity of floodplains, northern Missouri-Implications for management and restoration of floodplain forest communities in disturbed landscapes. River Research and Applications, 30, 269–286.
Jiang, B., Adebayo, A., Jia, J., Xing, Y., Deng, S., Guo, L., Liang, Y., & Zhang, D. (2020). Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 362, 187–195.
Jiang, B., Zhang, B., Li, L., Zhao, Y., Shi, Y., Jiang, Q., & Jia, L. (2021). Analysis of microbial community structure and diversity in surrounding rock soil of different waste dump sites in Fushun western opencast mine. Chemosphere, 269(128777), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128777
Kan, X., Dong, Y., Feng, L., Zhou, M., & Hou, H. (2021). Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China’s lead-zinc mine tailings: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere, 267(128909), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128909
Kang, X. H., Leng, Y., & O, M. M., Zeng, X. Y., & Li, S. W. . (2020). The seasonal changes of core bacterial community decide sewage purification in sub-plateau municipal sewage treatment plants. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 43, 1609–1617.
Katiyar, P., Pandey, N., & Sahu, K. K. (2020). Biological approaches of fluoride remediation: Potential for environmental clean-up. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 13044–13055.
Kuang, J. L., Huang, L. N., Chen, L. X., Hua, Z. S., Li, S. J., Hu, M., Li, J. T., & Shu, W. S. (2013). Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage. ISME Journal, 7, 1038–1050.
Li, H., Ye, D., Wang, X., Settles, M., Wang, J., Hao, Z., Zhou, L., Dong, P., Jiang, Y., & Ma, Z. (2014a). Soil bacterial communities of different natural forest types in Northeast China. Plant and Soil, 383, 203–216.
Li Zeng He Chen Han Wang, H. X. C. Z. X. E. G. Y. Y. (2016). Long-term performance of rapid oxidation of arsenite in simulated groundwater using a population of arsenite-oxidizing microorganisms in a bioreactor. Water Research., 101, 393–401.
Li, J., Xin, Z., Yan, J., Li, H., Chen, J., & Ding, G. (2018). Physicochemical and microbiological assessment of soil quality on a chronosequence of a mine reclamation site. European Journal of Soil Science, 69, 1056–1067.
Li, Q., You, P., Hu, Q., Leng, B., Wang, J., Chen, J., Wan, S., Wang, B., Yuan, C., Zhou, R., & Ouyang, K. (2020). Effects of co-contamination of heavy metals and total petroleum hydrocarbons on soil bacterial community and function network reconstitution. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 204(111083), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111083
Li, Z., Ma, Z., Kuijp, T. J. V. D., Yuan, Z., & Huang, L. (2014b). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 843–853.
Liang, X., Chen, L., Liu, Z., Jin, Y., He, M., Zhao, Z., Liu, C., Niyungeko, C., & Arai, Y. (2018). Composition of microbial community in pig manure biochar-amended soils and the linkage to the heavy metals accumulation in rice at harvest. Land Degradation & Development, 29, 2189–2198.
Lin, Y., Ye, Y., Hu, Y., & Shi, H. (2019). The variation in microbial community structure under different heavy metal contamination levels in paddy soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 180, 557–564.
Liu, B., Ai, S., Zhang, W., Huang, D., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Assessment of the bioavailability, bioaccessibility and transfer of heavy metals in the soil–grain–human systems near a mining and smelting area in N.W China. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 822–829.
Liu, J., Sui, Y., Yu, Z., Shi, Y., Chu, H., Jin, J., Liu, X., & Wang, G. (2014). High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 70, 113–122.
Lopez, S., Piutti, S., Vallance, J., Morel, J. L., Echevarria, G., & Benizri, E. (2017). Nickel drives the bacterial community diversity in the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Alyssum murale. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 114, 121–130.
Mani, D., & Kumar, C. (2014). Biotechnological advances in bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystems, an overview with special reference to phytoremediation. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 843–872.
Margesin, R., Plaza, G. A., & Kasenbacher, S. (2011). Characterization of bacterial communities at heavy-metal-contaminated sites. Chemosphere, 82(11), 1583–1588.
Mehrani, M. J., Sobotka, D., Kowal, P., Ciesielski, S., & Makinia, J. (2020). The occurrence and role of Nitrospira in nitrogen removal systems. Bioresource Technology, 303, 122936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122936
Mudd, G. M., Jowitt, S. M., & Werner, T. T. (2017). The world’s lead–zinc mineral resources, scarcity, data, issues and opportunities. Ore Geology Reviews, 80, 1160–1190.
Nottingham, A. T., Fierer, N., Turner, B. L., Whitaker, J., Ostle, N. J., McNamara, N. P., Bardgett, R. D., Leff, J. W., Salinas, N., Silman, M. R., Kruuk, L. E. B., & Meir, P. (2018). Microbes follow Humboldt, temperature drives plant and soil microbial diversity patterns from the Amazon to the Andes. Ecology, 99, 2455–2466.
Oliveira, A., & Pampulha, M. E. (2006). Effects of long-term heavy metal contamination on soil microbial characteristics. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 102, 157–161.
Onireti, O. O., Lin, C., & Qin, J. (2017). Combined effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on mobilization of arsenic and lead from multi-contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 170, 161–168.
Osman, J. R., Wang, Y., Jaubert, C., Nguyen, T. N., Fernandes, G. R., & DuBow, M. S. (2021). The bacterial communities of surface soils from desert sites in the eastern Utah (USA) portion of the Colorado Plateau. Microbiological Research, 244, 126664. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICRES.2020.126664
Pan, J., & Yu, L. (2011). Effects of Cd or/and Pb on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure. Ecological Engineering, 37, 1889–1894.
Pereira, S. I, Lima, A. I, & Figueira, E. M. (2006). Screening possible mechanisms mediating cadmium resistance in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae isolated from contaminated Portuguese soils. Microbial Ecology, 52(2), 176-186
Reijonen, I., Metzler, M., & Hartikainen, H. (2016). Impact of soil pH and organic matter on the chemical bioavailability of vanadium species, the underlying basis for risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 210, 371–379.
Schloss, P. D., Westcott, S. L., Ryabin, T., Hall, J. R., Hartmann, M., Hollister, E. B., Lesniewski, R. A., Oakley, B. B., Parks, D. H., Robinson, C. J., Sahl, J. W., Stres, B., Thallinger, G. G., Van Horn, D. J., & Weber, C. F. (2009). Introducing mother, open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 7537–7541.
Shi, W., Becker, J., Bischoff, M., Turco, R. F., & Konopka, A. E. (2002). Association of microbial community composition and activity with lead, chromium, and hydrocarbon contamination. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3859–3866.
Šípková, A., Száková, J., & Tlustoš, P. (2013). Affinity of selected elements to individual fractions of soil organic matter. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 225, 1–11.
Song, W., Qi, R., Zhao, L., Xue, N., Wang, L., & Yang, Y. (2019). Bacterial community rather than metals shaping metal resistance genes in water, sediment and biofilm in lakes from arid Northwestern China. Environmental Pollution, 254, 113041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113041
Strawn, D. G., & Sparks, D. L. (2000). Effects of soil organic matter on the kinetics and mechanisms of Pb (II) sorption and desorption in soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 144–156.
Tilman, D., & Kareiva, P. (2018). Spatial ecology, the role of space in population dynamics and interspecific interactions (MPB–30). Princeton University Press.
Tsiknia, M., Tzanakakis, V. A., Oikonomidis, D., Paranychianakis, N. V., & Nikolaidis, N. P. (2014). Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil carbon and nitrogen cycling. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98, 2739–2749.
Vig, K., Megharaj, M., Sethunathan, N., & Naidu, R. (2003). Bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium to microorganisms and their activities in soil, a review. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 121–135.
Wang, F., Yao, J., Si, Y., Chen, H., Russel, M., Chen, K., Qian, Y., Zaray, G., & Bramanti, E. (2010). Short-time effect of heavy metals upon microbial community activity. Journal of Hazardous Materials., 173(1), 510–516.
Xu, S., Wang, B., Li, Y., Jiang, D., Zhou, Y., Ding, A., Zong, Y., Ling, X., Zhang, S., & Lu, H. (2020). Ubiquity, diversity, and activity of comammox Nitrospira in agricultural soils. Science of the Total Environment, 706, 135684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135684
Zhang, C., Nie, S., Liang, J., Zeng, G., Wu, H., Hua, S., Liu, J., Yuan, Y., Xiao, H., Deng, L., & Xiang, H. (2016). Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 557–558, 785–790.
Zhang, R., Chen, L., Niu, Z., Song, S., & Zhao, Y. (2019). Water stress affects the frequency of Firmicutes, Clostridiales and Lysobacter in rhizosphere soils of greenhouse grape. Agricultural Water Management, 226, 105776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105776
Zhang, X., Yang, L., Li, Y., Li, H., Wang, W., & Ye, B. (2012). Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 2261–2273.
Zhao, X., Huang, J., Lu, J., & Sun, Y. (2019). Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 170, 218–226.
Zhou, X. K., Li, W. C., Dong, W. C., & Zhou, B. (2020). A preliminary study of the characteristics of lead-zinc deposits in Shaanxi Province and their distribution laws. Northwest Geology, 3, 127–139.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to all the colleagues whose comments that have improved the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31860176, 31700059, 41977204), Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (2020ZDLSF06-06), Key Research and Development Program of Gansu (20YF3FA037), Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2021JM-510, 2021JQ-791, 2021JQ-792), Science and Technology Program of Xi’an (20NYYF0013), XAWLKYTD012, YZJJ202102, YZJJ202110, and National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (S202011080011).
Availability of Data and Materials.
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Tianpeng Gao, Haijuan Li, Yueqing He, Yuanyuan Shen, Guangwen Li, Xiangkai Li, Yueli Chen, Yubing Liu, Changming Li, Jing Ji, Jing Xu, and Guohua Chang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tianpeng Gao and Haijuan Li, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Tianpeng Gao and Haijuan Li have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, T., Li, H., He, Y. et al. The Variations of Bacterial Community Structures in Tailing Soils Suffering from Heavy Metal Contaminations. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05338-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05338-2