Abstract
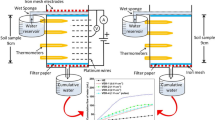
Electrokinetic remediation of groundwater pollutants uses electrical fields to draw contaminants towards electrodes, where they are removed through diverse mechanisms. Conventional electrodes are installed in discrete positions in the soil. Here, we develop unconventional electrodes for the electrokinetic remediation of Cr(VI). Our electrodes are fluids comprised of sodium alginate and graphene particles in aqueous solution and can therefore be injected in the location of interest to facilitate their installation. The subsequent injection of CaCl2 solutions induces gelation (as demonstrated by shear rheology), forming a conductive material (as demonstrated by voltammetry experiments). This material sorbed Cr(VI), as demonstrated in sorption experiments conducted under no-flow conditions and even without any applied electric potential. Therefore, it could be placed downstream of the pollutant to act as a barrier, controlling Cr(VI) migration and providing protection for human or ecological receptors. In a saturated model sandy aquifer, Cr(VI) was drawn towards our unconventional electrode barrier using a 12 V differential voltage, thereby decreasing its concentrations by approximately 70% in 30 min (starting from 0.35 mM Cr(VI), as demonstrated using a spectrophotometer). The net reduction of Cr(VI) concentrations in water was achieved without its extraction from the electrode proximity, because our graphene-alginate electrodes sorbed Cr(VI). Our findings provide a proof of concept of a novel remediation approach, which combines electrokinetic remediation with injectable barriers.
Graphic Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besharat F., Manteghian M., Gallone G., Lazzeri A., Electric field induced alignment of graphene oxide nanoplatelets in polyethersulfone matrix, Nanotechnology, 31 (2020) 155701.
Chen, R., Tanaka, H., Kawamoto, T., Asai, M., Fukushima, C., Na, H., Kurihara, M., Watanabe, M., Arisaka, M., & Nankawa, T. (2013). Selective removal of cesium ions from wastewater using copper hexacyanoferrate nanofilms in an electrochemical system. Electrochimica Acta, 87, 119–125.
Di Palma, L., Gueye, M. T., & Petrucci, E. (2015). Hexavalent chromium reduction in contaminated soil: A comparison between ferrous sulphate and nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 281, 70–76.
Dinesh, M., & Pittman, C. U. (2006). Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri-and hexavalent chromium from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 762–811.
Dong, S., Xia, L., Guo, T., Zhang, F., Cui, L., Su, X., Wang, D., Guo, W., & Sun, J. (2018). Controlled synthesis of flexible graphene aerogels macroscopic monolith as versatile agents for wastewater treatment. Applied Surface Science, 445, 30–38.
Elgrishi, N., Rountree, K. J., McCarthy, B. D., Rountree, E. S., Eisenhart, T. T., & Dempsey, J. L. (2018). A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. Journal of Chemical Education, 95, 197–206.
Estepa, K. M. O., Lamont, K., Malicevic, S., Paschos, A., Colaruotolo, L., Corradini, M., Marangoni, A. G., Lim, L. T., & Pensini, E. (2020). Chitosan-based biogels: A potential approach to trap and bioremediate naphthalene. Colloids and Surfaces A, 605, 125374.
Guan, X., Sun, Y., Qin, H., Li, J., Lo, I. M. C., He, D., & Dong, H. (2015). The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Research, 75, 224–248.
Heyrovsky, M., & Jirkovsky, J. (1995). Polarography and voltammetry of ultrasmall colloids: Introduction to a new field. Langmuir, 11, 4288–4292.
Hou, T., Kong, L., Guo, X., Wu, Y., Wang, F., Wen, Y., & Yang, H. (2016). Magnetic ferrous-doped graphene for improving Cr (VI) removal. Materials Research Express, 3, 045006.
Hu, Z., Cai, L., Liang, J., Guo, X., Li, W., & Huang, Z. (2019). Green synthesis of expanded graphite/layered double hydroxides nanocomposites and their application in adsorption removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209, 1216–1227.
Huang, W.-H., Dong, C.-D., Chen, C.-W., Surampalli, R. Y., & Kao, C.-M. (2017). Application of sulfate reduction mechanisms for the simultaneous bioremediation of toluene and copper contaminated groundwater. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 124, 215–222.
Ionita, M., Pandele, M. A., & Iovu, H. (2013). Sodium alginate/graphene oxide composite films with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 94, 339–344.
Iyer, A., Pensini, E., & Singh, A. (2019). Removal of hexavalent chromium from water using hydrochar obtained with different types of feedstock. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 47, 567–583.
Karn, B., Kuiken, T., & Otto, M. (2009). Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: A review of the benefits and potential risks. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 1813–1831.
Kim, S. O., Jeong, J. Y., Lee, W. C., Yun, S. T., & Jo, H. Y. (2020). Electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils: Performance comparison between one-and two-dimensional electrode configurations. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 1–15.
Kim, W. S., Jeon, E. K., Jung, J. M., Jung, H. B., Ko, S. H., Seo, C. I., & Baek, K. (2014). Field application of electrokinetic remediation for multi-metal contaminated paddy soil using two-dimensional electrode configuration. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 4482–4491.
Lamont, K., Marangoni, A., & Pensini, E. (2019a). ‘Emulsion locks’ for the containment of hydrocarbons during surfactant flushing. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 90, 98–109.
Lamont, K., Pensini, E., & Marangoni, A. G. (2019b). Gelation on demand using switchable double emulsions: A potential strategy for the in situ immobilization of organic contaminants. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 562, 470–482.
Lee, T. Y., Lee, K., Lim, H. H., Song, M. S., Yang, S. M., Yoo, H. K., Suh, D. I., Zhu, Z., Yoon, A., MacDonald, M. R., & Lei, X. (2018). Ferroelectric polarization-switching dynamics and wake-up effect in Si-doped HfO2. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11, 3142–3149.
Liu, Z., Peng, P., Liu, Z., Fang, W., Zhou, Q., Liu, X., & Liu, J. (2018). Electric-field-induced out-of-plane alignment of clay in poly (dimethylsiloxane) with enhanced anisotropic thermal conductivity and mechanical properties. Composites Science and Technology, 165, 39–47.
Lu, P., Feng, Q., Meng, Q., & Yuan, T. (2012). Electrokinetic remediation of chromium-and cadmium-contaminated soil from abandoned industrial site. Separation and Purification Technology, 98, 216–220.
Lu, T., Tian, Y., Studer, A., Li, Q., Withers, R. L., Jin, L., Yu, D., Xu, Z., Wei, X., & Liu, Y. (2020). Structure-driven, ferroelectric wake-up effect for electrical fatigue relief. Chemistry of Materials, 32, 6456–6463.
Mabbott, G. A. (1983). An introduction to cyclic voltammetry. Journal of Chemical Education, 60, 697.
Manassero, M., Dominijanni, A., Foti, S., & Musso, G. (Eds.). (2013). Coupled phenomena in environmental geotechnics. CRC Press.
Marshall, T., Estepa, K., Corradini, M., Marangoni, A. G., Sleep, B., & Pensini, E. (2020b). Selective solvent filters for non-aqueous phase liquid separation from water. Scientific Reports (accepted), 10, 1–13.
Marshall, T., Gravelle, A., Laredo, T., Rodriguez-Uribe, A., Misra, M., Mohanti, A., Marangoni, A. G., Lim, L. T., & Pensini, E. (2020d). Zein-based materials: Effect of nanocarbon inclusion and potential applications. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 1–10.
Marshall, T., Gravelle, A., Marangoni, A. G., Elsayed, A., & Pensini, E. (2020c). Zein for hydrocarbon remediation: Emulsifier, trapping agent, or both? Colloids and Surfaces A, 589, 124456.
Marshall, T., Marangoni, A. G., Corradini, M. G., Rodriguez-Uribe, A., Misra, M., Mohanty, A. K., Rodriguez, B. M., & Pensini, E. (2020a). Path-dependent rheology of carbon particle-hydroxyethylcellulose fluids. Colloids and Surfaces A, 612, 126000.
Marshall, T., Marangoni, A. G., Lim, L. T., Tchoukov, P., & Pensini, E. (2020e). Oxidizing emulsifiers: Gelators for water in hydrocarbon reactive emulsions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 104998.
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N., & Gibbs, B. F. (2001). Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: An evaluation. Engineering Geology, 60, 193–207.
Němeček, J., Pokorný, P., Lacinová, L., Černík, M., Masopustová, Z., Lhotský, O., Filipová, A., & Cajthaml, T. (2015). Combined abiotic and biotic in-situ reduction of hexavalent chromium in groundwater using nZVI and whey: A remedial pilot test. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 670–679.
Němeček, J., Pokorný, P., Lhotský, O., Knytl, V., Najmanová, P., Steinová, J., Černík, M., Filipová, A., Filip, J., & Cajthaml, T. (2016). Combined nano-biotechnology for in-situ remediation of mixed contamination of groundwater by hexavalent chromium and chlorinated solvents. Science of the Total Environment, 563, 822–834.
Pensini, E., Elsayed, A., Rodriguez, B. M., Marangoni, A. G., Singh, A., Sleep, B., Hayward, G., Lamont, K., & Collier, C. M. (2018). In situ trapping and treating of hexavalent chromium using scleroglucan-based fluids: A proof of concept. Colloids and Surfaces A, 559, 192–200.
Pokharel, P., Xiao, D., Erogbogbo, F., & Keles, O. (2019). A hierarchical approach for creating electrically conductive network structure in polyurethane nanocomposites using a hybrid of graphene nanoplatelets, carbon black and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Composites Part b: Engineering, 161, 169–182.
Reddy, K. R., & Chinthamreddy, S. (2004). Enhanced electrokinetic remediation of heavy metals in glacial till soils using different electrolyte solutions. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 130, 442–455.
Reddy, K. R., Maturi, K., & Cameselle, C. (2009). Sequential electrokinetic remediation of mixed contaminants in low permeability soils. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 135, 989–998.
Russo, R., Malinconico, M., & Santagata, G. (2007). Effect of cross-linking with calcium ions on the physical properties of alginate films. Biomacromolecules, 8, 3193–3197.
Sawada, A., Mori, K. I., Tanaka, S., Fukushima, M., & Tatsumi, K. (2004). Removal of Cr (VI) from contaminated soil by electrokinetic remediation. Waste Management, 24, 483–490.
Siwik, A., Pensini, E., Elsayed, A., Rodriguez, B. M., Marangoni, A. G., & Collier, C. M. (2019). Natural guar, xanthan and carboxymethyl-cellulose-based fluids: Potential use to trap and treat hexavalent chromium in the subsurface. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 102807.
Su, H., Fang, Z., Tsang, P. E., Fang, J., & Zhao, D. (2016). Stabilisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron with biochar for enhanced transport and in-situ remediation of hexavalent chromium in soil. Environmental Pollution, 214, 94–100.
Sun, G., Li, B., Ran, J., Shen, X., & Tong, H. (2015). Three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbon/graphene composites derived from graphene oxide-chitosan hydrogels for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 171, 13–22.
Tarhini, A., Tehrani-Bagha, A., Kazan, M., & Grady, B. (2021). The effect of graphene flake size on the properties of graphene-based polymer composite films. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 138, 49821.
Thatoi, H., Das, S., Mishra, J., Rath, B. P., & Das, N. (2014). Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 146, 383–399.
Virkutyte, J., Sillanpää, M., & Latostenmaa, P. (2002). Electrokinetic soil remediation — Critical overview. Science of the Total Environment, 289, 97–121.
Walker, J., Miranti, R., Skjærvø, S. L., Rojac, T., Grande, T., & Einarsrud, M. A. (2020). Super-coercive electric field hysteresis in ferroelectric plastic crystal tetramethylammonium bromotrichloroferrate (III). Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 8, 3206–3216.
Wang, L., Huang, L., Xia, H., Li, H., Li, X., & Liu, X. (2019). Application of a multi-electrode system with polyaniline auxiliary electrodes for electrokinetic remediation of chromium-contaminated soil. Separation and Purification Technology, 224, 106–112.
Yan, Y., Xue, F., Muhammad, F., Yu, L., Xu, F., Jiao, B., Shiau, Y., & Li, D. (2018). Application of iron-loaded activated carbon electrodes for electrokinetic remediation of chromium-contaminated soil in a three-dimensional electrode system. Scientific Reports, 8, 1–11.
Yin, H., Ma, Q., Zhou, Y., Ai, S., & Zhu, L. (2010). Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of 4-aminophenol based on graphene–chitosan composite film modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 55, 7102–7108.
Zhou, H., Xu, J., Lv, S., Liu, Z., & Liu, W. (2020). Removal of cadmium in contaminated kaolin by new-style electrokinetic remediation using array electrodes coupled with permeable reactive barrier. Separation and Purification Technology, 239, 116544.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (provided through an NSERC Discovery grant, awarded to Dr. Erica Pensini, RGPIN-2018-04636).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telepanich, A., Marshall, T., Gregori, S. et al. Graphene-Alginate Fluids as Unconventional Electrodes for the Electrokinetic Remediation of Cr(VI). Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05278-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05278-x