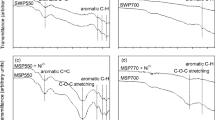
Abstract
The use of rice straw for biochar production has been widely proved as a great alternative energy source, which not only is cheaper than other commercial coals but also helps mitigation of climate change. In this study, the rice straw–derived biochar was assessed as a sorption material used for livestock wastewater treatment, which has not much been studied so far. The biochar derived from rice straw had moisture content of 4.9 ± 0.5 %, bulk density of 0.38 ± 0.03 g/cm3, iodine number of 958.0 ± 37.0 mg/g, and pH was determined at 7.6 ± 0.1. The optimal contact time, biochar mass concentration, and pH were determined as 3.0 h, 4.0 g/L, and 9.0, respectively. The COD and BOD5 removal efficiencies were up to 40.0% via the batch experiment. However, the column test results showed the higher removal efficiencies which were 79.0 ± 6.1% for COD and 84.0 ± 2.5% for BOD5 with the influent COD concentration of 373.0 ± 8.0 mg/L and BOD5 concentration of 240.0 ± 3.0 mg/L. The effluent all met the current livestock wastewater discharge standard of Vietnam (QCVN 62-MT:2016/BTNMT). These findings indicate the potential of using straw-derived biochar as a good material for removing organic pollutants from livestock wastewater.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Sung, J. K., Yang, J. E., & Ok, Y. S. (2012a). Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresource Technology, 118, 536–544.
Ahmad, M., Usman, A. R. A., Lee, S. S., Kim, S. C., Joo, J. H., Yang, J. E., & Ok, Y. S. (2012b). Eggshell and coral wastes as low cost sorbents for the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18, 198–204.
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., Vithanage, M., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33.
Ajibade, O.F., Wang, H.-C., Guadie, A., Fausat Ajibade, T., Ying-Ke, F., Muhammad Adeel Sharif, H., Wang, A.-J. (2020). Total nitrogen removal in biochar amended non-aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands for secondary wastewater effluent with low C/N ratio: Microbial community structure and dissolved organic carbon release conditions. Bioresource Technology, 124430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124430
Anh, B. T. K., Thanh, N. V., Phuong, N. M., Ha, N. T. H., Yen, N. H., Lap, B. Q., & Kim, D. D. (2020). Selection of suitable filter materials for horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland treating swine wastewater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4449-6.
Batista, E. M. C. C., Shultz, J., Matos, T. T. S., Fornari, M. R., Ferreira, T. M., Szpoganicz, B., de Freitas, R. A., & Mangrich, A. S. (2018). Effect of surface and porosity of biochar on water holding capacityaiming indirectly at preservation of the Amazon biome. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 10677. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28794-z.
Byrne, C. E., & Nagle, D. C. (1997). Carbonized wood monoliths – characterization. Carbon, 35, 267–273.
Cantrell, K. B., Ducey, T., Ro, K. S., & Hunt, P. G. (2008). Livestock waste-to-bioenergy generation opportunities. Bioresource Technology, 99, 7941–7953.
Cao, X., & Harris, W. (2010). Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresource Technology, 101, 5222–5228.
Cao, X., Ma, L., Liang, Y., Gao, B., & Harris, W. (2011). Simultaneous immobilization of lead and atrazine in contaminated soils using dairy-manure biochar. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 4884–4889.
Cheng, Q., Xu, C., Huang, W., Jiang, M., Yan, J., Fan, G., Song, G. (2020). Improving anaerobic digestion of piggery wastewater by alleviating stress of ammonia using biochar derived from rice straw. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 100948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100948
Dai, J., Meng, X., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y. (2020). Effects of modification and magnetization of rice straw derived biochar on adsorption of tetracycline from water. Bioresource Technology, 123455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123455
Dang, H. T. T., Dinh, C. V., Nguyen, K. M., Tran, N. T. H., Pham, T. T., & Narbaitz, R. M. (2020). Loofah Sponges as Bio-Carriers in a Pilot-Scale Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge System for Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 12(11), 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114758.
Deng, Y., Huang, S., Dong, C., Meng, Z., & Wang, X. (2020). Competitive adsorption behaviour and mechanisms of cadmium, nickel and ammonium from aqueous solution by fresh and ageing rice straw biochars. Bioresource Technology, 122853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122853.
Deng, S., Chen, J., & Chang, J. (2021). Application of biochar as an innovative substrate in constructed wetlands/biofilters for wastewater treatment: Performance and ecological benefits. Journal of Cleaner Production, 293(2021), 126156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126156.
Do, P. T. M., Ueda, T., Kose, R., Nguyen, L. X., Okayama, T., & Miyanishi, T. (2019). Properties and potential use of biochars from residues of two rice varieties, Japanese Koshihikari and VietnameseIR50404. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21, 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0768-8.
EBC (European Biochar Foundation). (2012). European biochar certificate – Guidelines for a sustainable production of biochar. Arbaz.
Enaime, G., Baçaoui, A., Yaacoubi, A., & Lübken, M. (2020). Biochar for wastewater treatment—Conversion technologies and applications. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103492.
Feng, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Li, C., & Wu, H. (2020a). Dynamic variation in nitrogen removal of constructed wetlands modified by biochar for treating secondary livestock effluent under varying oxygen supplying conditions. Journal of Environmental Management, 260, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110152.
Feng, L., Wang, R., Jia, L., & Wu, H. (2020b). Can biochar application improve nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands for treating anaerobically-digested swine wastewater? Chemical Engineering Journal, 379, 122273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122273.
Gadde, B., Bonnet, S., Menke, C., & Garivait, S. (2009a). Air pollutant emissions from rice straw open field burning in India, Thailand and the Philippines. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1554–1558.
Gadde, B., Menke, C., & Wassmann, R. (2009b). Rice straw as a renewable energy source in India, Thailand and the Philippines: Overall potential and limitations for energy contribution and greenhouse gas mitigation. Biomass and Bioenergy, 33, 1532–1546.
Gai, X., Wang, H., Liu, J., Zhai, L., Liu, S., Ren, T., & Liu, H. (2014). Effects of feedstock and pyrolysis temperature on biochar adsorption of ammonium and nitrate. PLoS One, 2014(9), e113888.
Ghezzehei, T. A., Sarkhot, D. V., & Berhe, A. A. (2014). Biochar can be used to capture essential nutrients from dairy wastewater and improve soil physico-chemical properties. Solid Earth, 5, 953–962.
Guo, J., & Chen, B. (2014). Insights on the molecular mechanism for the recalcitrance of biochars: Interactive effects of carbon and silicon components. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(16), 9103–9112.
Hu, H., Li, X., Wu, S., & Yang, C. (2020). Sustainable livestock wastewater treatment via phytoremediation: Current status and future perspectives. Bioresource Technology, 123809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123809.
Hung, N. T. Q., Le, K. T., Nguyen, M. K., & Le, T. N. H. (2018). Potential of biochar production from agriculture residues at household scale: A case study in Go Cong Tay District, Tien Giang Province, Vietnam. Environment and Natural Resources Journal, 16(2), 68–78.
Ibrahim, M., Khan, S., Hao, X., & Li, G. (2016). Biochar effects on metal bioaccumulation and arsenic speciation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) grown in contaminated soil. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13, 2467–2474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1081-5.
Kaetzl, K., Lübken, M., Gehring, T., & Wichern, M. (2018). Efficient low-cost anaerobic treatment of wastewater using biochar and woodchip filters. Water, 10(7), 818.
Kaetzl, K., Lübken, M., Uzun, G., Gehring, T., Nettmann, E., Stenchly, K., & Wichern, M. (2019). On-farm wastewater treatment using biochar from local agroresidues reduces pathogens from irrigation water for safer food production in developing countries. Science of The Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.142.
Karthikeyan, P., Banu, H. A. T., & Meenakshi, S. (2019). Removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous solution using La3+ incorporated chitosan biopolymeric matrix membrane. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 124, 492–504.
Koh, K. Y., Wang, C., & Chen, J. P. (2019). A new adsorbent of gadolinium-1,4-benzenedi-carboxylatecomposite for better phosphorous removal in aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 543, 343–351.
Ky, N.M., Hung, N.T.Q., Manh, N.C., Lap, B.Q., Dang, H.T.T., Ozaki, A. (2020). Assessment of nutrients removal by constructed wetlands using reed grass (Phragmites australis L.) and Vetiver grass (Vetiveria Zizanioides L.). J. Fac. Agr., Kyushu Univ., 65 (1), 149–156
Lehmann, J., & Joseph, S. (2009). Biochar for environmental management: Science and technology. Earthscan.
Li, R., Wang, J. J., Zhou, B., Zhang, Z., Liu, S., Lei, S., & Xiao, R. (2017). Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 147, 96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.069.
Li, J., Hu, Z., Li, F., Fan, J., Zhang, J., Li, F., & Hu, H. (2019). Effect of oxygen supply strategy on nitrogen removal of biochar-based vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland: Intermittent aeration and tidal flow. Chemosphere, 223, 366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.082.
Lou, L., Wu, B., Wang, L., Luo, L., Xu, X., Hou, J., Xun, B., Hu, B., & Chen, Y. (2011). Sorption and ecotoxicity of pentachlorophenol polluted sediment amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Bioresource Technology, 102, 4036–4041.
Luo, L., Wang, G., Shi, G., Zhang, M., Zhang, J., He, J., & Deng, O. (2019). The characterization of biochars derived from rice straw and swine manure, and their potential and risk in N and P removal from water. Journal of Environmental Management, 245, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.072.
Mei, Y., Li, B., & Fan, S. (2020). Biochar from Rice Straw for Cu2+ Removal from aqueous solutions: Mechanism and contribution made by acid-soluble minerals. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 231, 420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04791-9.
Mendoza, T.C., Samson, R. (1999). Strategies to avoid crop residue burning in the Philippine context. Proceedings of the International Conference on Frostbites and Sun Burns, 1999 April 24, San Salvador, QC Canada: 2011
Mohan, D., Sarswat, A., Ok, Y. S., & Pittman, C. U. (2014). Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low-cost and sustainable adsorbent: A critical review. Bioresource Technology, 160, 191–202.
MONRE (Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment). (2014). National environment report in rural areas. Vietnam Publishing House of Natural Resources, Environment and Cartography.
Mwaanga, P., Carraway, E., & Schlautman, M. (2014). The pH dependence of natural organic matter sorption to nanoparticles and its ability to stabilize nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. European Scientific Journal, 64–76.
Nguyen, T. H. (2017a). An overview of agricultural pollution in Vietnam: The crops sector. World Bank.
Nguyen, T. H. (2017b). The actual situation of dealing with animal husbandry environment in Vietnam and propose management solutions. Environmental Journal, 6, 28–29.
Nguyen, T. H., & Ho, T. H. (2008). Adsorption studies on the removal of color/COD from dyeing wastewater using activated carbon developed from cotton dust. VNU Journal of Science: Natural Sciences and Technology, 24, 16–22.
Nguyen, T. H., Cho, H. H., Poster, D. L., & Ball, W. P. (2007). Evidence for a pore-filling mechanism in the adsorption of aromatic hydrocarbons to a natural wood char. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(4), 1212–1217. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0617845.
Perez-Mercado, L. F., Lalander, C., Joel, A., Ottoson, J., Dalahmeh, S., & Vinnerås, B. (2019). Biochar filters as an on-farm treatment to reduce pathogens when irrigating with wastewater-polluted sources. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109295.
Pham, T.L.P., Nguyen, T.T., Brennan, D., Marsh, S., Bui, H.N. (2010). CARD 030/05 VIE Project: Developing a strategy to enhance the competitiveness of rural small and medium enterprises in the agricultural value chain. Institute of Policy and Strategy for Rural Development.
Popa, M., Ungureanu, N., Vlăduţ, V., Şt Biriş, S., Zăbavă, B.Şt. (2019). Types of treatment plants for livestock wastewater. Proceeding of 6th International Conference “Research People and Actual Tasks on Multidisciplinary Sciences”. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334064218
Rice, E. W., Baird, R. B., Eaton, A. D., & Clesceri, L. S. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association.
Saeed, A., Akhter, M. W., & Iqbal, M. (2005). Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using papaya wood as a new biosorbent. Separation and Purification Technology Journal, 45, 25–31.
Salih, H. H., Patterson, C. L., Sorial, G. A., Sinha, R., & Krishnan, R. (2011). The fate and transport of the SiO2 nanoparticles in a granular activated carbon bed and their impact on the removal of VOCs. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 193, 95–101.
Shen, Z., Hou, D., Jin, F., Shi, J., Fan, X., Tsang, D. C. W., & Alessi, D. S. (2018). Effect of production temperature on lead removal mechanisms by rice straw biochars. Science of The Total Environment. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.282Sun, X., Zhong, T., Zhang, L., Zhang, K., & Wu, W. (2019). Reducing ammonia volatilization from paddy field with rice straw derived biochar. Science of The Total Environment, 660, 512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.450.
Tang, J.X., Jin, Y.T., He, Z.L., Hou, Q.Y., Zhao, C.T. (2018). A review of researches on biochar adsorbing organic contaminants and its mechanism and influence factors. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering 392(2018), https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/392/5/052030
Tran, V.T. (2015). Suitable advanced technologies for Vietnamese conditions to treat environmental pollution in combination with making use of waste from pig farms. The scientific research project no. 11511/2015, National Department of Information Science and Technology
Vu, T., & Nguyen, H. S. (2011). Application of biochar to improve soil productivity - Affecting the type and amount of biochar applied to rice growth and productivity. Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 1, 56–60.
Vu, T.T.H., Vu, Q.C., Nguyen, T.H.C., Le, V.C. (2013). The current situation and environmental management solutions in household farming and small farms in some Northern provinces. Journal of Water Resources Science and Technology, 18
Warnock, D. D., Lehmann, J., Kuyper, T. W., & Rilling, M. C. (2007). Mycorrhyzal responses to biochar in soil – concepts and mechanisms. Plant and Soil, 300, 9–20.
Xiao, X., Chen, B., & Zhu, L. (2014). Transformation, morphology, and dissolution of silicon and carbon in rice straw-derived biochars under different pyrolytic temperatures. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(6), 3411–3419.
Xu, X., He, C., Yuan, X., Zhang, Q., Wang, S., Wang, B., Zhang, L. (2020). Rice straw biochar mitigated more N2O emissions from fertilized paddy soil with higher water content than that derived from ex situ biowaste. Environmental Pollution, 114477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114477
Yang, X. B., Ying, G. G., Peng, P. A., Wang, L., Zhao, J. L., Zhang, L. J., Yuan, P., & He, H. P. (2010). Influence of biochars on plant uptake and dissipation of two pesticides in an agricultural soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 7915–7921.
Yang, J. E., Skogley, E. O., & Ok, Y. S. (2011). Carbonaceous resin capsule for vapor-phase monitoring of volatile monoaromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 20, 205–220.
Yang, Y., Lin, X., Wei, B., Zhao, Y., & Wang, J. (2014). Evaluation of adsorption potential of bamboo biochar for metal-complex dye: Equilibrium, kinetics and artificial neural network modeling. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0306-0.
Younis, S.A., El-Salamony, R.A., Tsang, Y.F., Kim, K.H. (2019). Use of rice straw-based biochar for batch sorption of barium/strontium from saline water: Protection against scale formation in petroleum/desalination industries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 119442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119442
Yu, X. Y., Ying, G. G., & Kookana, R. S. (2009). Reduced plant uptake of pesticides with biochar additions to soil. Chemosphere, 76, 665–671.
Yu, J., Hu, H., Wu, X., Zhou, T., Liu, Y., Ruan, R., & Zheng, H. (2019). Coupling of biochar-mediated absorption and algal-bacterial system to enhance nutrients recovery from swine wastewater. Science of The Total Environment, 134935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134935
Zhang, X., Wang, H., He, L., Lu, K., Sarmah, A., Li, J., Bolan, N. S., Pei, J., & Huang, H. (2013). Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environmental Science and SollutionSolution Research, 20(12), 8472–8483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356013-1659-0.
Zheng, W., Guo, M., Chow, T., Bennett, D. N., & Rajagopalan, N. (2010). Sorption properties of greenwaste biochar for two triazine pesticides. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 121–126.
Acknowledgements
We also highly acknowledge the support of Nong Lam University for wastewater supply.
Funding
The Ministry of Education and Training (B2020-NLS-04) provided the research fund. This research was also funded by Thuyloi University Foundation for Science and Technology to support the ROOM team to jointly study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lap, B.Q., Thinh, N.V.D., Hung, N.T.Q. et al. Assessment of Rice Straw–Derived Biochar for Livestock Wastewater Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05100-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05100-8