Abstract
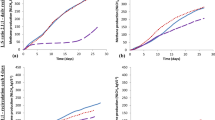
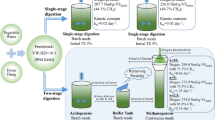
The high organic content of food waste (FW), which represents the largest proportion of municipal solid waste (MSW) (in Latinamerican countries 50–75%), makes its treatment increasingly common trough technologies such as anaerobic digestion (AD), to obtain value-added by-products, such as renewable energy in the form of methane, digestates and other by-products of biotechnological applications such as long-chain fatty acids. In this study, the influence of semi-continuous reactors in single-stage (R1) and two-stage (R2: acidogenic and R3: methanogenic reactors) configurations on the AD-FW was evaluated (including parameters related to process monitoring, organic matter conversion and process reactions) with the following organic loading rate (OLR: kgVS m-3 d-1) values: i. R1: 0.7, 1.5, 3.0 and 6.0; ii. R2: 3.0, 4.0, 9.0 and 15.0; and R3: 1.0, 2.0, 4.0 and 7.0. The two-stage configuration showed a better performance in terms of: i. the OLRs: 35% higher than that in the single-stage configuration, with chemical oxygen demand (CODtotal) and volatile solid (VS) removal efficiencies > 80%; ii. the best performance in terms of methane production, with statistically significant differences (p<0.05) in the quantity and quality of biogas and iii. obtaining other by-products with high added value, such as behenic and caproic acid, which are useful in biotechnological applications. Additionally, it was found that total reducing sugars (TRS) are an important parameter in the monitoring and conversion of matter organic, mainly in two-stage configuration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed, A., Chen, C. L., Rajagopal, R., Wu, D., Mao, Y., Ho, I. J. R., Lim, J. W., & Wang, J. Y. (2015). Multi-phased anaerobic baffled reactor treating food waste. Bioresource Technology, 182, 239–244.
Aldin, S., Nakhla, G., & Ray, M. B. (2011). Modeling the influence of particulate protein size on hydrolysis in anaerobic digestion. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50(18), 10843–10,849.
Angulo-Padilla, J., Lozano-De La Ossa, L., González-Delgado, A., Sánchez-Tuirán, E., & Ojeda-Delgado, K. (2018). Monitoring anaerobic digester parameters of biogas production from corn (Zea mays) leaf and stalk residual biomass. Contemporary Engineering Sciences, 11(26), 1291–1299.
APHA (2005). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington DC: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. 21st ed.p282.
Arzate, J. A., Kirstein, M., Ertem, F. C., Kielhorn, E., Ramirez Malule, H., Neubauer, P., Cruz-Bournazou, M. N., & Junne, S. (2017). Anaerobic digestion model (AM2) for the description of biogas processes at dynamic feedstock loading rates. Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 89(5), 686–695.
Aslanzadeh, S., Rajendran, K., & Taherzadeh, M. J. (2014). A comparative study between single- and two-stage anaerobic digestion processes: Effects of organic loading rate and hydraulic retention time. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 95, 181–188.
Baldi, F., Pecorini, I., & Iannelli, R. (2019). Comparison of single-stage and two-stage anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and activated sludge for hydrogen and methane production. Renewable Energy, 143, 1755–1765.
Cappai, G., De Gioannis, G., Muntoni, A., Spiga, D., Boni, M. R., Polettini, A., Pomi, R. & Rossi, A. (2018). Biohydrogen production from food waste: Influence of the inoculum-to-substrate ratio. Sustainability, 10 (12), 1–15.
Capson-Tojo, G., Ruiz, D., Rouez, M., Crest, M., Steyer, J. P., Bernet, N., Delgenès, J. P., & Escudié, R. (2017). Accumulation of propionic acid during consecutive batch anaerobic digestion of commercial food waste. Bioresource Technology, 245, 724–733.
Casallas-Ojeda, M. R., Marmolejo-Rebellón, L. F., & Torres-Lozada, P. (2020). Evaluation of simultaneous incidence of head space and temperature on biochemical methane potential in food waste. Cogent Engineering, 7(1), 1729514.
Dahiya, S., Lakshminarayanan, S. S., & Venkata, M. S. (2019). Steering acidogenesis towards selective propionic acid production using co-factors and evaluating environmental sustainability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 379, 122–135.
De Gioannis, G., Muntoni, A., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., & Spiga, D. (2017). Energy recovery from one- and two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste. Waste Management, 68, 595–602.
Fernández-Domínguez, D., Astals, S., Peces, M., Frison, N., Bolzonella, D., Mata-Alvarez, J., & Dosta, J. (2020). Volatile fatty acids production from biowaste at mechanical-biological treatment plants: Focusing on fermentation temperature. Bioresource Technology, 314, 123729.
Gomes, S. D., Fuess, L. T., Mañunga, T., & Feitosa de Lima Gomes, P. C. & Zaiat, M. (2016). Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria as a hindering factor for biohydrogen production from cassava flour wastewater in a continuous multiple tube reactor. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(19), 8120–8131.
Gómez-Camacho, C. E., Ruggeri, B., Mangialardi, L., Persico, M., & Luongo Malavé, A. C. (2019). Continuous two-step anaerobic digestion (TSAD) of organic market waste: rationalising process parameters. International Journal of Energy and Environmental Engineering, 10(4), 413–427.
Gourdon, R., & Vermande, P. (1987). Effects of propionic acid concentration on anaerobic digestion of pig manure. Biomass, 13(1), 1–12.
Goux, X., Calusinska, M., Fossépré, M., Benizri, E., & Delfosse, P. (2016). Start-up phase of an anaerobic full-scale farm reactor – Appearance of mesophilic anaerobic conditions and establishment of the methanogenic microbial community. Bioresource Technology, 212, 217–226.
Guo, X., Kang, K., Shang, G., Yu, X., Qiu, L., & Sun, G. (2018). Influence of mesophilic and thermophilic conditions on the anaerobic digestion of food waste: focus on the microbial activity and removal of long chain fatty acids. Waste Management and Research, 36(11), 1106–1112.
Hidalgo, D., & Martín-Marroquín, J. M. (2014). Effects of inoculum source and co-digestion strategies on anaerobic digestion of residues generated in the treatment of waste vegetable oils. Journal of Environmental Management, 142, 17–22.
Holliger, C., Alves, M., Andrade, D., Angelidaki, I., Astals, S., Baier, U., Bougrier, C., Buffière, P., Carballa, M., De Wilde, V., Ebertseder, F., Fernández, B., Ficara, E., Fotidis, I., Frigon, J. C., De Laclos, H. F., Ghasimi, D. S. M., Hack, G., Hartel, M., Heerenklage, J., Horvath, I. S., Jenicek, P., Koch, K., Krautwald, J., Lizasoain, J., Liu, J., Mosberger, L., Nistor, M., Oechsner, H., Oliveira, J. V., Paterson, M., Pauss, A., Pommier, S., Porqueddu, I., Raposo, F., Ribeiro, T., Pfund, F. R., Strömberg, S., Torrijos, M., Van Eekert, M., Van Lier, J., Wedwitschka, H., & Wierinck, I. (2016). Towards a standardization of biomethane potential tests. Water Science and Technology, 74(11), 2515–2522.
Jo, Y., Kim, J., Hwang, K., & Lee, C. (2018). A comparative study of single- and two-phase anaerobic digestion of food waste under uncontrolled pH conditions. Waste Management, 78, 509–520.
Le Hyaric, R., Chardin, C., Benbelkacem, H., Bollon, J., Bayard, R., Escudié, R., & Buffière, P. (2011). Influence of substrate concentration and moisture content on the specific methanogenic activity of dry mesophilic municipal solid waste digestate spiked with propionate. Bioresource Technology, 102(2), 822–827.
Li, L., He, Q., Wei, Y., He, Q., & Peng, X. (2014). Early warning indicators for monitoring the process failure of anaerobic digestion system of food waste. Bioresource Technology, 171, 491–494.
Liu, N., & Jiang, J. (2020). Valorisation of food waste using salt to alleviate inhibition by animal fats and vegetable oils during anaerobic digestion. Biomass and Bioenergy, 143, 105826.
Margallo, M., Ziegler-Rodriguez, K., Vázquez-Rowe, I., Aldaco, R., Irabien, Á., & Kahhat, R. (2019). Enhancing waste management strategies in Latin America under a holistic environmental assessment perspective: A review for policy support. Science of the Total Environment, 689, 1255–1275.
Micolucci, F., Gottardo, M., Pavan, P., Cavinato, C., & Bolzonella, D. (2018). Pilot scale comparison of single and double-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 1376–1385.
Montecchio, D., Astals, S., Di Castro, V., Gallipoli, A., Gianico, A., Pagliaccia, P., Piemonte, V., Rossetti, S., Tonanzi, B., & Braguglia, C. M. (2019). Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and waste activated sludge: ADM1 modelling and microbial analysis to gain insights into the two substrates’ synergistic effects. Waste Management, 97, 27–37.
Montgomery, D. C. (2004). Diseño y Análisis de Experimentos. México D.F. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons. p 682
Morais, D. R., Rotta, E. M., Sargi, S. C., Bonafe, E. G., Suzuki, R. M., Souza, N. E., Matsushita, M., & Visentainer, J. V. (2017). Proximate composition, mineral contents and fatty acid composition of the different parts and dried peels of tropical fruits cultivated in brazil. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 28, 308–318.
Nakasima-López, M., Taboada-González, P., Aguilar-Virgen, Q., & Velázquez-Limón, N. (2017). Inoculum adaptation during start-up of anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste. Información Tecnológica, 28(1), 199–208.
Nzeteu, C. O., Trego, A. C., Abram, F., & O'Flaherty, V. (2018). Reproducible, high-yielding, biological caproate production from food waste using a single-phase anaerobic reactor system. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 11, 108.
Parra-Orobio, B. A., Torres-Lozada, P., & Marmolejo-Rebellón, L. F. (2017). Anaerobic digestion of municipal biowaste for the production of renewable energy: effect of particle size. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(2), 481–491.
Parra-Orobio, B. A., Angulo-Mosquera, L. S., Loaiza-Gualtero, J. S., Torres-López, W. A., & Torres-Lozada, P. (2018a). Inoculum mixture optimization as strategy for to improve the anaerobic digestion of food waste for the methane production. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(1), 1529–1535.
Parra-Orobio, B. A., Donoso-Bravo, A., Ruiz-Sánchez, J. C., Valencia-Molina, K. J., & Torres-Lozada, P. (2018b). Effect of inoculum on the anaerobic digestion of food waste accounting for the concentration of trace elements. Waste Management, 71, 342–349.
Parra-Orobio, B. A., Donoso-Bravo, A., & Torres-Lozada, P. (2020a). Energy balance and carbon dioxide emissions comparison through modified anaerobic digestion model No 1 for single-stage and two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste. Biomass and Bioenergy, 142, 105814.
Parra-Orobio, B. A., Torres-López, W. A., & Torres-Lozada, P. (2020b). Response surface methodology as an optimization tool for anaerobic digestion of food waste. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(8), 385.
Peces, M., Pozo, G., Koch, K., Dosta, J., & Astals, S. (2020). Exploring the potential of co-fermenting sewage sludge and lipids in a resource recovery scenario. Bioresource Technology, 300, 122561.
Quintero, M., Castro, L., Ortiz, C., Guzmán, C., & Escalante, H. (2012). Enhancement of starting up anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic substrate: fique’s bagasse as an example. Bioresource Technology, 108, 8–13.
Ratanatamskul, C., Wattanayommanaporn, O., & Yamamoto, K. (2015). An on-site prototype two-stage anaerobic digester for co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge for biogas production from high-rise building. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 102, 143–148.
Rojas, G. A. F., & Flórez, M. C. (2019). Fruit waste valorization for combustion and pyrolysis. Revista Politécnica, 15(28), 42–53.
Shen, F., Yuan, H., Pang, Y., Chen, S., Zhu, B., Zou, D., Liu, Y., Ma, J., Yu, L., & Li, X. (2013). Performances of anaerobic co-digestion of fruit & vegetable waste (FVW) and food waste (FW): Single-phase vs. two-phase. Bioresource Technology, 144, 80–85.
Song, H., Zhang, Y., Kusch-Brandt, S., & Banks, C. J. (2020). Comparison of variable and constant loading for mesophilic food waste digestion in a long-term experiment. Energies, 13(5), 1279.
Soto-Paz, J., Oviedo-Ocaña, E. R., Manyoma-Velásquez, P. C., Torres-Lozada, P., & Gea, T. (2019). Evaluation of mixing ratio and frequency of turning in the co-composting of biowaste with sugarcane filter cake and star grass. Waste Management, 96, 86–95.
Torres-Lozada, P., Díaz-Granados, J. S., & Parra-Orobio, B. A. (2015). Effects of the incorporation of drinking water sludge on the anaerobic digestion of domestic wastewater sludge for methane production. Water Science and Technology, 72(6), 1016–1021.
Uludag-Demirer, S., Liao, W., & Demirer, G. N. (2019). Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Residues. In V. Balan (Ed.), Microbial Lipid Production. Methods in Molecular Biology (pp. 357–367). New York: Springer New York.
Verstraete, W., Morgan-Sagastume, F., Aiyuk, S., Waweru, M., Rabaey, K., & Lissens, G. (2005). Anaerobic digestion as a core technology in sustainable management of organic matter. Water Science and Technology, 52, 59–66.
Voelklein, M. A., Jacob, A., & O’ Shea, R. & Murphy, J. D. (2016). Assessment of increasing loading rate on two-stage digestion of food waste. Bioresource Technology, 202, 172–180.
Xiao, B., Qin, Y., Wu, J., Chen, H., Yu, P., Liu, J., & Li, Y. Y. (2018). Comparison of single-stage and two-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: performance, energy balance and reaction process. Energy Conversion and Management, 156, 215–223.
Zhang, Y., & Banks, C. J. (2013). Impact of different particle size distributions on anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Management, 33n(2), 297–307.
Zhang, L., Lee, C. H., & Jahng, D. (2011). Restriction of linoleic acid inhibition of methanization of piggery wastewater and enhancement of its mineralization by adding calcium ions. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 86(2), 282–289.
Zhu, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, B., Lu, H., Duan, N., Si, B., Shen, R., & Lu, J. (2016). Recovery of reducing sugars and volatile fatty acids from cornstalk at different hydrothermal treatment severity. Bioresource Technology, 199, 220–227.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank COLCIENCIAS for supporting to Brayan A. Parra Orobio as a scholar of the National Doctorates Convocation Program (617 - 2013 –Second Cut) and the Universidad del Valle for funding the project “Evaluation of the anaerobic digestion of food waste under conditions of temperature lower than 20 °C for the production of renewable energy-CI 21118”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 466 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parra-Orobio, B.A., Cruz-Bournazou, M.N. & Torres-Lozada, P. Single-Stage and Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Effect of the Organic Loading Rate on the Methane Production and Volatile Fatty Acids. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05064-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05064-9