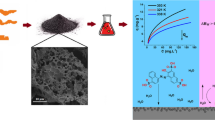
Abstract
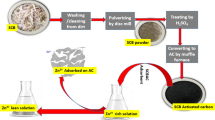
Large volumes of sugarcane-bagasse ash are produced as residues from the sucro-alcohol industry and have some practical applications. The use of this ash as an adsorbent for the removal of Ni(II) and Zn(II) is studied in the present paper. Effects of pH, adsorbent concentration and equilibrium time have been studied in order to establish the best conditions for the removal of metal ions. The kinetic parameters, i.e. the constant rate, equilibrium sorption capacity and related coefficients of each kinetic model (pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order and Elovich), have been evaluated by means of nonlinear regression fit: the pseudo-second order best describes the kinetics of the process. The experimental data obtained from the equilibrium study were analysed using nonlinear Freundlich, Langmuir, Temkin and Toth models: the Langmuir and Toth isotherms best represent the sorption of the metal ions. The highest experimental sorption capacities obtained as regards the removal of Ni(II) and Zn(II) from the sugarcane-bagasse ash were 0.0298 and 0.0416 mmol g−1, respectively. The adsorption mechanism through the formation of covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds demonstrates the affinity between the adsorbent and the adsorbates. The studies were conducted separately, using independent solutions of each metal.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhafez, A. A., & Li, J. (2016). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by using biochars derived from sugar cane bagasse and orange peel. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 61, 367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.01.005.
Ahmed, A.-M. M., Ali, A. E., & Ghazy, A. H. (2019). Adsorption separation of nickel from wastewater by using olive stones. Advanced Journal of Chemistry-Section A, 2(Issue 1), 79–93. https://doi.org/10.29088/sami/AJCA.2019.2.7993.
Andrade, M. F., & Colodette, J. L. (2014). Dissolving pulp production from sugar cane bagasse. Industrial Crops and Products, 52, 58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.041.
Andrade, C. A., Zambrano-Intriago, L. A., Oliveira, N. S., Vieira, J. S., Quiroz-Fernández, L. S., & Rodríguez-Díaz, J. M. (2020). Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Oxytetracycline on Rice Husk Ash: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamics of the Process. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04473-6.
Barreto, S. R. G., Barreto, W. J., & Deduch, E. M. (2011). Determination of partition coefficients of metals in natural tropical water. [Article]. Clean: Soil, Air, Water, 39(4), 362–367. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000271.
Bayat, B. (2002). Comparative study of adsorption properties of Turkish fly ashes: I. The case of nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 95(3), 251–273.
Bezerra, T. L., & Ragauskas, A. J. (2016). A review of sugarcane bagasse for second-generation bioethanol and biopower production. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 10(5), 634–647. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1662.
Campos, N. F., Guedes, G. A. J. C., Oliveira, L. P. S., Gama, B. M. V., Sales, D. C. S., Rodríguez-Díaz, J. M. et al. (2020). Competitive adsorption between Cu2+ and Ni2+ on corn cob activated carbon and the difference of thermal effects on mono and bicomponent systems. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(5), 104232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104232.
Cha, N.-R., Lee, J.-K., Lee, Y.-R., Jeong, H.-J., Kim, H.-K., & Lee, S.-Y. (2010). Determination of Iron, copper, zinc, lead, nickel and cadmium in cosmetic matrices by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Analytical Letters, 43(2), 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710903325781.
Davranche, M., Lacour, S., Bordas, F., & Bollinger, J.-C. (2003). An easy determination of the surface chemical properties of simple and natural solids. Journal of Chemical Education, 80(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed080p76.
Dias, M. O. D. S., Maciel Filho, R., Mantelatto, P. E., Cavalett, O., Rossell, C. E. V., Bonomi, A., et al. (2015). Sugarcane processing for ethanol and sugar in Brazil. Environment and Development, 15, 35–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2015.03.004.
Divband Hafshejani, L., Hooshmand, A., Naseri, A. A., Mohammadi, A. S., Abbasi, F., & Bhatnagar, A. (2016). Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by modified sugarcane bagasse biochar. Ecological Engineering, 95, 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.035.
Fideles, R. A., Ferreira, G. M. D., Teodoro, F. S., Adarme, O. F. H., da Silva, L. H. M., Gil, L. F., et al. (2018). Trimellitated sugarcane bagasse: a versatile adsorbent for removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution. Part I: Batch adsorption in a monocomponent system. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 515, 172–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.025.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Ghiaci, M., Dorostkar, N., & Gil, A. (2014). Chicken bone ash as an efficient metal biosorbent for cadmium, lead, nickel, and zinc from aqueous solutions. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52(16-18), 3115–3121.
Gopinath, A., Bahurudeen, A., Appari, S., & Nanthagopalan, P. (2018). A circular framework for the valorisation of sugar industry wastes: review on the industrial symbiosis between sugar, construction and energy industries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 203, 89–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.252.
Gupta, V. K., Jain, C. K., Ali, I., Sharma, M., & Saini, V. K. (2003). Removal of cadmium and nickel from wastewater using bagasse fly ash--a sugar industry waste. Water Research, 37(16), 4038–4044. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(03)00292-6.
House, J. E., & House, K. A. (2010). CHAPTER 5 - Acids, bases, and nonaqueous solvents. In J. E. House & K. A. House (Eds.), Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed., pp. 119–152). Amsterdam: Academic Press.
Islam, M. A., Awual, M. R., & Angove, M. J. (2019). A review on nickel(II) adsorption in single and binary component systems and future path. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(5), 103305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103305.
Kołodyńska, D., Wnętrzak, R., Leahy, J. J., Hayes, M. H. B., Kwapiński, W., & Hubicki, Z. (2012). Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 197, 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.025.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38(11), 2221–2295 citeulike-article-id:1616089.
Lee, C.-G., Lee, S., Park, J.-A., Park, C., Lee, S. J., Kim, S.-B., et al. (2017). Removal of copper, nickel and chromium mixtures from metal plating wastewater by adsorption with modified carbon foam. Chemosphere, 166, 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.093.
Li, G.-X., Yan, C.-Z., Zhang, D.-D., Zhao, C., & Chen, G.-Y. (2013). Cadmium(II) biosorption from aqueous solutions using Hydrilla verticillata. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 91(6), 1022–1030. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.21734.
Memon, G. Z., Bhanger, M. I., Akhtar, M., Talpur, F. N., & Memon, J. R. (2008). Adsorption of methyl parathion pesticide from water using watermelon peels as a low cost adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 138(1–3), 616–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.09.027.
Nguyen, T. C., Loganathan, P., Nguyen, T. V., Kandasamy, J., Naidu, R., & Vigneswaran, S. (2018). Adsorptive removal of five heavy metals from water using blast furnace slag and fly ash. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(21), 20430–20438.
Noonpui, S., Thiravetyan, P., Nakbanpote, W., & Netpradit, S. (2010). Color removal from water-based ink wastewater by bagasse fly ash, sawdust fly ash and activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 162(2), 503–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.051.
Peng, G., Deng, S., Liu, F., Li, T., & Yu, G. (2020). Superhigh adsorption of nickel from electroplating wastewater by raw and calcined electroplating sludge waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 246, 118948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118948.
Potgieter, J. H., Potgieter-Vermaak, S. S., & Kalibantonga, P. D. (2006). Heavy metals removal from solution by palygorskite clay. Minerals Engineering, 19(5), 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.07.004.
Puigdomenech, I. (2004). HYDRA (Hydrochemical Equilibrium-Constant Database) and medusa (make equilibrium diagrams using sophisticated algorithms). (18Feb2004 ed., pp. Inorganic Chemistry Software). Estocolmo: Royal Institute of Technology.
Rajasimman, M., Rajamohan, N., & Sujatha, S. (2020). Recovery of zinc from electroplating wastewater using green emulsion liquid membrane. Water Supply, doi:https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.294.
Ramos, S. N. D. C., Xavier, A. L. P., Teodoro, F. S., Elias, M. M. C., Gonçalves, F. J., Gil, L. F., et al. (2015). Modeling mono- and multi-component adsorption of cobalt(II), copper(II), and nickel(II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto a new carboxylated sugarcane bagasse. Part I: Batch adsorption study. Industrial Crops and Products, 74, 357–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.05.022.
Rodríguez-Díaz, J. M., García, J. O. P., Sánchez, L. R. B., da Silva, M. G. C., da Silva, V. L., & Arteaga-Pérez, L. E. (2015). Comprehensive characterization of sugarcane bagasse ash for its use as an adsorbent. [journal article]. Bioenergy Research, 8(4), 1885–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9646-6.
Sočo, E., & Kalembkiewicz, J. (2013). Adsorption of nickel(II) and copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by coal fly ash. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 1(3), 581–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.06.029.
Souza, A. E., Teixeira, S. R., Santos, G. T., Costa, F. B., & Longo, E. (2011). Reuse of sugarcane bagasse ash (SCBA) to produce ceramic materials. [Article]. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(10), 2774–2780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.020.
Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2007). Adsorption thermodynamics and isosteric heat of adsorption of toxic metal ions onto bagasse fly ash (BFA) and rice husk ash (RHA). [Article]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 132(1-3), 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.01.007.
Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2009). Equilibrium Modeling of Ternary Adsorption of Metal Ions onto Rice Husk Ash. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 54(3), 705–711. https://doi.org/10.1021/je8003029.
Subramanian, S., Pande, G., De Weireld, G., Giraudon, J.-M., Lamonier, J.-F., & Batra, V. S. (2013). Sugarcane bagasse fly ash as an attractive agro-industry source for VOC removal on porous carbon. Industrial Crops and Products, 49, 108–116.
Teixeira, S. R., Pena, A. F., & Miguel, A. G. (2010). Briquetting of charcoal from sugar-cane bagasse fly ash (scbfa) as an alternative fuel. Waste Management, 30(5), 804–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.01.018.
Visa, M., Bogatu, C., & Duta, A. (2010). Simultaneous adsorption of dyes and heavy metals from multicomponent solutions using fly ash. Applied Surface Science, 256(17), 5486–5491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.12.145.
Volkov, A. G., Paula, S., & Deamer, D. W. (1997). Two mechanisms of permeation of small neutral molecules and hydrated ions across phospholipid bilayers. Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics, 42(2), 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0302-4598(96)05097-0.
Wang, F., Pan, Y., Cai, P., Guo, T., & Xiao, H. (2017). Single and binary adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using sugarcane cellulose-based adsorbent. Bioresource Technology, 241, 482–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.162.
Wasewar, K. L., Prasad, B., & Gulipalli, S. (2009). Adsorption of selenium using bagasse fly ash. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 37(7), 534–543. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200800183.
Zambrano-Intriago, L. A., Gorozabel-Mendoza, M. L., Córdova Mosquera, A., Delgado-Demera, M. H., Duarte, M. M. M. B., & Rodríguez-Díaz, J. M. (2020). Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics of the blue 19 dye adsorption process using residual biomass attained from rice cultivation. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00944-2.
Zhang, Z., O’Hara, I. M., Kent, G. A., & Doherty, W. O. S. (2013). Comparative study on adsorption of two cationic dyes by milled sugarcane bagasse. Industrial Crops and Products, 42, 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.05.008.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their upmost gratitude to the CNPq, CAPES, FACEPE/NUQAAPE, CNPq/INCTAA and USINA J.B for supporting the research. This work is especially dedicated to the memory of Professor Valdinete Lins da Silva, for her outstanding career and contributions to science.
Funding
The research was supported by the CNPq, CAPES, FACEPE/NUQAAPE and CNPq/INCTAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. M. R-D., C. A. A. and L. A. Z-I. carried out laboratory work and data analysis. E. S-V. contributed to the experimental development and writing the manuscript. L. S. Q-F. acquisition of funds and analysis of the final results. M. G. C. DS. and V. L. DS. designed and analysed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Professor Valdinete died during the submission period of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M., Andrade, C.A., Zambrano-Intriago, L.A. et al. Laboratory Adsorption Studies on Ni(II) and Zn(II) Solutions by Sugarcane-Bagasse Ash. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05046-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05046-x